Mesenchymal Flashcards
Mesenchymal CT Lesions5
- Fibrous
- Vascular
- Neural
- Muscle
- Fat
Fibroma
Occurence
Cause
App
Tx
- Most common tumor of oral cavity
- True tumor of fibrous tissue rare
- Reactive hyperplasia of fibrous CT
- Ap
- Smooth, sessile, pink nodule
- Tx surgical excision
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma
occurence
Location
App
tx
prog

- Common, reactive
- Exclusively on the gingiva, usually interdental papilla
- App
- Nodule red to pink firm may be ulcerated
- Excisional biopsy
- Good prognosis but high recurrence
Peripheral vs Central
Loc
Why is distinction imp
- Indication of location
- Central= inside the jaw bone
- Peripheral=specifically on gingiva (outside bone)
- Distinction imp for treatment purposes
- Peripheral- excision
- Some central extensive excision or resection
Fibrosarcoma
- Malignant tumor of fibroblasts
Pyogenic Granuloma
What and where
Generally…
Some categorize as
Common during
- Tumor-like growth of oral cavity
- Generally non-neoplastic
- Cause reastive lesion to irritation or injury
- Some categorize it as vascular tumor: lobular capillary hemangioma
- Common during pregnancy or puberty
- assoc with hormones
- Can happen anywhere bc vascular
Pyogenic Granuloma
Growth
App
Location
Tx
Prog

- Rapid growth initially
- App
- Well circumscribed, vascular: always red-blue, bleeds, blanches
- Common on gingiva, but can occur anywhere
- Often ulcerated & covered with psudomembrane
- Tx
- Excision, for gingival extend to periosteum
- Prog
- Recurrence, pregnancy lesions may resolve on own
Peripheral Giant Cell Lesion
Cause
APP
Location
Arises from

- Tumor like growth reactive to local irritation or trauma
- App
- Peripheral=only gingiva
- Firm, vascular, may be ulcerated
- Exclusively in gingiva or edentulous alveolar ridge
- Arises from periodontal ligament or periosteum
- Tx
- excision
The 5 Gingival Masses
- Can happen anywhere
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Plain fibroma
- Gingiva only
- Peripheral ossifying fibroma
- Peripheral giant cell granuloma
- Parulis
Lymphangioma
What is it
Blanchable?
Cause
App
Tx

- Benign growth of lymphatic tissues
- Does NOT blanch bc vessels dont contain blood
- Thought to be congenital
- Half of all lesions noted at birth, 90% before 2 yo
- App
- Diffuse, compressible
- Dorsum of tongue, causing macroglossia
- Cluster of translucent vesicles, frog egg apperance
- Cystic usually found in head and neck
- Tx excision
Angiosarcoma
Malignancy of vascular endothelium
Traumatic Neuroma
Cause
Symptoms
Loc
Tx
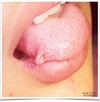
- Reaction proliferation of neural tissue after transection or trauma
- Hx of trauma tooth extraction
- Proliferation of axons
- App
- Anesthesia or dysthesia
- Pain upon palpation
- Loc
- Mental foramen, tongue and lower lips
- Tx excision
Schwannoma
Cause
Location Tx

- Benign neural neoplasm of Schwann cells
- Not painful on palpation
- Common on tongue
- Tx excision
- Doesnt blanch
Neurofibroma
Type of
what kind of cells
Dist
app

- Most common tye of peripheral nerve neoplasm
- Mix of cell types ( Schwann cells and perineural fibroblasts)
- Solitary or part of syndrome(neurofibromatoses)
- Oral
- tongue and buccal mucosa
- All pts should be eveluated for NF
Granular Cell Tumor
Def, locaton
Type of cells
May look like
Tx

- Benign neoplasm, favors oral cavity
- Studies say Schwann cells
- 1/2 cases on tongue
- May look like fibroma
- Tx excision
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
Age
Location
Tx
Prog
- Head/neck, young adults
- Oral
- Mandible lips buccal mucosa
- Intrabony
- Widening or mandibular canal or mental foramen
- Tx excision poor prognosis
Leiomyoma
Def
Common in
App
Tx

- Benign tumor of smooth muscle
- Common in
- Uterus, gi tract skin
- Slow growing, firm, mucosal nodule with pink or blue hue (vascular variant)
- Tx excision
Leiomyosarcoma
- Malignancy of smooth muscle
Rhabdomyoma
Def
2 types ( gender, location)
- Benign tumor of skeletal muscle
- Adult type
- Men
- Pharynx oral cavity larynx
- Fetal type
- young male
- Face periauricular regions
- Can only occur where there is skeletal muscle
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Malignancy of skeletal muscle
Lipoma
def
Common location on body and orally
App

- Benign tumor of fat tissue
- Most on trunk and extremities
- Common in obese
- Oral
- buccal mucosa buccal vestibule
- App
- yellow or pink hue
Liposarcoma
Malignancy of fatty origin
Congenital Epulis
Age
Location
App
gender

- Occurs at birth only on alveolar ridge tissue
- Pink red smooth
- single or polypoid mass
- Females
Conclusions of mesenchymal
- All mesenchymal tissues may give rise to lesions
- Benign or malignant
- Biopsy required to diagnose
- Surgical excision most often required


