dentistry ch 9 Flashcards
Difference between brachydont & hypsodont teeth
- Brachydont teeth - relatively short crowns and long roots, found in carnivores and some omnivores such as the pig-> all porcine teeth are brachydont with the exception of the tusks/canines A newly erupted adult brachydont tooth will not erupt past the crown-root junction of the tooth. Therefore brachydont teeth remain static within the oral cavity
- Hypsodont teeth have long crowns and comparatively short roots. Grazers typically have hyposodont teeth w long reserve crowns that erupt over a prolonged period
What are the 2 subdivisions of hypsodont teeth?
Radicular hypsodont teeth, found in cattle and small ruminants, have well-formed roots that mature completely. These teeth can erupt for a prolonged period, but the root apices eventually close and tooth development ceases.
Aradicular hypsodont teeth do not have true roots. The root apices never close, and the crown continues to develop throughout the animal’s life. Continual development occurs via dental progenitor cells at the tooth apex, adding complexity to considerations for treatment of endodontically infected or broken teeth needing extraction or endodontic therapy
Main method of prehension in cattle & small ruminants
Cattle - tongue
Samll ruminants - lips
Deciduous and permant dental formulae in cattle
Deciduous = 0/3, 0/1, 3/3 (no deciduous molars as in horse)
Permanent 0/3, 0/1, 3/3, 3/3
3 molars & 3 pre-molars as in horse
NB the canine is adjacent to & same mophology as incisors so looks like a fourth incisor
Ruminants have infundibulae in their maxillary & mandibular teeth
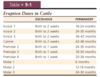
Deciduous & permanent dental formulae in sheep/goats`
Deciduous - 0/3, 0/1, 3/3 - no deciduous molars
Permanent 0/3, 0/1, 3/3, 3/3
Cattle & sheep (like horses) have 3 roots to maxillary PM/M (mesio & distobuccal & palatal)
& 2 to mandibular.
the 3rd lower molar (ie 11) has a widened distal root almost double width

Deciduous & permanent dental formulae in pigs
Deciduous dental formula = 2(Di 3/3, Dc 1/1, Dp 3/3)
Permanent dental formula = 2(I 3/3, C 1/1, P 4/4, M 3/3)
Premolars have 2 roots. Molars have 4-6 roots
First premolar is located caudal to canines (tusks); latter continually reupt throughout life but remaining teeth are brachydont

3 classes of dental malocclusions
Class 1 - neutroclusion; malalignment of individual teeth with normal rostrocaudal relationship of mandible/maxilla
Class 2 - mandibular bracynathia/distoclusion (parrot mouth)
Class 3 - maxiallry brachygnathia/madibula prognathia/mesioclusion (undershot jaw)

Causative agent of ‘lumpy jaw’
and wooden tongue?
Lumpy jaw = Actinomyces bovis (affects primarily bone)
Wooden tongue = Actinobacillus lignierisi (affects primarily soft tissues)
Tx of lumpy jaw
IV sodide plus ABs (pen, oxytet, florphenicol)
+/- debridement of affected bone/extraction of affected teeth. Weakened bone may break
Management options for jaw fractures
1) Conservative - NSAID, wound management, soft diet. Indicated if minimal instability (eg uniaxial mandibualr ramus fx)
2) Surgical - Stableisation options incl. include external splints, intraoral acrylic splints, cerclage wires, interdental wires, tension band wires, intramedullary pins, lag screws, metal U bars, compression plates, and external fixators. Preserve any affected teeth wherever poss. Even severly damage may recover & can always remove later. Early removal compromises stability of fixation
Odontoplasty definition
Removal of enamel (usually only) +/- other hard dental tissues to change the shapr of the tooth
eg routine rasping = odontoplasty
Recommendations for reduction of hypsodont teeth (same as for horses)
3-4mm reduction every 3 months. Limits risk of removing too much 2ary dentine & exposing pulp = pulpitis +/- apical infection
How to perform odontoplasty in pigs
Only the canines require any routine odontoplasty
Sedate & trim regularly
Can use gigli wire, motorised cutting wheels, and dental drills
Avoid cutters and nippers because longitudinal fractures of the tusk may occur.
Tusks should be trimmed or crown amputated to roughly 1 cm above the gingiva and contoured to a smooth finish to limit the risk of pulp exposure
Principles of dental extractions in pigs
Typically similar to human/SA extractions.
Most teeth can be accessed intra-orally with SA instruments UGA
Molars may req. mucoperiosteal flaps, tooth sectioning before removal (see fig)
Main exceptions are
1) Canine - extraction can be complicated & usually req extra-oral approach or intra-oral mucoperiosteal flap with alveolar bone removal with high speed drill.
2) Last molar - size of the third molar tooth combined with limited access in the caudal aspect of the mouth makes extraction of this tooth a serious challenge - do only if there are no other options

Wiring of rostral dental fractures in ruminants
Simiar principles to EQ but the premolars don’t provide adequate strength, so caudal wire loop needs to be passed around the first molar, twisted in the interdental space & then around incisors as required. Ideally then apply dental composite over wiresto splint & improve stability.



