Mutations Flashcards
What is a Mutation?
- A change in the nucleotide (base) sequence
- Results in translation of proteins being affected.

Forms of Mutagens?
X-rays, UV rays (sunlight), chemicals, tobacco and pollution

Why don’t new mutations occur frequently now?
- Because species have already mutated a lot to fit best into the current, unchanging environment.
Forms of Mutations?
Deletion
Insertion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
(DIDIT)

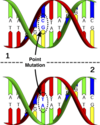
Point Mutation?
A single base is changed.
Block Mutation?
More than one base but less than a whole gene is changed
Silent Mutation?
No effect

Missense Mutation?
Substitution of a nucleotide (base) causes a new amino acid.

Nonsense Mutation?
Substitution of a nucleotide (base) causes a tRNA to bring the STOP codon rather than another amino acid. Therefore, correct protein is not made and the resulting protein is severely shortened or non-functioning.

Frameshift Mutation?
Insertion/Deletion of nucleotides “push” the rest of the codons which creates a new sequence, resulting in all new amino acids.


