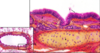
Respiratory Atlas Flashcards
what type of epithelium lines the nasal cavity
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
1

olfactory epithelium
2

respiratory epithelium
3

lamina propria
4

conchae
1

supportive cells
2

bipolar olfactory neurons (4-6 nuclei deep) occupy the middle of the epithelium
3
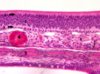
basal cells who’s nuclei lie adjacent to the lamina propria
4

thin walled veins
5

bone
6

bundles of pink-staining axons with flat dark staining nuclei of schwann cells (contain unmyelinated axons of bipolar neurons)
7

serous gland (bowman’s gland)
1

tall columnar supportive cells
2

olfactory neurons (bipolar)
3

basal cells
what is this image of?

olfactory epithelium
1

vocal ligament
2

vocalis muscle
1

seromucous glands
1

false vocal cord
2

laryngeal ventricle
3

true vocal cord
4

vocal ligament
5

vocalis muscle