Repro Flashcards
(32 cards)
What side do inguinal hernais usually occur and why?
Vast majority are left sided - likely dt incr intra-abdominal pressure dt the rumen
Site for testicular biopsy
Dorsolateral testicle - superficial vasculature is most minimal here
Excessive haem if performed at other sites may necessitate castration
Which side are more likely to be cryptorchid in cattle?
And goats?
Cattle - LEFT sided crypts occur twice as commonly vs right side
Goats - more commonly RIGHT sided
Clinical signs & treatment of seminal vesiculitis
CSs- infertility (dt leukospermia), palpable gland enlargement
Seminal vesiculetomy - epidural & evacuate rectum. Cresent shaped incision in ishiorectal fossa curved around anus. Bluntly dissect cranially between rectum & sacroschiatic ligament. Laborious dissection of gland free from surrounding adhesions etc. Once free, chain ecreaseur placed around gland to remove. Close as much deadspace as poss & close skin.
Surgical management of ‘corkscrew penis’
Why does this occus?
Occurs dt premature slippage of the apical ligament before intromission (normally occurs around point of ejaculation), preventing intromission
sx - 10cm longitudinal incision along dorsal penis 3cm from tip to transverse preputial reflection. Expose apical ligament & suture its free edges to underlying tunical albuginea
Alternative - augment ligament w implantation of fascia lata strips
NB need to observe natural breeding for dx as can be artificially induced by electroejaculation or not present at all
What surgical options can be used to create teaser bulls
- Epididymectomy
- Vasectomy
- Penile tie-down (phallopexy)
- Attach penis to skin of the escutcheon
- Penectomy/phallectomy
- Preputial relocation
- Preputial obliteration
Ideal procedure would render animal infertile & unable to achieve intromission, therefore often combine procedures to achieve this
Describe procedure for epididimectomy
2cm skin incision ventral scrotum, extended into tail of epididymis. Bluntly separate tail from distal testis, ligate and remove. Avoid testicular damage.
Describe procedure for vasectomy
2cm incision in scrotal neck cranially, caudally or laterally. Or a single incision on median raphe Incisie skin & parietal tunic vertically, ductus located caudomedial aspect of cord in its own fold of mesorchium. ID & remove 3cm section. Repeat both sides
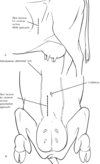
Features of testicular anatomy & differences from the horse
In the bull, the scrotum is located between the cranial parts of the thighs. On the cranial face of the scrotum are small, rudimentary teats that vary in number and spacing.
Testes are vertical vs horizontally (in the horse) within the scrotum.
Epididymis runs along caudomedial border of the testes.
At the distal pole of the testes, the ductus deferens begins at the tail of the epididymis and ascends the medial border of the testes
Procedure for penile tie down
permanent adhesion between penis & body wall
Dorsal recumbency, 5cm longitudinal incision midway between scrotal neck & preputial orifice, deepened to expose linea alba.
ID urethra (to avoid it), & suture dorsal tunica albuginea to linea alba w multiple interrupted large gauge nonabsorbable sutures. Skin closed routinely
Procedure to attach penis to skin of escutcheon
standing epidural, skin incision at palpable distal loop of sigmoid flexure & dissect to penis
Place large gauge nonabsorbable sutures through tunica albuginea & skin on each side of the incision avoiding urethra. Including retractor penis in closure ↑’s security
Penectomy/phallectomy:
performed at same site; dorsal to the neck of the scrotum
Dissect down to distal loop of sigmoid flex & free penis from its abdominal attachments by blunt dissection, then exteriorise & transect at an angle so a ventral flap can be used to cover CCP
Ligate dorsal aa of the penis then spatulate urethra to the skin incision
Alternative - dorsal recumbency, 15cm longitudinal skin incision from 5cm cranial to the scrotal neck extending cranially
ID & bluntly free penis, exteriorise & transect following straightening of sigmoid flex w tourniquet
Transect obliquely as before w ventral portion longer 10cm proximal to the preputial attachment
Spatulate urethra to penile stump & remove free portion of penis from prepuial attachments
Penile stump then sutured to the prepuce
Preputial relocation
Dorsolateral recumbency, so midline & 1 flank can be accessed
Circumferential incision around preputial orifice; skin around the remaining preputial orifice is notched or marked to preserve correct orientation & prevent torsion
Extend skin incision over caudal midline to within 5cm of the scrotal neck
Free internal preputial lamina bluntly, ligate vessels as required. Needs to be completely freely mobile while preserving some connective tissue and blood supply
Move freed prepuce to the side without stretching, marking new position lateral to the flank fold
Remove a circular portion of skin 1” smaller than what your freed up prepuce is
Create a tunnel bluntly toward base of scrotum & pull freed preputial orifice through toward its new location - needs to be lateral to the flank fold, if it is more medial than this then many can still achieve intromission
Close all incisions
Ideally do vasectomy as well as some learn to achieve intromission
Preputial obliteration
preputial orifice permanently closed & fistula created for drainage of urine
Lateral recumbency. 1” Penrose onto tip of penis
Remove 1-2cm strip of skin ventrally 5cm caudal to external opening of prepuce, & lamina interna incised, & sutured to skin, creating a fistula with the free end of the Penrose passed through it
End of prepuce removed by cutting through skin, SQ & internal lamina; closed in same 3 layers
Penrose left in for approx 3 weeks
Technique for std castration of calves (ideally approx 4 weeks)
- Scrotum grasped, & horizontal incision made through skin & fascia at its widest (junction of middle & distal 1/3). Entire distal segment of the scrotum is transected & common vaginal tunic is left intact.
- Traction placed on testes, & skin is pushed proximad so fascia is separated from spermatic cords enclosed in the common tunics. Don;t touch proximal spermatic cords.
- Alt: Newberry knife; makes a vertical incision from middle of the scrotum leaving cranial & caudal flaps of scrotal skin. Testes are dissected same as above. Incision heals by these flaps contracting on themselves → better drainage
- Emasculate cords proximally without tension on the cord during emasculation. Any redundant adipose tissue is removed
- In larger bulls, may ligate cords w no. 2 absorbable suture rather than trust the emasculators alone.
- In younger bulls, slow constant tension can be used to remove the testes instead of emasculators. Stretching the cord to failure takes advantage of natural hemostasis

Most common site of urethral calculi obstruction in cattle
Distal bend of the sigmoid flexure, close to attachment of retractor penis mm
Occurs more commonly in steers (castrated males) dt smaller urethral size

Types of urolith commonly seen in cattle
Silicate calculi, which are rough and hard, occur in steers grazing stubble & pastures consisting largely of grasses.
Phosphate calculi; soft, smooth, & often multiple, are more common in steers in feedlots
Most common procedure to treat steers w urethral obstruction
What sites can this be performed at?
Urethrostomy most commonly used to allow recovery to permit reaching slaughter weight. Not a good long term solution as commonly stricture & obv can’t breed if entire bulls as urethra not continuous
- Usually standing or can be cast in dorsal.
- Can be performed at multiple sites - ‘high’ is just ventral to anus - ++ scalding & generally penilised market value. Lower is in region of the distal bend of sigmoid flexure. Advantage of low incision is that penis can be directed so urine is forced caudad,∴↓ scalding, & also more likely to encounter the obstructing calculus for removal
- A low urethrostomy may also be performed cranial to the scrotum or scrotal remnant.
Describe technique for urethrostomy at the distal sigmoid flexure
- Penis is palpated immediately caudal to scrotal remnant; latter grasped & stretched craniad, & distal bend of sigmoid flexure is located.
- 10cm skin incision on midline directly over the penis, & blunt dissection to locate penis; generally deeper than anticipated & is firm fibrous structure the thickness of index finger.
- With traction, a portion of penis is exposed through skin incision
- Retractor penis mm are a useful guide to location of ventral surface of penis where they attach at the distal bend of the sigmoid flexure. May be possible to palpate urethral calculi.
- Can make small incision directly over calculus on ventral penis for removal. Catheter inserted into the urethra, both proximally & distally, to search for further stones and to ensure urethral patency. The urethra may be sutured if there is no necrosis, w SI or simple continuous absorbable sutures going down to, but not through, urethral mucosa.
- Penis replaced & dorsal 1/3 of skin incision is closed
- With necrosis of, urethra & skin incisions left to heal by 2nd intention.
- With damage to the penis & surrounding tissues, transection & extirpation of the penis are performed: penis is dissected from dorsal arteries & veins & transected to leave 8-12cm proximal stump. Arteries & vv appear ventral to the exposed stump of the penis. These vessels are ligated (some surgeons do not consider this necessary).
- Penile stump should be of sufficient length so no tension when sutured to skin
- Exposed penis is directed caudoventrad & is anchored to skin w 2 sutures, passing through skin, tunica albuginea, CCP, without compromising urethral lumen
- Urethra at end of penile stump is split, & edges sutured to lateral aspects of penis.
- W urethral rupture - ++ cellulitis; make several bold, longitudinal incisions lateral to the prepuce with a scalpel, for drainage
Most common site of penile haematomas in bulls
What is the usual cause?
Penile hematomas usually result from a rupture of tunica albuginea on the dorsal aspect of the distal bend of the sigmoid flexure, opposite insertion of retractor penis mm.
Swelling dt hematoma usually occurs near distal sigmoid flexure, which in standing bulls is near the base of the scrotum, or in the proximal half of the sheath.
The size of the defect in the tunica albuginea varies & probably related to the amount of intracorporeal blood pressure at the time of rupture. The amount of extravasated blood may be related to the length of time erection is maintained after injury or more likely the number of subsequent attempts to achieve an erection
Penile hematomas occur during breeding when the bull fails to achieve intromission prior to the copulatory thrust, resulting in a bending of the erect penis. Preputial prolapse frequently accompanies penile hematomas & has been reported as 1 of the most common presenting complaints .

Treatment of penile haematomas
- Medical tx = hot packs, warm hydrotherapy, penicillin 2 weeks, & US tx to speed resorption of the hematoma.
- Decision for sx usually based on size of the hematoma, length of time between accident & tx, and value of the bull. Generally larger haematoms more likely to req sx. Sx success much worse @ 14d post injury, so generally operate sooner the better
- Lateral w local or GA
- 13cm skin incision in a cranioventral direction over most prominent part of swelling, through SQ into haematoma (not incising penis itself)
- Manually remove clots
- In acute cases, rent in tunica albuginea readily ID. More difficult where chronic - fibrin & granulation tissue; req careful dissection to locate rent. Beware/avoid dorsal nerves of penis
- Edges of the rent are debrided & sutured w SI 0 or 2-0 synthetic absorbable suture.
- Alt: continuous bootlace pattern to minimize knots
- Preferable to suture the defect as vascular shunts may form between CCP & dorsal vessels.
- Fascial layers of the penis are sutured w 2-0 synthetic absorbable simple continuous pattern.
- Skin closed w SI or vertical mattress nonabsorbable sutures.
- W marked preputial inflammation, swelling, or prolapse (difficulty w manual retraction of the penis); umbilical tape suture is placed through the dorsal aspect of the penis under the apical ligament and tied. NOT through tunica abugenia or urethra

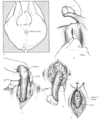
Whats the diagnosis?
What is important to observe diagnostically?
How is this condition managed?

Dx - spiral deviation/corkscrew penis, dt slippage of the APICAL ligament
Important to observe natural breeding - this is a normal penile position that usually occurs after intromission. Occurring before prevents intromission. Can be missed or artificially induced by electroejaculation so not useful diagnostically.
Tx - anchoring of the apical ligament
- GA or standing
- 10cm incision over dorsal penis w penis extended, from 3cm caudal to tip
- Dissect to expose apical ligament, identify lateral borders & suture to adjacent tunica albuginea (without penetrating TA full thickness) w absorbable SI suture.
- Routine skin closure & 6-8wk sexual rest
- Alt: augment apical ligament w graft of strips of fascia lata or synthetic materail.
- Graft harvested via 15cm skin incision from TC to patella. Take 3-4 0.5cm wide 10cm long strips
- Suture via open (as above) or closed techniques - 2cm longitudinal incision dorsal penis then tread fascial strips along dorsum of penis - not sutures in place.
Whats the diagnosis?
Tx options?
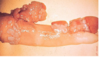
FIBROPAPILLOMA most common penile tumour in bulls - vs SCC in EQ
Many regress but may take time & interfere w intromission
Sx tx incl. sharp dissection, electrocautery & cryotherapy
Diagnosis & treatment
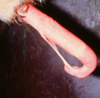
Persistent frenulum - most preputial/penile separation complete by 9-12mo - some retain 1 or more strands of tissue, usually along ventral edge
Sx - extend penis as much as poss. Place ligatures & cut between. Can use 1wk PO