puberty & HPG Flashcards
define puberty
A stage of human development when sexual maturation and growth are completed and result in ability to reproduce
what determines onset of puberty?
Switching on the HPG axis via hormones!
at what stage is the reproductive system active?
at puberty
what things occur during puberty
–Maturation of primary sexual characteristics (gonads and genitals)
– Appearance of secondary sexual characteristics (pubic and axillary hair, female breast development, male voice changes,…)
– Menstruation and spermatogenesis begin
environmental influences in puberty?
pineal tumors can influence puberty in humans!
In girls, what is the weight set point for puberty, what happens if it falls below this?
critical weight 47 kg
falls below> puberty comes late
why does weight effect puberty?
Body weight (Leptins may be involved in signalling )
Leptins tied to adipose tissue, they signal the presence of fat in the body!
they interact w/ the hypothalamus and effect the release of GnRH.
what hormones do BOTH males and females have before puberty?
testosterone and estrogen,
levels stay fairly constant until puberty!
Normal age of puberty in females? males?
9-13 yrs
10-14 years
in males and femlaes, pubic hair growth is a response to which hormones?
TESTOSTERONE!
although we females have testosterone, what keeps their levels lower in our body?
we have testosterone binding proteins!
TBP
functions of aromatase enzmye?
what inhibits it?
enzyme found in fatty tissue,
converts testosterone into excess estrogen
ZINC
functions of estrogen in the growth spurt phase?
- important in mainting bone mass
- closing the epiphyseal plate
Appearance of secondary sexual characteristics – girls
• 9-13 years
– Breast bud (thelarche)
– Pubic hair growth (T)
• begins (adrenarche)
– Growth spurt
– Onset of menstrual
• cycles (menarche) –
Pubic hair adult –
Breasts adul
Appearance of secondary sexual characteristics -boys (testosterone anabolic androgenic steroid
how can we access kids thats r goign through puberty?
and acess what stage theyre in?
TANNER SCALE

Genital development in boys depends on?
testosterone
the growth spurt is later in males or females?
later in boys!
why does somatic growth end earlier in women?
cuz of estrogen>>closes epiphyseal plates earlier
Somatic (body) growth, what does it depend on?
diff btw boys and girls
at what age ta8reeeban do girls stop growing?
boys r later, but rapid, and plates r slower to close!
girls>>16
boys>>18, 19
thats why guys faj2a y6ooloon!

describe girl/ boy growth pattern from 8-18 yrs
how does it end? in who does it end firsT?
Earlier and shorter in women

Ended in both sexes by epiphyseal fusion
Oestrogen>> closes epiphyses earlier in girls
Normal Pubertal development


just for extra: why do men get acne?
testosterone causes increased secretion of the body’s sebaceous glands, escpecially those on the face!
what is responsible for switching this axis on?!
GnRH
what gene codes for the GnRH?
what happens if this is blocked?
GnRH -1 gene
Lack of gonadotrophin synthesis and secretion and reproductive development occurs if GnRH is blocked
how can we treat prepubertal primates?
by giving GnRH gradually
what r the characterisitcs of the hypothalamic releasing hormones?

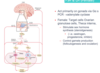
describe the HPG axis
what structure in the anterioir pituitary makes LH & FSH?
Gonadotrophs
which r cells
what role does leptin and photoperoid have on the HPG axis?
they interact w/ the hypothalamus and effect the release of GnRH.
funcitons of lepitin
pattern of release?
Signals information about energy stores to CNS
pulsatile!> associated with variation in LH
Leptin can regulate GnRH levels, and its secretion may, in turn, be influenced by gonadal steroids but appears to be independent of LH control

GnRH path in activating the HPG
timing of release?
intensity of release affected by?
its path from hypothalamus to pituitary
its is pulsatile
Every 1-3 hrs
Intensity of GnRH stimulus is affected by
- Frequency of release
- Intensity of release
GnRh neurons at the median eminence in hypothalamus secrete it > hypophyseal portal sys > anterior pit> bind to gonadotropes> FSH & LH secreted

what time of the day does the intital pulsitility of LH happen in males?
switches on in sleep
pic just showing that pulsitility of LH mimics GnRH
(LH is GNrH’s puppy)

Precocious puberty?
development of puberty at an EARLIER AGE

maybe due to pineal tumor
name other axis’s of the hypothalamic-pituitary
– Thyroid (hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis HPT)
– Adrenal (hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis HPA)
– reproductive glands (hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis HPG)
HPG axis in the Male
LH stimulates Leydig cells in testis (diggin at the surface)
the past their digging test lol>> and realeased TESTosterone
FSH stimulates sertoli cells to release ABP, which keeps the concenctrstion of testosterone in spermatogenic cells high>stimulates spermatogenesis.
leydig cells r completely independent of the seminerfrous tubules, but the Seminefrous tubules, need the leydig cells to produce testosterone.
add ur pic alaa
testosterone peaks?
EARLY MORNING
every morning is a new “TEST” for us
describe the strucutre of the Seminiferous Tubule cells
btw sertoli cells, theres tight junctions bc it provides the testes blood barrier!
prevents bits of sperm from entering our BS!
this could causes an atuoimmune response from the bits of sperms floating around chilling in our blood stream!

function of Inhibin
secreted by Sertoli, checking levels of spermatogenesis
ex: when sperms is so much, it send negative feedback to anterior p. to inhibit release of FSH
* otherwise ur testes will explode with sperms*

HPG axis in the females
which cells respond to FSH? LH?
Granulosa cells respond to FSH
Theca cells respond to LH
granny likes fish
Explain the potential effect that precocious puberty can have on adult stature
Short final stature as precocious puberty can cause rapid skeletal maturation which can cause linear bone growth to cease too early
Growth spurt begins and ends earlier and therefore epiphyses close earlier / shorter final stature.
Why might precocious puberty be stimulated by intracranial pathology such as meningitis?


