S13) Muscle Flashcards
Define the following terms:
- Myalgia
- Myasthenia
- Myalgia: muscle pain
- Myasthenia: muscle weakness
Define the following terms:
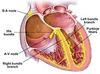
- Myocardium
- Myopathy
- Myoclonus
- Myocardium: muscular component of the heart
- Myopathy: disease of the muscles
- Myoclonus: sudden spasm of the muscles
Define the following terms:
- Sarcolemma
- Sarcoplasm
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Sarcolemma: outer membrane of a muscle cell
- Sarcoplasm: cytoplasm of a muscle cell
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum: smooth endoplasmic reticulum of a muscle cell
What are the three histological forms of muscle?
- Skeletal muscle (striated)
- Cardiac muscle (striated)
- Smooth muscle (non-striated)

Describe the morphology, connections, control and power of skeletal muscle

- Morphology: long parallel cylinders, multiple nuclei, striations
- Connections: fascicle bundles, tendons
- Control: somatic, voluntary
- Power: rapid, forceful
Describe the morphology, connections, control and power of cardiac muscle

- Morphology: short branched cylinders, central nucleus, striations
- Connections: junctions
- Control: intrinsic rhythm, involuntary autonomic
- Power: lifelong variable rhythm
Describe the morphology, connections, control and power of smooth muscle

- Morphology: spindle-shaped, tapering ends, central nucelus
- Connections: connective tissue, gap junctions
- Control: involuntary, autonomic
- Power: slow, sustained or rhythmic
What is myoglobin and what does it do?
Myoglobin is a red protein containing haem, which functions as an oxygen-storing molecule, providing oxygen to the working muscles
Which type of muscle contains myoglobin?
It is present in skeletal and cardiac muscle only
Explain the relationship between haemoglobin and myoglobin
- Haemoglobin gives up oxygen to myoglobin, especially when pH is lowered
- Active muscles produce CO2 (or lactic acid - anaerobic respiration) both of which result in the more acidic conditions that promote this transfer
What is a muscle fibre?
A muscle fibre is a striated muscle cell
Describe skeletal muscle structure

What is muscle atrophy?
Muscle atrophy is a decrease in the mass of the muscle due to a reduction in the number of cells and/or size of cells
Destruction > replacement

What is muscle hypertrophy?
Muscle hypertrophy involves an increase in size of skeletal muscle through a growth in size of its component cells
Replacement > destruction
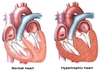
What are the causes of atrophy?
- Muscle inactivity
- Malnutrition
- Cancer
- Neurogenic
What are the changes that accompany hypertrophy?
- More contractile proteins (increase in fibre diameter)
- Metabolic increases: enzyme activity for glycolysis, mitochondria, stored glycogen, blood flow
Outline the arrangement of skeletal muscle
- Skeletal muscle is composed of fascicles
- Fasciscles are composed of muscle fibres (cells)
- Muscle fibres are composed of myofibrils
- Myofibrils are composed of myofilaments (actin& myosin)
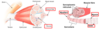
Explain and describe the use of Troponin in enzyme assays
- Troponin is used as a marker for cardiac ischaemia as it is released from ischaemic cardiac muscle within an hour
- The smallest changes in troponin levels in the blood are indicative of cardiac muscle damage
Describe the structure of a myosin molecule
- A myosin molecule has a rod-like structure with two protruding ‘heads’
- Each thick filament contains many myosin molecules, whose heads protrude at opposite ends

Describe the structure of a thin actin filament
- The actin filament forms a helix around which tropomyosin molecules coil, to reinforce it
- A troponin complex is attached to each tropomyosin molecule

What is creatine kinase and what is it used for?
- CK is an important enzyme in metabolically active tissues like muscle
- Used to measure and diagnose heart attacks as the enzyme increase is proportional to infarct size (superseded by troponin assay)
CK is an enzyme that is also released into the blood by damaged skeletal muscle and brain.
A rise in plasma CK can result from which events/conditions?
- Intramuscular injection
- Vigorous physical exercise
- A fall
- Rhabdomyolysis (severe muscle breakdown)
Identify the steps in the contraction mechanism
- Stage 1: Attachment
- Stage 2: Release
- Stage 3: Bending
- Stage 4: Force Generation
- Stage 5: Reattachment
Outline the 5 stages in the contraction mechanism
⇒ Attachment – myosin head tightly binds to actin molecule
⇒ Release – ATP binds to myosin head causing it to uncouple from the actin filament
⇒ Bending – ATP hydrolysis causes uncoupled myosin head to bend and advance a short distance
⇒ Force Generation – myosin head binds weakly to actin filament, releasing Pi which strengthens binding, (power stroke → myosin head returns to former position)
⇒ Reattachment – ATP binds to the myosin head causing detachment from actin.