Chemical Reactions Definitions and Formulas Flashcards
Ions in Aqueous Solutions
- Pure water does not conduct electricity
- Water can dissolve many things, referred to as the “Universal Solvent”
- Reactions taking place in water are called aqueous solutions.
- water becomes a conductor of electricity due to the production of ions
Who is Svante Arrhenius?
- Swedish Chemist
- Proposed the idea that some substances dissociate into cations and anions when dissolved in water.
- His ideas are now known as the theory of electrolytic dissociation.
Electrolyte
Substance that dissolves in water to give an electrically conducting solution.
e.g NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Most ionic compounds are strong electrolytes, but there are a few exceptions.
Non-Electrolytes
Substance that dissolves in water to give a non-conducting or very poorly conducting solution.
e.g. C12H22O11(s) + H2O(l) → C12H22O11(aq)
How do you determine the strength of an electrolyte?
The strength of an electrolye depends on the extent of the dissociation or ionization in the solution.
Dissociation
Seperation or splits apart as the salt dissolves
Ionization
Formation of ions
Strong electrolyte
an electrolyte that exists in solution almost entirely as ions
dissociates to a large extent; 70 to 100%
Weak Electrolyte
dissolves in H2O to give a small percentage of ions, about 1%
Summary of Electrolytes
- Most ionic compounds are strong electrolye with a few exceptions
- Few molecular compounds are strong electrolytes
- Most molecular compounds are weak electrolytes or non-electrolytes
- Most organic compounds are molecular and non-electrolytes; however, carboxylic acids and amines are week electrolytes.
Solubility
- Ability to dissolve in water varies according to the substance.
- Some substances are very soluble while others are insoluble.
Describe reactions involving ions.
- Molecular equation
- Complete or total ionic equation
- Net Ionic equation
Molecular equation
Chemical equation in which the reactants and products are written as if they were molecular substances, even though they may acutually exist in solution as ions.
Pb(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2K I(aq) 2KNO₃(aq) + PbI₂(s)
Complete or total ionic equation
Chemical equation in which strong electrolytes such as soluble ionic compounds are written as seperate ions in the solution.
Pb²⁺(aq) + 2NO₃⁻(aq) + 2K ⁺(aq) + 2I⁻(aq) → 2K⁺(aq) + 2NO₃⁻(aq) + PbI₂(s)
Soluble solutions have (aq) subscripts and insoluble solid substances have (s) subscripts.
Spectator Ions
- Ions the do not undergo any change in the reaction and appear on both sides of the equation.
- They are there to balance the charge
Net ionic equation
- An ionic equation from which spectator ions have been canceled.
- Only the ions undergoing change are shown
Pb²⁺(aq) + 2NO₃⁻(aq) + 2K ⁺(aq) + 2I⁻(aq) → 2K⁺(aq) + 2NO₃⁻(aq) + PbI₂(s)
to
Pb²⁺(aq) + 2I⁻(aq) → PbI₂(s)
Rules for writing Net Ionic Equations
- Write strong electrolytes in their ionic form
- Write weak electrolytes in molecular form
- Write non-electrolytes in molecular form
- Insoluble substances, solids or precipitates, and gases in their molecular form
- Should only have substances that have undergone a chemical change.
- Equation must be balances
What are the 3 types of chemical reactions
There are three types:
- Precipitaton reaction
- Acid-base reeaction
- Oxidation - Reduction reaction
Precipitation Reaction
- When you mix two ionic substances and a solid precipitate result.
- Soluble reactants yield an insoluble product that drops out of the solution.
- The driving force for the reaction is the formation of the stable solid product which removes material from the aqueoaus solution
Acid-Base reactions
An acid substance that involve the transfer of a proton (H+)
Oxidation-Reduction reaction
Reaction that involves the transfer of an electron.
Precipitate
- An insoluble solid compound formed durinf a chemical reaction in solution.
- To predict whether a precipitate will form on mixing aqueous solutions of two substances, you need to know the solubility of each potential product
Solubility
- How much of each compound will dissolve in given amount of solvent at a given temperature.
- Low solubility in water
- it is likely to precipitate from an aqueous solution
- Hight solubility in water
- no precipitate will form
Exchange reaction
- Also known as metahesis reaction.
- reaction between two compounds that, when written as a molecular equation, appears to involve the exchange of parts between the two reactants.
- The two cations exchange partners
- AB + CD → CB + AD
- Note: if an insoluble precipitate forms, then reaction is possible, if no precipitate, then no reaction.
Acid-Base Reaction
- Important class of chemicals
- acids:
- have a sour taste
- No feel
- litmus change from blue to red
- bases:
- bitter taste
- soapy feel.
- litmus change from red to blue
Acid-Base indicator
- A dye used to distinguish between acidic and basic solutions by means of the color changes it undergoes in these solutions.
- Note: phenolphthalein sn indicator which is colorless in acid and pink in basic solution.
Arrhenius Acid Definition
A substance that produces H+ when dissolved in water
Arrenius base definition
Substance that produces hydroxide ions, OH- when dissolved in water.
Problems with Arrhenius acid-base definition
- Reactions has to be in water
- Some bases, such as NH3, ammonia and amines do not have hydroxides in their formula.
Bronsted-Lowry Acid Definition
- the molecule or ion that donates a proton to another molecule or ion in a proton-transfer reaction
- A proton H+ donor

Bronsted-Lowry Base Definition
- Molecule or ion that accepts a proton in a proton-transfer reaction.
- a H+ acceptor

Bronsted-Lowry acid-base concept
- Note that the acid becomes a base because it is lacking a proton and the base becomes an acid because it aquired a proton.
- For simplicity, H+ is usually written but it is really H3O+, called a hydronium ion.

Hydronium Ion
- it is nothing more than a bare proton and does not exist by itself in aqueous solution
- in water, it combines with a polar water molecule to form a hydrated hydrogen ion
- the H+ is attached to to a polar water molecule forming a bond with one of the two pairs of unshared electrons.
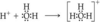
Neutralization Reaction
- Reaction of an acid and base to form an ionic compound (salt) and possibly water
- Driving force of a neutrilization reaction is the ability of H+ ion and an OH- ion to react to form a molecule of unionized water.
- If the spectator ions, in a neutralization reaction are soluble salts,they remain in the solution.
- Evaporation of the solution to dryness yields the pure salts.

What is the exception to the neutralization Reaction?
- Water is produced in most neutralization reactions
- except for when the reaction of an acid is with a weak base (ammonia)
Monoprotic acids
one acidic hydrogen atom per acid
e.g. HCl, HNO3, HCN, HBr,HI, HClO4
Polyprotic acids
- two or more acidic hydrogens per molecule.
- e.g. H₂CO₃, H₃PO₄, H₂SO₄,etc .
- They can form a series of salts with different amounts of base.
- Some of the salts formed have hydrogen atoms so they are acidic salts and can undergo neutralization with bases.
H₃PO₄(aq) + NaOH → NaH₂PO₄( aq) + H₂O(l)
H₃PO₄(aq) + 2NaOH → Na₂HPO₄( aq) + 2H₂O(l)
H₃PO₄(aq) + 3NaOH → Na₃PO₄( aq) + 3H₂O(l)
- So salts, NaH₂PO₄ and Na₂HPO₄ are acidic salts.
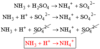
Acid-Base reactions with Gas Formation
- Some salts like carbonates, sulfites, and sulfides react with acid to produce gas.
- Baking soda (NaHCO₃) reacts with an acid to produce carbonic acid, H₂CO₃, which decomposes to CO₂ and water.
- The net ionic equations for some gas forming reactions are :
- HCO₃⁻ + H⁺ →CO₂(g) + H₂O(l)
- CO₃²⁻ + 2H⁺ → CO₂(g) + H₂O(l)
- HSO₃⁻ + H⁺ → SO₂(g) + H₂O(l)
- SO₃²⁻ + 2H⁺ → SO₂(g) + H₂O(l)
- S²⁻ + 2H⁺ → H₂S(g)
- HS⁻ + H⁺ → H₂S(g)
Oxidation-reduction reactions
- Transfer of electrons, known as redox reactions
- Oxidation
- Loss of electrons (or increase of oxidation number)
- Reduction
- Gain of electrons (or decrease of oxidation number)
- Mnenomic
- LEO the lion goes GER
- LEO: Lose electrons - oxidation
- GER: Gain electrons - reduction
- OIL RIG
- OIL: Oxidation is loss of electrons
- RIG: Reduction is gain of electrons
- LEO the lion goes GER
Oxidation Number
- Actual charge on a monatomic ion or a hypothetical charge assigned to the atom in the substance by simple rules.
- It is a way to keep track of electrons in a redox reaction
- by comparing the oxidation number of an atom before and after reaction, we can tell whether it has gain or lost electrons.
- For the oxidation number, the plus or minus sign is in front of the number to differentiate it from the electronic charge.
Rules for assigning oxidation numbers
- Elements
- is zero
- Monatomic ions
- equal to the charge on it
- Oxygen
- most compounds is -2, except for H2O2 where it is -1
- Hydrogen
- most compounds is 1, except in binary compounds with a metal then it is -1
- Halogens
- Flourine is -1
- Cl,Br,I is -1 in binary compounds, except when combined with a halogen above it or the other element is oxygen
- Compounds and Ions
- Algebraic sum in compounds is zero
- Algebraic sum in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion.
Describing Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
- They occur simultaneously.
- A half reaction tells you which is the oxidation and which is the reduction reaction.
- It is possible to identify the reducing and oxidizing agent by the half reaction.

Reducing Agent
- Causes reduction
- loses one or more electrons
- undergoes oxidation
- oxidation number of atom increases
Oxidizing Agent
- Causes oxidation
- Gains one or more electrons
- undergoes reduction
- oxidation number of atom decreases
Oxidizing and Reducing Agent
What are the four common oxidation-reduction reactions?
- Combination reaction
- Decomposition reaction
- Displacement reaction
- Combustion reaction
Combination Reaction
One of the oxidation-reduction reactions
Two substances combine to form a third:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Decomposition reaction
One of the oxidation-reduction reactions:
One compound decomposes to give several substances
2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
Displacement reaction
Combustion Reaction
- One of the oxidation-reduction reactions
- reaction with oxygen, with the rapid release of heat produces a flame.
- CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H20(g)
- Oxygen changes oxidation number from 0 to -2
Balancing Simple Oxidation-Reduction reaction
- Charges must be balanced in as well as each element.
- total increase in oxidation number equals total decrease in oxidation number
Half-Reaction Method
- Identify oxidation/reduction half reactions by assigning oxidation numbers
- Balance charge by adding electrons to the more positive side.
- Right (product) side for the oxidation half reaction
- Left (reactant) side for the reduction half reaction
- Multiply by a factor to make the number of electrons equal. Cancel the electrons.
Example:
Mg(s) + N2(g) → Mg3N2(s)
0 0 +2 -3
Balance oxidation half-reaction
Mg(s) → Mg2+ + 2e-
N2(g) + 6e- → 2N3-
Need to multiply each half-reaction by a factor that will cancel the electrons
3(Mg(s) → Mg2+ + 2e-)
1(N2(g) + 6e- → 2N3-)
3Mg(s) + N2(g) + 6e- → 3Mg2+ + 2N3- + 6e-
Get rid of the electrons:
3Mg(s) + N2(g) → 3Mg2+ + 2N3-
3Mg(s) + N2(g) → Mg3N2(s)
Solution
- Reactions in a solution in faster
- Parts of a Solution
- Solute: substance dissolved or less abundant
- Solvent: dissolving agent or more abundant
- Concentrion: quantity of solute in a standard quantity of solution
- Dilute: solute concentration is low
- Concentrate: solute concentration is high
Molar concentration
- also called Molarity (M)
- is moles of solute dissolved in one liter of solution
- Volume measurements are more convenient than mass measurements. Molarity can be used as a conversion factor.

Dilution of Solutions
- Process of preparing a more dilute solution by adding solvent to a more concentrated one.
- The addition of solvent does not change the amount of solute in a solution, but does change the solution concentration.
- Moles of solute = molarity x Liters of solution
- Formula:
- Minitial x Vinitial = Mfinal x Mfinal
Quantitative analysis
Determination of the amount of a substance or species present in a material.
Gravimetric Analysis
a type of analysis in which the amount of a species in a material is determined by converting the species to a product that can be isolated completely and weighed. Precipitation reactions are used in gravimetric analysis.
Volumetric analysis
- Determining the amount of a substance by using the volume of another substance of know concentration required for a complete reaction.
- Measures the volume of one reagent required to react with a measured mass or volume of another reagent.
- based on titration.
Titration
determining the concentration of a solution by allowing a carefully measured volume to react with a standard solution of another substance, whose concentration is known.





