Radiology II Flashcards
the MRI can be used to image what elements?
which element does it image in medicine?
why?
- can be used to image any element with an odd number of protons
- in medicine, it is tailored to image / manipulate H+ (one proton)
- this is b/c there are so many H+ atoms in the body
hydrogen is in what state when bound to a molecule within body tissues?
which body tissues most dense in hydrogem?
- when bound: H+ goes from having 1 elecron + 1 proton to just 1 proton.
- tissues most abundant with H+: water, fat
what is the significance of a spinning proton?
the spinning positive charge creates a tiny electrical current
how does hydrogen behave organically vs in the presence of an external magnetic field?
why is this important?
- no external magnetic field:
- protons oreinted different directions
- their individual electric signals cancel out
- external magentic field (in an MRI):
- protons align (either parallel or antiparallel)
- this generates magnetic field
how is an image generated from aligned protons in an MRI?
- a radiofrequency (RF) pulse is sent onto, inducing protons to temporal change their alignments
- the new spinning magnetic field produce an electrical signal
- this electrical signal is detected by a antenna (coil) then mapped into an image
what are TE and TR?
- TE (echo time): time between sending RF pulse and measuring the signal
- TR (reptition time): time between successive RF pulses
what is the difference between T1 and T2 weighted signals?
- T1: fat is white
- T2: fat AND fluid (CSF, for example) are white
label
T1 vs T2?

cerebellar tonsils
T1 (fluid is dark)
label
T1 vs T2?

cerebellar tonsils
T2 (eye fluid is white)
tonsillar herniation
- definition
- causes
- when tonsils pass inferior to foramen magnum
- causes:
- Chiari I malformation, often associated w/ syrnix - congenital, mild
- intracranial hemorrhage - acquired, life threatning
- tumor - aqcuired, life threatning
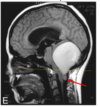
identify

tonsilar herniation (inf to foramen magnum)
d/t chiari I malformation
identify
tonsillar herniation (inf to foramen magnum)
d/t posterior fossa tumor
label
T1 vs T2


label
T1 vs T2

T2

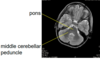
label
T1 vs T2
middle cerebellar peduncle
T2
how does multiple sclerosis appear on an MRI
- T2 intense plaques (lesions) within white matter, which if often:
- radiating perpendendicular from lateral ventricles
- within the corpus collosum
- in middle cerebellar peduncle

identify
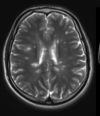
multiple sclerosis
plaque (lesion) perpendicular from lateral ventricle
identify

multiple sclerosis
plaque (lesions) perpendicular from lateral ventricles
identify

multiple sclerosis
plaque (lesion) in corpus collosum
identify

multiple sclerosis
plaque (lesion) in the middle cerebellar peduncle
label

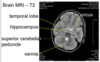
identify

uncal herniation

hippocampus
hippocampus atrophy - cause?
Athzheimers, commonly

identify
atrophied hippocampus
Alzheimers
label
T1 vs T2?


identify

epidural hemoatoma
(lens shape)
parkinson’s affects what part of the brain?
the substantia nigra
label
T1 or T2?

T2

label
T1 vs T2?

chronic lacunar infarction
- definition?
- presentation?
- cause: ischemic stroke to the caudate nucleus
- presentation: memory loss

identify
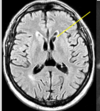
chronic lacunar infarction
identify

chronic lacunar infarction
identify
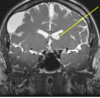
chronic lacunar infarction
label
T1 vs T2


acute cerebral infarction
- presents how on MRI?
- and why?
- how soon after event?
- with what kind of imaging?
- presents with with T2-hyperintensity
- d/t restircted water movement b/c of
- lack of blood flow
- cytotoxic edema
- seen as soon as pt appears for care
- on diffusion waited imaging
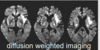
how does an acute cerebral infarction present on CT as opposed to MRI?
- with ribbon like insular cortex
- not for several hours after event

identify

acute cerebral infarction - MRI
T2-hyperintensity on diffusion weighted imaging
identify

acute cerebral infarction - CT
ribbon like insular cortex
identify

ependiymitis granularis
- a normal variant of ventricular ependyma that has
- less myelin
- increased ECF
- some ependymal degeneration
label

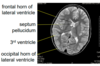
what is a “midfline shift”?
what is it caused by?
- aka subfalcine herniation
- a mass effect on one side of the brain cause a shift of the septum pellucidum away from the midline towards the opposite side
- ex - subdural hematoma
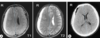
identify

subfalcine herniation
in this case, due to subdural hematoma (cresent shape)
first is T1, second is T2
label

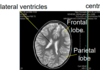
label
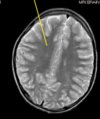
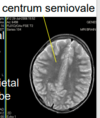
hydrocephalus
- cause
- variations
- presentation on MRI
- cause: abnormal increased CSF volume
- presentation on MRI: ventromegaly
- variations: non-communicating (no visible obstruction), communicating (visible obstruction)
how does normal pressure hydrocephalus present?
“wacky, wobby & wet”
- dementia (wacky)
- wobby (ataxia)
- wet (urinary incontinence)
label
T1 vs T2?


label


pituitary adenomas are divided into what two main types?
how do they differ?
- microadenomas (<1 cm): can produce hormones
- macroadenomas (>1 cm): can produce hormones & exert significant mass effect?
how are macroadenomas typically discovered?
how are they treated?
- by growing large enough to compress the optic chiasm and result in visual symptoms
- treatment: bromocriptine
identify

pituitary microadenoma
label


label


label

label


label


label


label


identify

cerebral aneurysm
identify



