Gametogenesis Flashcards
(53 cards)
define gametogenesis?
the process in which cells undergo meiosis to form gametes.
what determines the sex of the zygote? how many chromosomes do we have?
which sperm fuses w/ the ovum to form the zygote
- es: sperm containing y chromosome> boy*
- or sperm containing X >girl*

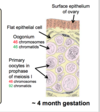
what r primodial germ cells? function?
developing gonads r colonised by primodial germ cells!
first recognized in the developing embryo in the WALL of the yolk sac! near the allintois.
the migrate through the developing embryo, migrating towards the gonadoridges.
depends on the type of primordial germ cells which colonize the gonads>> that will determine the sex
once they colonised the gonad, they proliferate via mitosis
then undergo meiosis!

difference btw spermatogenesis and oogenesis
feMale only has 400 chances to reproduce
while male nafs confetti, ishkithirr

where does spermatogenesis take place?
lumen of semineforus tubules
occuring in btw the gaps of these sertoli cells!

why r tight junctions formed by sertoli cells in the testes important? (2)
- they seperate the 2 compartments of the testes > Basal compartment & Adluminal .
- forms blood testis barrier > the gametes can be recognized as non-self by the males! prevents the membrane antigens of differtiating sperms from escaping into the BS where they would activate an immune response!

what r the 2 compartments of the testis?
why is it important that theu r sepertated by tight junctions?
Basal> spermatogonium or germ cells reside (in contact w/ blood)
Adluminal>
the cellular environmet and conditions to maintain our stock of germ cells r different than the cellular conditions that r needed for the differentiation of spermatids into sperm
Vasectomy risks
The blood–testes barrier can be damaged by trauma to the testes (including torsion or impact), or surgery or vasectomy.
When the blood–testes barrier is breached, and sperm enters the bloodstream, the immune system mounts an autoimmune response against the sperm,
functions of leydig cells?
makes testosterone which help to signal spermatogenesis to occur
when do these processes take place?
occur in male AFTER puberty has occured,
up until puberty we have our spermatogonium in a DORMANT stage (just chilling ya know)
difference btw spermatogenesis & spermiogenesis
spermatogenesis: is the process where we produce spermatozoa from spermatogonial stem cells by mitosis and meiosis
spermiogenesis: is the final stage of spermatogenesis, which sees the maturation of spermatids into mature, motile spermatozoa
name the raw material’ for spermatogenesis
Spermatogonia
2 types of spermatogonium?
Ad spermatogonium (“Resting”: reserve stock) not really doing much
Ap spermatogonium (“Active”: renew the stock of germ cells or go through mitosis to maintain the stock)
- Ad for dark (sitting in a dark place)*
- Ap for pale*
which types of spermatogonium go on to form gametes?
Type B spermatogonium
Following mitosis, the tight junctions of sertoli cells open to allow type B cell to pass into adluminal compartment
(like locks in canal that open to allow boats to pass!)
explain the stages of spermatogenesis

Distinguish spermatogenic cycle and wave
what is spermiogenesis
Each spermatid has the correct chromosomal # for fertilization… but is NONMOTILE
it still needs to undergo a process called spermiogenesis! during which it elongates, sheds it cytoplasmic baggage & forms a tail! on its way down to the lumen
transformation of a spermatid into a functional sperm
spermiation
Spermatids released into lumen of seminiferous tubules
when do sperms gain their motility?
once theyre in the epididymis!
if sperms gain their motility in the epididymis, then how did they even get their in the first place? (2)
via sertoli cells secretions & peristaltic contractions!
(sertoli secretion: testicular fluid pushes them)
which structure on the sperm gives it its motility?
Flagellum
which structure on the sperm is important in order to allow the sperm to penetrate the zona pellucida layer on the oocyte?
the Acrosome! (helmet)
it contain hydrolytic enzymes that form digestive holes on the zona pellucida!

the sperm has to travel along journey, where does it get its energy from
Mitochnodria provide energy (ATP) needed for whiplike movemnts of the flagellum tail
what r different types semen secretions and where do they occur
which one has the most %?