Cephalometics Flashcards
Cephalometrics
Interpretation of lateral head films taken under standardized conditions
Uses of cephalometrics
Diagnosis of skeletal and dental malocclusions
planning orthodontic treatment
evaluation of orthodontic treatment results
prediction and evaluation of growth related changes
Cephalostat
Distance between xray source and midsagittal plane of patient is kept constant at 5 feet
Distance between midsagittal place and film is 15cm
Pt’s head is positioned w/ frankfort horizontal plane parallel to the floor
Patient position
Bilateral ear rods are placed in the auditory meatus
Midsaggital plane is vertical and perpendicular to the xray beam and parallel to the film
Line connecting superior border of external auditory meatus to the infraorbital rim (Frankfort Horizontal plane) is parallel to the floor

Sella (Se): geometric center of the pituatary fossa
Nasion (Na): most anterior point of the frontonasal suture
Basion (Ba): Lowest point on the anterior rim of foramen magnum
SN plane: line joining Se and Na, anterior cranial base

Porion (Po): most superior point on the external auditory meatus
Orbitale (Or): most inferior point on the orbit
Pterygomaxillare (Ptm): jxn of the pterygomaxillary fissure and foramen rotundum
Frankfort Horizontal Plane: Line joining Po and Or

Anterior nasal spne (ANS): anterior tip of the sharp bone process of the maxilla at the lower border of the nasal opening
Posterior nasal spine (PNS): posterior spine of the palatine bone
Subspinale (Point A): the most posterior midline point in the concavity of the maxilla
Supramentale (Point B): The most posterior midline point in the concavity of the mandible

Pogonion (Pog): The most anterior point on the chin
Menton (Me): The lowest point on the symphysis of the mandible
Ganthion (Gn): Midpoint of the anterior and inferior points on the chin

Gonion (Go): Point on the curvature of the angle of the mandible located by bisecting the lines tangent to the posterior ramus and the inferior border of the mandible
Lines joining the tips of the incisal edges and the roots of upper and lower incisors
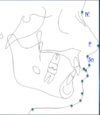
N’: soft tissue nasion
Pronasale: most prominent point on the nose
Subspinale (Sn): point at which the columella merges with the upper lip

Labrale superius (Ls): most anterior point on upper lip
Stomion superius (Stms): most inferior point on the upper lip
Stomion inferius (Stmi): most superior point on the lower lip
Labrale inferius (Li): Median point on the lower margin of the lower lip

Superior Labial sulcus (SLS): the point of greatest concavity in the midline of the upper lip
Inferior labial sulcus (ILS): the point of greatest concavity in the midline of the lower lip
Soft tissue pogonion (Pog’)
Soft tissue menton (Me’)
chin throat point

SNA: Sella-Nasion-A point angle
relation of maxilla to the cranial base
normal value: 82 +/- 2
greater value indicates prognathic maxilla
lesser value indicates retrognathic maxilla
relative to cranial base

SNB: Sella-Nasion-Point B angle
position of mandible relative to cranial base
normal value 80 +/- 2
greater value indicates prognathic mandible
lesser value indicates retrognathic mandible
relative to cranial base

ANB: A point-nasion-B point angle
relation of maxilla to mandible
normal value: 2 +/- 2 degrees
greater value indicates class II relation
lesser value indicates class III relation
doesnt indicate which jaw is affected

mandibular plane angle (FMA):
angle formed by FH plane with mandibular plane (Gonion-Gnathion)
indicates the direction of growth of the mandible in relation to the FH plane
normal value: 26 +/- 4

SN-MP:
angle formed by sella-nasion plane with mandibular plane (gonion-gnathion)
indicates the direction of mandibular growth in relation of the cranial base
normal base: 32 degrees

U1-NA (mm):
indicates the proclination of upper incisor w/ respect to the nasion
normal value: 4mm
U1-SN (degrees):
indicates the inclination of upper incisor w/ respect to cranial base
helps in planning for incisor retraction during orthodontic treatment

L1-NB (mm):
indicates lower incisor proclination w/ respect to nasion point
normal value: 4mm
L1-MP (degrees):
indicates lower incisor inclination w/ respect to mandibular plane
helps in planning treatment mechanics
normal value: 90 +/- 7 degrees
lower incisor inclination helps in planning orthodontic treatment in many cases

E line: Esthetic line
plane extending from soft tissue tip of nose to soft tissue chin
determines balance between nose, lips and chin
normal value:
U lip - E line: -6 +/- 2mm
L lip - E line: 2 +/- 2 mm
(at 9 yrs of age, lips become less protrusive w/ age)
Helps in planning for lip retraction
Superimpositions
Evaluation of growth changes
evaluation of effect of treatment mechanics
superimpositions on stable cephalometric landmarks (sella, Ptm, anterior cranial base) for skeletal changes
superimposition on maxillary plane (ANS-PNS) and internal maxillary structures and lower border of mandible along w/ developing third molar and inferior canal for dental changes


