Salivary Gland Lesions 2 Flashcards
Salivary Gland Tumors table

Benign Tumors
Pleomorphic adenoma
Warthin’s Tumors
Canalicular adenoma
Basal cell adenoma
Malignant Tumors
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
acinic cell adenocarcinoma
adenoid cystic carcinoma
polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma

Pleomorphic adenoma
Most common salivary gland tumor
origin: ductal and myoepithelial cells
painless, slow growing, firm mass, most between 30-60 yo, slightly more female
swelling overlying mandibular ramus
in parotid, 90% in superficial lobe
dome-shaped, smooth mass. Palate most common intra-oral site
stroma composed of fibrillary and chondromyxoid material
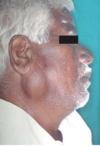
Warthin Tumor
Almost exclusive to parotid
Bilateral in 5-17% of cases
Associated w/ smoking - 10:1 M:F
Slow growing, painless mass
Tail of parotid, near MD angle
Mixture of ductal epithelium and lymphoid stroma
Epithelial lining shows double row of oncocytes
treatment - surgical removal is treatment of choice - superficial location facilitates surgery

Canalicular Adenoma
Almost exclusive to MSG
Most or second most common upper lip
Always in older adult - slightly more common in females
Slow growing, painless mass with striking predilection for upper lip
Uniform columnar cells forming canal-like ductal structures w/in a vascular stroma
Treatment - best treated by surgical excision - recurrences uncommon and may represent mutifocal cases
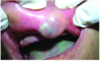
Basal Cell Adenoma
Basaloid appearance of cells
more common in parotid gland, followed by minor salivary glands - 2:1
Freely movable mass, usually smaller than 3 cm
Islands and cords of epithelial cells
Peripheral cells are basaloid in appearance
Treatment - complete surgical removal - recurrence is rare
Beastie Boy - Adam Yauch

Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
Most common malignant salivary galnd tumor U.S.
Seen in a wide age range. Most common malignant SG tumor children
Most common in parotid gland - pain or nerve palsy can occur
MSG second most common site, where it appears as asymtomatic swelling
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the buccal mucosa
Most common SG tumor of lower lip, floor of mouth, tongue and retromolar pad
Composed of mucus-producing and epidermal cells
Mucous cells: foamy cytoplasm
Epidermoid cells: squamoid features
Mucoepidermoid carcinomas can rarely present centrally in the jaws
Treatment: depends on clinical and histiopathological features

Acidic Cell Adenocarcinoma
Malignancy w/ cells that show serous acini differentiation
85% of cases occur in parotid gland nerve palsy ominous sign - 1.5:1
Slow growing mass often present for many years before a diagnosis is made
Represent 1-3% of all parotid tumors
About 10% see in minor salivary glands (buccal mucosa, lips and palate)
Sheets of basophilic cells w/features of serous acinar cells
Treatment -
parotid: partial or total parotidectomy
submandibular: total gland removal
minor gland: surgery w/ safety margins
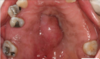
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
50-60% occurs in minor salivary glands - Palate is the most common location
Parotid = submandibular (most common subMD cancer)
slow growing mass. Constant, low-grade pain a common and important finding
Cribiform pattern: islands of cells w/ multiple cyst-like spaces
Treatment: surgical excision - prone to local recurrence and distant metastasis

Polymorphous Low Grade Adenocarcinoma
Polymorphous - has varied microscopic appearance
Low grade - non-aggressive compared to other tumors
Adenocarcinoma - Malignant and forms glands
Almost exclusive of minor salivary glands (65% palate, upper lip - buccal mucosa)
more common in older, white females
painless mass that may have been present for a long time
Treatment - wide surgical excision, overall good prognosis, recurrence rates 10-15%

