Quantum Theory Definitions and Formulas Flashcards
(23 cards)
Electromagnetic Radiation
Originate from the movement of electric charges. This movement causes oscillations or fluctuations in electric and magnetic fields that are propogated over distances.
Wave
a progressive, repeating disturbance that spreads through a medium from a point of origin to more distant points.
Frequency
Amplitude
Height of the wave measured from the centerline between peak and trough.
The wave nature of light
Electromagnetic Spectrum
- The range of frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation.
- The visible spectrum is between violet @ 400 nm to red @ wavelengths less than 800 nm
Planks Constant
value of 6.63 X 10-34 J • s
used the the formula to find the energy of a photon
E = n • h • nu, where n = a whole number, h = plank’s constant nu = frequency
Note: the vibrational energies of an atom is said to be quantized.
Photoelectric Effect
The ejection of electrons from the surface of a metal or from another material when light shines on it.
The wave and particle pictures of light should be regarded as complentary views of the same entity. This is called the wave-particle duality of light
E = energy of a light particle or wave
h = planks constant
v = frequency of wave (not v for velocity)
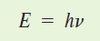
Continuous spectrum
a spectrum containing light of all wavelengths
Line Spectrum
spectrum showing only certain colors or specific wavelengths of light.
Bohr’s Postulates
- Energy level postulate
- electrons can have only specific energy values in an atom (energy levels)
- E = - (RH / n2) where n = levels, RH = Rydberg constant at 2.179 x 10-18
- Transitions between enegry levels
- electrons can change energy by going from one level to another
- E = (- RH / nf2) - (- RH / ni2)
Bohr’s Theory
- Emmision of light from atom is due to electron transitioning from upper energy level to lower level
- Ground state: electrons in their lowest possible energy level.
- Excited state: electrons in higher energy level due to electric discharge. an atom in an excited state eventulally emits photons as the electrons drops back to one of the lower energy levels and eventually to the ground state.
Quantum Mechanics
- Used to describe small particle behaviour based on wave properties of matter.
- Wave nature is shown when light is dispersed into a spectrum by a prism
- particle nature is shown when protons displace electrons from a metal in the photoelectric effect.
de Broglie Relation
Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle
- a relation that states that the product of the uncertainty in position and the uncertainty in momentum of a particle can be not smaller thatn planck’s constant divided by 4π
Atomic Orbital
- a wave function and a set of quantum numbers.
- denoted by the greek letter psi, squared
- example: (psi)2
- a region of space in which the probability of finding an electron is high. Three is needed because of 3D space.
- a fourth quantom number (Ms) is the magnetic property of electron called spin.
Quantum Numbers
- Principle Quantum Numbers: (n) The one on which the energy of an electron in an atom principally depends; it can have any positive value 1,2,3 etc.
- Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l): also called the azimuthal quantum number, this number distiguishes orbitals of given n having different shapes; it can have any integer value from 0 to (n - 1). eg. spdfg levels
- Magnetic Quantum Number (ml): distiguishes orbitals of given n and l – that is, of given energy and shape but having a different orientation in space; the allowed values are the integers from -l to +l
- Spin Quantum Numbers (ms): refers to the two possible orientations of the spin axis of an electon, possible values are +1/2 and-1/2
Atomic Orbital Shapes
- S-Orbital: all spherical. probability of finding an electron depends on distance from the nucleus not direction, ml = 0, only 1s orbital per shell
- P-Obital: dumbbell shaped, three orbitals: 2px, 2py, 2pz
- D-Orbital: five orbitals, more complex than s and p orbitals
- F-Orbitals: seven D-Orbitals, complex shapes.
The red spectral line of litium occurs at 671 nm, calculate the energy of one photon of this light.
What is the wavelength of light emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom undersoes a transition from energy level n = 4 to level n = 2?
Calcuulate the Wavelenght of a Moving Particle
- Calculate the wavelenght, in meters, of the wave associated with a 1.00 kg mass moving at 1.00 km/hr
- What is the wavelength, in picometers, associated with an eletron, whose mass is 9.11 x 10 -31 kg, traveling at a speed of 4.19 x 10 6 m/s
Wave Function
The branch of phyics that mathematically describes the wave properties of submicroscopic paarticles. Also called wave mechanics.










