Inflammatory Jaw Lesions Flashcards
Inflammatory jaw lesions
Pulpitis
Periapical abscess
Periapical granuloma
Radicular cyst
Osteomyelitis
Condensing osteitis
Osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis
Alveolar osteitis
Defense mechanisms
Nonspecific defenses: 1st line - skin, mucous membranes, chemicals
Nonspecific defenses: 2nd line - phagocytosis, complement, interferon, inflammation, fever
Specific defenses: 3rd line - lymphocytes, antibodies
Cardinal signs of inflammation
Calor
Dolor
Rubor
Tumor

Pulpitis
Pulp responds to injury like other tisisues. Final result is different since pulp is confined
most in children/young adult
large exposures of pulp
deciduous and molars

Reversible pulpitis
Hyperemia and Edema
Txt: removal of local irritant
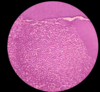
Irreversible Pulpitis
Acute inflammatory infiltrate
Txt: root canal or extraction

Chronic hyperplastic pulpitis
Chronically inflamed tissue filling the coronal defect
Txt: root canal or extraction

Periapical Abscess
Accumulation of inflammatory cells at tooth apex
Initial pathosis or exacerbation of previous lesion
Due to infection or trauma
Symptomatic or asymptomatic
Abscesses spread along the path of least resistance
Abscess can accumulate in soft tissue and create swelling
Parulis (gum boil): mass of granulation tissue seen at opening of sinus tract
Insertion of gutta-percha into sinus tract helpful to determine origin and path
May drain extra-orally through facial skin
Thickening of PDL and/or ill-defined radiolucency
Txt: drainage and elimination of infection focus
NSAIDs for pain control
Root canal or extraction

Periapical Granuloma
aka chronic apical periodontitis
Mass of chronically inflamed tissue at apex of non vital tooth
defensive reaction to the presence of microbes in canal and apex
Inflammatory cells release cytokines and destroy bone
75% of apical inflammatory lesions
Radiolucency located at apex of tooth, usually incidental finding
Inflamed granulation tissue surrounded by a fibrous connective tissue wall
Inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes intermixed w/ neutrophils, plasma cells and histiocytes
txt: if tooth is restorable, root canal therapy
If nonrestorable, extraction and curettage
Microscopic evaluation of removed tissue

Radicular Cyst
aka periapical cyst and apical periodontal cyst

Periapical cyst

Lateral Radicular Cyst

Residual Cyst
Treatment of radicular cyst


Pathogenesis of osteomyelitis

Acute osteomyelitis (<1 month)
Ill-defined radiolucency which may contain bone sequestrum
txt: antibiotics +/- surgery

Chronic Osteomyelitis (>1 month)
Patchy, ill-defined radiolucency with “moth-eaten” appearance
txt: IV antibiotic + surgery

Condensing Osteitis
Localized, uniform zone of increased radio density adjacent to tooth apex
Localized area of bone sclerosis on apex of teeth with pulpitis/necrosis
Most in children/young adults
Usually in premolar and molar areas
No clinical expansion noted
txt: Resolution of infection focus. 85% regress partially or fully with surgery or end. Bone scar: residual area that remains

Osteomyelitis w/ Proliferative periostitis
Frequently due cause dental caries
Mean age 13 years
No gender predilection
Premolar and molar mandible
Radiopaque laminations of bone that are roughly parallel (“onion-skin”)
Swelling of the border of the mandible
Parallel rows of reactive bone, forming an interconnected meshwork
Txt: directed at eliminating source of infection. Layers of bone consolidate in 6-12 months. If no infection present, biopsy indicated

Alveolar Osteitis
Dry Socket (blood clot doesn’t form or is lost too early) following tooth extraction
Impacted third molars, poor oral hygiene, inexperienced surgeons, traumatic extractions, contraceptive use, pre-surgical infections
Seen in 20% of patients who smoke. Increases to 40% w/in 24h of extraction
Extraction site filled w/dirty clot that is lost. Painful upon probing.
txt: Analgesic and saline irrigation. Avoid curettage as it increases pain. Use of antiseptic dressing controversial


