Salivary Gland 2 Flashcards
Salivary gland tumors
Tissue of origin
- Most arise from epithelium, especially glandular epi
- Benign glandular neoplasma: Adenomas
- Malignant: adenocarcinomas
Clinical features of salivary gland adenomas
- Encapsulated: freely movable except on hard palate
- Slow growth
- Nontender
- Firm or compressible
- Clinical features similar to some benign mesenchymal tumors
- Surgical excision and follow up
- Prog excellent
Clinical features of salivary gland adenocarcinomas
tx
- Infiltrated growth–> fixed to surrounding tissue
- Rapid or slow growth
- Larger, rapidly growing may cause pain, parasthesia
- Surgery, radiation
- Prog variable
Problem with malignant vs benign
4
- Malignant can mimic benign
- Low grade mucopidermoid carcinoma
- Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma
- Acinic cell adenocarcinoma
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Common location of salivary gland tumors
Prob of B vs Malig
- Parotid is most common
- Major glands
- The larger the gland, more likely benign
- Smaller gland, malignant
- Minor 50/50 chance
What causes salivary gland tumors
Radiation
Occupation: rubber, plumbing, wood working, beauty industries
Benign SG Tumors 4
- Pleomorphic adenoma
- Warthin tumor
- Canalicular adenoma
- Basal cell adenoma
Malignant SG tumors 4
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Acinic cell adenocarcinoma
- Adenoid cyst carcinoma
- Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma
Pleomorphic adenoma
Occurence
Characteristics
Derived from
App

- Benign mixed tumor
- Most common SG tumor
- Painless, slowly growing, firm enlargement
- Derived from ductal and myoepithelial elements
- WILL ASK WHICH IS THE MOST COMMON BENIGN SG TUMOR, this is the answer
- App
- swelling over mand ramus in front of ear
- Most in superficial lobe (subMand)
- 50% of palatal SG tumors are this

Microscopic Features of Pleomorphic Adenoma
- Epithelium forming ducts
- CT is variable and may contain cartilage or bone
- Tumor is encapsulated but capsule may be infiltraated by tumor cells
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Tx for diff glands
- Surgical excision
- Superficial lobe: superficial parotidectomy
- Deep lobe: total parotidectomy
- Submand: total removal
- Intraoral: enucleation
- Tx good
Warthin Tumor
Gland
Location
Dist
assoc
age gender
tx
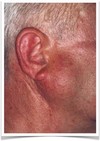
- AKA papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum
- Exclusively in parotid gland
- Near mandibular angle
- 5-17% bilateral (usually metachronous)
- Assoc with smoking
- Males
- Over 40
- Tx
- remove
Monomorphic Adenoma
Glands
2 types
Growth
Could also be Diff diag
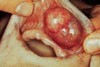
- Old term replaced by canalicular adenoma and basal cell adenoma
- Most common parotid and minor glands of upper lip, but can occur anywhere
-
Upper lip= canalicular adenoma (minor)
- Most common upper lip tumor
- Parotid= basal cell adenoma
-
Upper lip= canalicular adenoma (minor)
- Slowly growing, asymptomatic
- Diff diag: Neurofibroma, Schwannoma, pleomorphic granuloma
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
WILL BE ON EXAM
Occurrence
2 grades (features)
Glands
Symptom

- Most common malignant salivary gland
- Low grade mimics benign neoplasm
- Contains mucous pools compressible
- High grade
- Aggressive malignant
- Epithelial component more prominent
- dec mucus, appears similar to SCC
- Excision, radiation, poor prog
- Parotid most common, Minor second most common
- palsy may be present
Most uncommon places for SG tumors 4
- Lower lip
- Floor of mouth
- tongue
- retromolar pad
- Most common for Mucoepidermoid carcinoma





