Rapid Review 2 Flashcards
neutralizing substance for
Sda
guinea pig urine
neutralizing substance for
P1
hydatid cyst fluid
and
pigeon eggs
neutralizing substance for
H
saliva
Ulex europaeus
lotus tetragonolobus
neutralizing substance for
Le a
saliva
neutralizing substance for
I (big i)
breast milk
neutralizing substance for
chido
plasma
neutralizing substance for
rodgers
plasma
neutralizing substance for
A1
dolichos biflorus
neutralizing substance for
B
bandeiraea simplicifolia
neutralizing substance for
T
arachis hypogaea
neutralizing substance for
N
vicea graminea
generally insignificant allo antibodies
LoveLy & Pretty MeaNingless
Le a
Le b
P1
M
N
when should you use an F test?
to decide if one test is more precise than the other
(i.e. how different are the distributions of 2 data sets)
on a Lineweaver Burke plot, what is the y intercept?
1 over Vmax
on a Lineweaver Burke plot, what is the x intercept?
1 over Km (Michaelis constant)
how do competitive inhibitors relate to a drug without an inhibitor?
same y intercept
different x intercept (bc Km increases)
how do non-competitive inhibitors relate to a drug without an inhibitor?
same x intercept
different y intercept (bc they alter V and Vmax)
on a Lineweaver Burke plot, what is the x axis?
1 over [S]
on a Lineweaver Burke plot, what is the y axis?
1 over V
put the thyroid hormones in order from most to least metabolically active
T3 > T4 > rT3
Best marker for pancreatic insufficiency
fecal elastase test (abnormal = low, <100)
what happens to the pH, pO2, and pCO2 of blood if you leave it in the tube/syringe for a while?
pH goes down
pO2 goes down
pCO2 goes up
pO2 goes down & pCO2 goes up bc the pyruvate cycle is going
what happens to the pH, pO2, and pCO2 of blood if you leave it open to ambient air for a while?
pH goes up
pO2 goes up
pCO2 goes down
it starts to ~become the air
Wilson disease
mode of inheritance & gene
auto recessive
ATP7B mutation
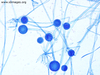
what’s this

cryptococcus neoformans
what’s this

cryptococcus neoformans
what’s this

cryptococcus neoformans
what’s this
cryptococcus neoformans
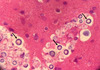
what’s this

coccidioides immitis
what’s this
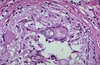
coccidioides
what’s this

coccidioides
fungus from southwestern US
coccidioides
what’s this

coccidioides
what’s the bat guano fungus
histoplasmosis
what’s this

histoplasma
what’s this
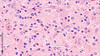
histoplasmosis
what’s this

entamoeba histoloytica
what’s this

balamuthia mandrillaris
amoeba
what’s this
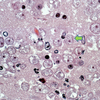
balamuthia mandrillaris
amoeba
what’s this

babesia
what’s this

babesia
what’s this

plasmodium falciparum
banana = gametocyte
rings in RBC = trophozoite
which malaria is quotidian?
plasmodium knowlesi
DAILY - fevers spike q24
quotidian = quotidien (Fr) = daily
which malaria is quartan?
plasmodium malariae
3 day cycle
which malaria is tertian?
B9: vivax & ovale
Malignant: falciparum
fevers q2days
which malaria is BENIGN tertian?
vivax more commonly than ovale
which malaria is MALIGNANT tertian
falciparum
what stage of RBCs does vivax preferentially penetrate?
young/reticulocytes
how does vivax enter the RBC
via Duffy blood group antigens
which malaria enters the RBC via the Duffy blood group antigen?
vivax
most diagnosed infections of P. vivax are thought to be due to what stage of the life cycle (and doing what)?
hypnozoite reactivation
hypnozoite = dormant in liver, released days-years after initial infxn
which malaria can reach higher levels of parasitemia than other species, and why?
falciparum
bc it infects ALL stages of RBCs, not just young ones
why is the malignant tertian malaria malignant?
FALCIP > inserts Pfemp1 into infected RBC membranes > adheres to CD36 on endothelial cells > microcirculation obstruction > organ dysfxn
this is called sequestration
what organ does falcip go to first?
after bloodstream
liver
what causes the cyclical fever in malaria?
the blood stages, where RBCs synchronously rupture to release merozoites
which malaria can have applique forms?
falciparum
which malaria can have maurer’s clefts?
falciparum
what malignancy is associated with p. falciparum?
Burkitt!
which malaria has Schuffner’s dots?
vivax and ovale
(the benign tertian ones)
which malaria prefers older RBCs?
p. malariae
which malaria has the characteristic band/basket form?
p. malariae
(it’s the trophozoite)
which malaria has comet/fimbriated cells?
ovale
(the RBCs will be ovoid)
which malaria is this?
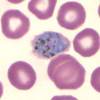
ovale
which malaria is this?

ovale
which malaria is this?

vivax
(Schuffner’s dots)
which malaria has a headphone-shaped ring/merozoite form?
falciparum
which malaria is this?

falciparum
(left arrow = headphone, right arrow = applique form)
which malaria is this?

malariae
(band form)
which malaria is this?
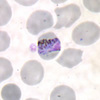
malariae
(band form)
which malaria is this?

p. malariae
(basket)
(schizont)
which malaria is this?
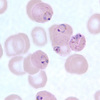
falciparum
(Maurer’s clefts = the red dots in the RBCs)
what’s this

coccidioides immitis
what’s this

balantidium coli (ciliated)
what’s this?

entamoeba histolytica
what’s this

entamoeba histolytica
what’s the big difference between necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale?
necator has cutting plates
ancylostoma has teeth
what’s the other word for roundworms?
nematodes
whose egg is this?

hookworm
(could be necator or ancylostoma, they look the same)
hookworms are under the umbrella “roundworm/nematode”
whose egg is this?
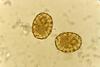
ascaris lumbricoides
whose egg is this?

ascaris lumbricoides
unfertilized on left, fertilized on right