Protein Synthesis Flashcards
(16 cards)
Summary?
Gene on DNA carries instructions for making a particular protein.
Each cell transcribes only those genes concerned with its particular function, leaving the other genes inactive.
Where are proteins produced?
The Cytoplasm
What happens to the coded instructions for it to be read?
Must pass from the Nucleus to the Cytoplasm
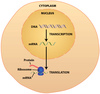
What is Transcription?
Making a RNA copy of a gene sequence with existing DNA.
What is Translation?
Protein is made by reading the sequence of triplets in mRNA to create specific amino acids
Two types of RNA
mRNA - Messenger RNA
tRNA - Transfer RNA
RNA in which genetic information transcribed from DNA is transferred to a ribosome.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)

RNA consisting of folded molecules which transport amino acids from the cytoplasm of a cell to a ribosome.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)

Protein Synthesis - First Step
- Region of DNA with necessary coded instructions opens up.
- Controlled by RNA Polymerase
Protein Synthesis - Second Step
- The exposed single strand of DNA builds up into a double strand again in similarly to DNA duplication, except that the second strand is made up of mRNA.
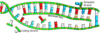
Protein Synthesis - Third Step
- mRNA moves into the cytoplasm, where it becomes attached to a ribosome.
- The cytoplasm of the cell contains millions of amino acids.
Protein Synthesis - Fourth Step
- tRNA moves around the cytoplasm to collect a specific amino acid.
- tRNA transfers the amino acid to the mRNA at a ribosome to link up to make the protein molecule.
Codons
Three nucleotides that form a unit of genetic code in DNA.

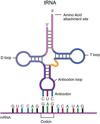
AntiCodon?
One end of tRNA that joins onto mRNA.
Protein Synthesis - Fifth Step
- tRNA molecule arrives at a ribosome
- Amino acid carried by tRNA links up with amino acids on adjacent tRNA molecules.
- Repetition results in a molecule of protein
Role of Other end of tRNA?
Carries a specific Amino Acids



