Radiology Imaging + Pathology Flashcards
How can you determine whether a CXR is adequately inspired?
Anterior ends of at least 6 ribs should be visible

Name the different mediastinal borders on this image:
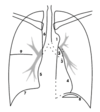
- Aorta
- Pulmonary artery
- Left auricle
- Left ventricle
- Right atrium
- Trachea
- Hemidiaphragm (right)
- Stomach bubble
- Horizontal fissure
What are some potential causes of Lobar Collapse?
Occurs when obstruction of a lobar bronchus
Causes of bronchial obstruction include tumours, aspirated foodstuffs, mucus impaction
(lobe supplied by obstructed bronchus no longer ventilation and air is resorbed = loses volume)
Identify this pathology:

Left Lower Lobe Collapse

Identify this pathology:

Left Upper Lobe Collapse

Identify this pathology:

Right Upper Lobe Collapse

Identify this pathology:

Right Middle Lobe Collapse

Identify this pathology:

Right Lower Lobe Collapse

What type of lobar collapse is visible here?

Right Middle & Lower Collapse

What area of the lung is affected by consolidation here?

Right Middle Lobe Consolidation
- Increased density in right lower zone
- Loss of clarity of right heart border but preservation of hemidiaphragm

Identify this pathology:

Left Lower Lobe Consolidation
- Increased density in left upper + lower zones
- Loss of clarity of left upper medistinum
- Volume preserved
- Air Bronchograms

What kind of pathology is visible on this CXR?

Right pleural effusion
What pathology is visible on this CXR?

Pneumothorax

What are the 4 main signs of pulmonary oedema on CXR in order of severity/occurence?
- Dilatation of upper lobe vessels/cardiomegaly
- Interstitial opacities (Kerley B lines, peribronchovascular cuffing)
- Airspace opacification (filling of alveoli with fluid, severe - batwing)
- Pleural effusion

What typical feature of pulmonary oedema is highlighted on this CXR?

Alveolar oedema/ BAT WINGS

Describe the placement of this endotracheal tube:

- Tube inserted too far
- Passed into right main bronchus
- Signs of early collapse (due to unventilated left lung)
Normal = tip 5cm above carina, width 2/3 tracheal diameter (should not expand trachea)
Describe the placement of this endotracheal tube:

- Correctly placed
- Tip 5cm above carina
- Width should be roughly 2/3 diameter of trachea (cuff should not expand trachea)
- Both lungs are ventilated
Describe the ideal placement of a nasogastric tube?
- Subdiaphragmatic position in stomach
- Overlying gastric bubble
- Should be at least 10cm beyong gastro-oesophageal junction

Describe the placement of this nasogastric tube:

NG tube misplaced
Located in right lower lobe bronchus
High change of infection/complications
The following image shows the pathways of various central venous catheters - where does each line originate from?

Yellow - peripheral central catheter (cephalic, basilic, brachial)
Purple - Right subclavian vein
Light blue - Right jugular vein
Dotted blue - Left jugular vein
What point in the heart is highlighted by the red circle in this image?

Cavoatrial Junction
The tip of a venous catheter should sit at the cavoatrial junction (SVC meets and melds with superior wall of right atrium)
What abnormality is visible on this CXR?

Pneumoperitoneum
(perforation of hollow viscus resulting in gas within peritoneal cavity)
What artery is affected in this ischaemic stroke?

Left PCA (posterior cerebral artery)

Which artery is affected in this ischaemic stroke?

Right ACA (anterior cerebral artery)

Which artery is affected in this ischaemic stroke?

Right MCA (middle cerebral artery)

What is visible in this CT and at what stage would you expect to see this during the evolution of a stroke?

= Hyperdense segment of a vessel
Direct visualisation of intravascular thrombus/embolus
Often EARLIEST visible sign on CT
What is visible on this CT and at what point in a stroke evolution would you expect to see this?

- = Loss of grey-white differentiation, and hypoattenuation of deep nuclei
- Cortical hypodensity with associated parenchymal swelling (with resultant gyral effacement)
- Typically seen within first few hours of presentation
What is visible on this CT and at what stage in a stroke evolution would you expect to see this?

- This is a later sign in a stroke presentation
- With time, the hypoattenuation and swelling becomes more profound
- Results in significant mass effect
True or False:
Gliosis is an early finding on CT in stroke?
FALSE

Gliosis develops over time, eventually appearning as a region of low density with volume loss
What type of cerebral haemorrhage is this?

Intra-axial haemorrhage/Intra-cerebral haemorrhage
Bleeding into brain parenchyma
What type of cerebral haemorrhage is this?

Extra-dural haemorrhage

What type of cerebral haemorrhage is this?

Sub-dural Haemorrhage

What type of cerebral haemorrhage is this?

Sub-dural haemorrhage

What type of cerebral haemorrhage is this?

Subarachnoid Haemorrhage

What are the names of these different types of herniation?

A - Subfalcine
B - Central
C - Uncal
D - Tonsillar
What pathology is imaged here?

Hydrocephalus
What is the correct descriptions for this fracture types?

A - Transverse
B - Oblique
C - Spiral
D - Comminuted

What is the correct descriptions for these fracture types?

A - Avulsion
B - Impacted
C - Torus
D - Greenstick

What fracture is shown here?

Humerus surgical neck fracture
What abnormality in this X-ray indicates there could be a possible pathology?

The anterior fat pad (and posterior slightly) is more visible than it would usually be
This indicates perfusion within that joint (blood or fluid)
Which fractures (adults + children) will most commonly show abnormal fat pad?
Adults - radial head fracture
Children - supracondylar fracture (anterior sail sign)
What is a Colles fractures and who is at most risk?
Fracture of distal forearm in which broken end of radius moves dorsally
Common in elderly, fall onto outstretched hand

What is a Smith’s fracture?
Fracture of distal radius
With associated volar angulation of distal fracture fragments
(aka Reverse Colles fracture)
True or False:
Intracapsular fracture of the femur have better healing than extracapsular fractures
FALSE
Intracapsular - lose blood supply to femoral head = AVN
Extracapsular - blood supply remains so improved healing
What type of femur fracture is shown here?

Intracapsular fracture of femur
What type of femur fracture is shown here?

Intertrochanteric fracture of femur
What are some advantages and disadvantages of CT?
A - quick, accurate, allows better planning of surgery or intervention
D - radiation exposure, renal impairment,
What pathology is seen on this CT?

Acute Appendicitis
What pathology is this most likely to be?

Acute Cholecystitis
What type of test is this?

MRCP
MR Cholangiopancreatography
(Can be used to show stones in common bile duct or GB causing obstruction)
What pathology is shown here and who is most likely to get it?

Emphysematous Cholecystitis
= acute infection of GB wall caused by gas-forming organisms
(Air in gallbladder wall visible)
Seen in Diabetics
What are some common causes and symptoms of Small Bowel Obstruction?
Causes - adhesions, cancer, herniae, gallstone ileus
Symptoms - vomiting, pain, distension
Signs - increased bowel sounds, tenderness, palpable loops
What are some common causes of large bowel obstruction?
Colorectal cancer (60%)
Volvulus (15%)
Diverticulitis (10%)
What are some potential causes of perforation?
Common:
- Perforated ulcer (decreasing incidence as treatment improved)
- Diverticular perforations (1-2% generalised, most localised)
Less common:
- Secondary to cancer
- Secondary to ischaemia
What is the normal blood flow to the GI tract and at what level does ischaemia develops?
Normal GI blood flow - 20% cardiac output
If <20% ischaemia develops
What are some symptoms + signs of bowel ischaemia?
Severe abdominal pain
Vomiting
Diarrhoea
Distension inconsistent
Borderline amylase
Raised WCC
Acidotic
What pathology is seen on this scan?

Right Ureteric Calculus
What pathology is seen on this scan?

Leaking AAA


