Respiratory Syncitial Virus Flashcards
RSV Epidemiology
More common in infants and children
2/3 infected by 12 mos;
90% infected by 2 y/o
At risk populations: premature babies, newborns, immunocompromised, cardiac/pulmonary problems
Transmission of RSV
Large particle droplet spread Lives on surfaces for 1 hour Very high (40-60%) attack rate in children <2 y/o
Mainstay of prevention of RSV
Wash yo hands! And avoid the sickos
Vaccines for RSV
There are currently no licensed vaccines for RSV
RSV belongs to which virus family?
Paramyxoviridae
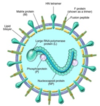
Structure of RSV
Single-stranded, non-segmented RNA virus
F protein: fusion of viral envelope to host cell; fusion of membranes of infected cells to each other –> “syncitia”
G protein: initial binding of virus to host cell
Subtypes of RSV
Two subtypes: A and B
A causes worse disease in general
Usually one predominates during a given season, but both can circulate at same time
Don’t type them for clinical reasons
RSV Pathophysiology
Invades conjunctiva/nasopharynx
- initially replicates in nasopharynx
- primariy replicates in respiratory epithelium
- spreads to lower resp tract by inlaation of secretions or spread via resp epithelium
3-5 day incubation period
RSV clinical manifestations
Causes severe damage to epithelium and bronchiolar ciliary apparatus
Obstruciton of bronchioles and alveoli
Bronchiolar smooth muscle contraction
Hypoxia
Mucous plugging
Clinical signs and symptoms
- Respiratory distress
- Wheezing/rhonchi
- Hypoxia
- Copious secretions
- Bronchiolitis
Testing for RSV
- Cell culture (not common anymore)
- Direct antigen detection; used in outpt, poor sensitivity
- PCR
Cell culture for RSV
Not very common anymore
Two methods:
- Conventional culture
- Shell vial –> much quicker, concentrate virus on cell layer to optimize infection

Why is immunity to RSV difficult to achieve?
- Antibody protection is incomplete (although it may help prevent lower tract disease)
- RSV “drifts” like influenza, which results in new mutations that make the virus difficult for immune system to recognize
RSV Vaccine Study
Some kids got inactivated RSV vaccine
Rates of contracted RSV vaccine and control group were the same, but 80% of the RSV vaccine recipients wound up in the hospital with RSV
Hypothesized that serum antibody without local respiratory antibody may worsen disease; RSV is an immunologic disease
Respigam
Human pooled antibody with high RSV titer
- Decrease in disease severity and hospitalization in RSV
Palavizumab (Synagis)
Once monthly IM injection during RSV season for high risk groups: premis, congenital heart disease
VERY expensive


