Respiratory Flashcards
(51 cards)
Oxygenation of Hb promotes dissociation of H+ from Hb, this shifts equilibrium toward CO2 formation;therefore, CO2 is released from RBCs
Haldane effect
- in the lung
Increase in H+ from tissue metabolism shifts curve to righ,unloading O2.
Bohr effect
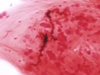
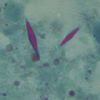
interdifitating ares of pink(platelets) and red(RBCs) found ONLY IN THROMBI FORMED BEFORE DEAD
LINES OF ZAHN
↓↓FEV/↓FVC<80%
↑RV
V/Q mismatch
Obstructive lung diseases
- chronic bronchitis
- blue bloater
- emphysema
- pink puffer
- Asthma
- bronchiectasia
- lead pulmanry hypertention(>25mmHg)and finally to corp pulmonale (decrease in O2 casues pulmonar vasoconstrctition)
Ththickness of gland layer/total thickness of bronchial wall>50%
Reid index
- greater tahn 50% in chronic bronchitis
- productive cough for >3 months per year for > 2 years.
dysnea,cough ,minim sputum and purse libs exalation
Emphysema
- exalation through pursed lips to increase airway pressure and prevent airway collapse during respiration.
- decrease lung recoil, increase compliance resulting from destruction of alveolar walls
ration of the pulmonary artery yo the blonchus at each lung hilus is described by?
RALS
right anterior
left superior
aspirate peanut:
while upright
while supine
- while upright:lower portion of right inferior lobe
- while supine:superior portion of right inferior lobe
structures perforatin diaphragm
at T8
at T10
at T12
I (IVC) ate(8) ten(10) eggs(esophagus) at(aorta) twelve(12)
at T8=IVC
at T10=esophagus,vagus
at T12=aorta,thoracic duct,azygos veins
air that can still be breathed in after normla inspiration
inspiratory reserve volume
air can still be breathed out after normal expiration
Expiratory reserve volume
Air in the lungs after maximal expiration
Residual volume
- cannot be mesure by spirometry
- incrased in obstructive lung disease
Determination of pysiologic dead space:anatomic dead space +functional dead space in alveoli.
VD=VT*PaCO2-PECO2/PaCO2
total volume of gas entering the lungs per minute
MINUTE VENTILATION(VE)
VE=VT*RR(respiratoy rate)
volumen of gas per unit of time that reaches the alveoli
Alveolar ventilation(VA)
VA=(VT-VD)*RR
Tau HB
Relaxed Hb
-
Tau in Tissue has low affinity to O2 leading to increase O2 unloading(curv to the right)
- CL,H+,Co2 and temperature favor tau
- Relaxed Hb high affinity for O2 in the respiratory tract
Methemoglobin treatment
Methylene blue
Whats Methemoglobyn
It is FERRIC Fe3+ hemoglobin that does not bing O2 readily, but has increase affinity for cyanide.
nitrates cause poisoning by oxidizing Fe+2 to Fe+3
Cyanide poisoning treatment(present in nitroprusside)
use nitrites to oxidaze Hb to methemoglobin,which binds cyanide.use thiosulfate to bind this cyanide,foming thiocyanate,which is renally excreted
cherry red skin and dead
CO posioning
- carboxyhemoglobin shift curve to the left, decreasing unloading in tissues
- normal pulsoxymeter
- TX:100% O2
what does a decrese in PAO2 does to the pulmonary circulation?
↓ in PAO2 causes a hypoxic vasoconstriction
In an effort to shift blood away from poorly ventilated regions of the lung to well-ventilated regions of lung
what does an increase in A-a gradient (normal 10-15) means
An incresea in A-a(>15) means Hypoxemia
- shunting
- V/Q mismatch
- intertitial lung disease
normal A-a gradient with hypoxemia(decreased PaO2)
- hypoventilation
- High altitude
V/Q=0
Airway obstruction(shunt) in shunt 100% does nor improve PO2