S9) The Respiratory System Flashcards
How can you locate the 2nd rib?
- Finding the sternal angle (between manubrium and the sternum)
- Move laterally
- Palpate the attachment of the 2nd rib

Why is the inferior aspect of each lung curved upwards?
The inferior aspect lies on top of the domed diaphragm

What sort of membranes are found in the respiratory system and what do they do?
- A mucous membrane; which lines the conducting portion of the respiratory tract, bearing mucus-secreting cells
- Serous membranes; which line the pleural sacs, enveloping each lung
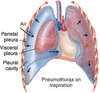
The pleural cavity can fill with four different substances.
What are they and what is the resulting condition named?
- Air – pneumothorax
- Blood – haemothorax
- Pus – empyema
- Transudate/exudate – pleural effusion

How can fluid be drained from the pleural cavity?
Fluid is drained by the insertion of a wide-bore needle through an intercostal space (usually 7th posteriorly), performed under ultrasound guidance

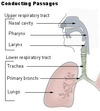
Identify the different lobes and respiratory airways observed in the image below:


Identify the 7 components of the conducting portion of the respiratory tract
- Nasal cavity
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Primary bronchi
- Secondary bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Terminal bronchioles
Identify the 3 components of the respiratory portion of the respiratory tract
- Respiratory bronchioles
- Alveolar ducts
- Alveoli

What does one observe as you progress down the respiratory tract?
The walls of the passageways become thinner as their lumens decrease in diameter

Which components of the respiratory tract are extrapulmonary?

What are the intrapulmonary components of the respiratory system?

There are epithelial changes in the respiratory system.
What sort of epithelium can be found in the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, primary bronchi and secondary bronchi?
Pseudostratified epithelium, with cilia and goblet cells

There are epithelial changes in the respiratory system.
What sort of epithelium can be found in the bronchioles and terminal bronchioles?
Simple columnar epithelium with cilia, Clara cells and no goblet cells

There are epithelial changes in the respiratory system.
What sort of epithelium can be found in the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts?
Simple cuboidal epithelium with Clara cells and a few sparsely scattered cilia

There are epithelial changes in the respiratory system.
What sort of epithelium can be found in the alveoli?
- Simple squamous cells (type 1)
- Septal cells (type 2)

Identify 3 characteristics of olfactory regions
- Particularly thick pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- No goblet cells
- Located in posterior, superior region of each nasal fossa

Identify 4 characteristics of non-olfactory regions
- Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
- Venous plexuses swell often to prevent overdrying
- Arterial blood flow warms inspired air
- Patency maintained by surrounding cartilage/ bone

Identify some key anatomical features on the larynx diagram below:


Describe the features of the ventricular folds of the larynx
- Lined by pseudostratified epithelium
- Contain mucous glands
- Contain numerous lymph nodules

Which 2 structures contribute to the resonance of the voice?
- Ventricles
- Ventricular folds

What are the components of each vocal cord of the larynx?
- A vocal ligament (large bundle of elastic fibres)
- A vocalis muscle (bundle of skeletal muscle)

Identify 2 functions of the vocal cords
- Stop foreign objects from reaching the lungs
- Close to build up pressure when coughing is required

The trachea divides into two primary bronchi in the mid-thorax.
How does the cartilage in these structures differ?
- Trachea has cartilage crescents which partially enclose the lumen
- Primary bronchi have cartilage rings which completely encircle the lumen

What are the features of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?
- There is goblet cell hyperplasia
- A smaller proportion of ciliated cells
- Hypertrophy of the submucous glands