REVIEW 1 (Cardiac) Flashcards
An anterior wall infarct is typically caused by occlusion of the _______ coronary artery?
LAD
An infarct of the lateral wall of the left ventricle is usually caused by occlusion of the ______
Left circumflex coronary artery
What % of people survive their first MI?
75%
Among the 75% of survivors of their first MI, most develop what?
- Most develop signs of heart failure and cardiogenic shock.
- This hypoperfusion results in multisystemic major organ failure
- Most dangerous= consequences of cerebral ischemia, which may lead to permanent mental injury and loss of CNS functions.
An infarct of the right ventricle and posterior wall of the left ventricle is usually caused by occlusion of the _________
right coronary artery.
The following is the cause of ________ which occurs in ~25% of MIs:
- Major cardiac arrhythmia (i.e. V-fib)
- or later complete heart block and pump failure.
Sudden Cardiac Death from MI
What are the 3 complications of post MI?
- LV myocardial rupture
- Cardiac tamponade
- LV aneurysm with Mural thromus (can embolize to brain and cause stroke)
What are the two types of MIs?
- Transmural
- Subendocardial or Intramural
Which type of MI?
- infarction involves all three layers of the heart
- usually involves the free wall of the LV and/or the interventricular septum.
Transmural
*this is the worst MI- can lead to rupture b/c entire side is necrotic
Which type of MI?
-the infarction is usually concentric around the subendocardial layer of the left ventricle.
Subendocardial or Intramural
Which side of the heart is more likely to have an MI?
Occlusion of the LAD accounts for over 50%
What is the “Tiger Effect” and what condition causes this?
-pathology relates to pale and congested areas with mild hypertrophy, along with biventricular dilatation and generalized hypokinesis of the myocardium (Tiger effect)
*Seen in Acute Viral Myocarditis

Over 80% of Myocarditis cases are caused by what?
***Coxsackie B Virus***
Which Pericarditis causes a “Bread and Butter” pericarditis?
Fibrinous pericarditis
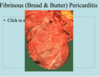
Which pericarditis is described by the following:
- surface of the heart is covered w/ shaggy, yellowish layers of fibrin that bridges the space b/w the 2 layers of the pericardial sac
- When the friable fibrin strands are separated, the epicardium and pericardium resemble bread and butter taken apart
Fibrinous pericarditis
What type of inflammation is seen in “bread and butter” pericarditis?
Fibrinous inflammation
(exudate is rich in fibrin, formed by long strands of polymerized fibrinogen)
What is considered a multifactorial disease (genetic+environmental) with the following risk factors (4 of 9):
- Old Age
- Sex (M>F, differences less after menopause)
- Heredity
- Lipid metabolism
- HTN
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Cigarette smoking
- Stress
Atherosclerosis
What hormone has a protective effect against atherosclerosis?
Female sex hormones
-women who take replacement estrogen therapy after menopause reduce progression of atherosclerosis
What are the risk factors of Atherosclerosis?
“Cigarrettes HOLDS ASH”
- Age (old)
- Sex (M>F, differences less after menopause)
- Heredity
- Lipid metabolism
- HTN
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Cigarette smoking
- Stress
What is the best known cause for familial atherosclerosis that is considered a hereditary risk factor of Atherosclerosis?
Familial Hypercholesterolemia (defect of LDL receptors)
What condition:
- genetic defect of LDL receptors, which does not allow lipoproteins into the liver
- causes atherosclerosis at an early age
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Which Atherosclerotic risk factor has to do with the following:
triglycerides directly correlate with the extent and severity, and with the early onset of clinical symptoms (ex: serum cholesterol >260 increases risk 5x)
Lipid Metabolism
Which Atherosclerotic risk factor has to do with the following:
- direct correlation with the acceleration of atherosclerosis if not properly controlled
- exact role in the development in not fully understood
HTN
Which atherosclerotic risk factor causes a secondary hyperlipidemia due to increased total body fat
-These pts develop atherosclerosis at an earlier age and is more pronounced
Obesity
- This is b/c the tissue fat is in equilibrium with the circulating lipids
How does DM predispose individuals to atherosclerosis?
- Hyperglycemia alters the metabolism of basement membranes and damages small blood vessels (diabetic microangiopathy) of the glomerular capillaries and larger renal arterioles.
- Diabetes also accelerates atherosclerosis in larger arteries (coronaries, cerebral, and aortic).
Where do occlusions occur most often? What location of the infact ?
MC is from occlusion of the LAD-
Causes an anterior wall infarct
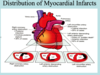
Occlusion of _________ accounts for 30-40%
Causes an infarct of the right ventricle and posterior wall of the left ventricle
RCA
usually causes an infarct of the right ventricle and posterior wall of the left ventricle

CAD:
Occlusion of _________ accounts for 10-20% (least common)
-Usually causes infarct of the lateral wall of the left ventricle
Left Circumflex Artery

What is the only way we get right sided heart vegetations (esp. of the tricuspid valve)?
IVDA
most cases are caused by St. aureus (followed by Strept. species and Candida)
Where do LEFT sided heart vegetations most commonly embolize to?
MC: The brain
-1/3 of patients: Retinal (blindness), coronary (MI), cerebral (strokes), splenic, and renal (from renal abscesses to glomerulonephritis)

Where do RIGHT sided heart vegetations most commonly embolize to?
Pulmonary embolism
(from IVDA’s)


