Renal Replacement Therapy 2 Flashcards
Where is the transplanted kidney usually located in the body?
Iliac fossa

What vessels is the transplanted kidney anastomosed to?
Iliac vessels

What happens to the native kidney when a kidney is transplanted?
Is usually left in situ
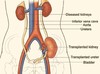
What are indicates for native nephrectomy?
Size (polycystic kidneys)
Infection (chronic pyelonephritis)
How is preservation of the donor kidney achieved?
- Cold storage solutions
- Minimise oedema
- Preserve integrity of tissues
- Buffer free radicals
What are some complications with kidney transplants?
- Vascular complications
- Bleeding
- Usually anastomotic sites
- Perirenal haematoma can be arterial or venous
- Arterial thrombosis
- Venous thrombosis
- Lymphocele
- Bleeding
- Ureteric
- Urine leak
- Infections
How is immunosuppression achieved after a kidney transplant?
- Corticosteroids
- Calcineurin inhibitors
- Tacrolimus, cyclosporine
- Anti-proliefratives
- Mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine
- mTOR inhibitors
- Sirolimus
- Costimulatory signal blockers
- Belatacept
- Deleting agents
- Basiliximab ( anti-CD25), Anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG), Rituximab (anti-CD20)
What are side effects of corticosteroids?

What are side effects of tacrolimus?

What are side effects of cyclosporin?

What are side effects of mycophenolate mofetil?

What are side effects of sirolimus?

What are side effects of belatacept?

What are side effects of ATG?

Explain the typical immunosuppression protocol?
- Induction
- Basiliximab
- Maintenance
- Tacrolimus and mycophenolate and steroids
- Steroid free is possible
- Others
- CNI-free using belatacept
What are some different types of donors?
- Decreased donors
- Donation after brain death/DBD
- Standard/extended criteria
- Donation after cardiac death/DCD
- Standard/extended criteria
- Donation after brain death/DBD
- Living donors
- Living related donor
- Living unrelated donor
- Spousal
- Altruistic
- Paired/pooled
What does DBD stand for?
Donation after brain death
What does DCD stand for?
Donation are cardiac death
What is the criteria to be considered a donor after brain death?
- Coma, unresponsive to stimuli
- Apnoea off ventilator (with oxygenation) despite build-up of CO2
- Absence of cephalic reflexes
- Pupillary
- Oculocephalic
- Oculovestibular
- Corneal
- Gag
- Purely spinal reflexes may be present
- Body temperature above 34oC
- Absence of drug intoxication
What are the 2 kinds of donor criteria?
- Standard criteria (SCD)
- Extended criteria (ECD)
- Donor aged over 60
- Donor aged 50-59 with history of hypertension, death from cerebrovascular accident or terminal creatinine of over 123umol/L
What does SCD stand for?
Standard criteria donor
What does ECD stand for?
Extended criteria donor
When is somone considered to be an extended criteria donor?
- Donor aged 50-59 with history of hypertension, death from cerebrovascular accident or terminal creatinine of over 123umol/L
Is there a gap between supply and demand for kidney transplants?
There is way more demand than supply










