Prodrugs Flashcards
What are prodrugs
- Compounds, which undergo biotransformation before exhibiting a biological response

Introduction prodrug
Prontosil a historical example
- Prontosil was a dye that was accidentally found to be antimicrobial
- Prontosil is a dro drug
- Forms sulphanilamide

Prontosil
- Diazo- compound, organic dye
- Enzyme, reductase
- Discovery of sulfonamides, first class of antibacterials
- Discovery of drug by chance
Design concepts
How to design a prodrug
- Identify: formulation or delivery problems (toxicity, absorption, stability)
- Chemical design:
- A reactive handle on the drug molecule available
- Usually OH, COOH, NH to derivatise to form amide or ester bond
- Derivatise the drug, form ester e.g.
- To produce appropriate molecular properties
- Usually with alcohol (for COOH) or carboxylic acid (OH)
- Ensure activation in the body (to get back the original active drug)
- Degradation without stability
- Usually enzymatic- esterases
- Still active/working after modifications
- A reactive handle on the drug molecule available
Carboxylic acid-containing drugs (linked as esters)
- Ester are readily synthesized from carboxylic acids-containing parent drug and an alcohol-containing carrier
- Esters are easily hydrolyzed by various and ubiquitous esterases
- Large libaryof alcohols allow great variety of properties to the prodrug

Use & applications of prodrugs
- Reduction of toxicity e.g. cyclophosphamide
- Improve water solubility e.g. chloramphenicol
- Modify lipophilicity- sustained release
- Improve chemical stability e.g. dinoprostone
- Modify metabolic stability- PK e.g. esters
- Improve taste e.g. clindamycin palmitate
- Site-specific delivery e.g. dopamine/levodopa
Enhanced lipophilicity- Sustained release
- Flupenthixol- potent neuroleptic and tranquilliser used in the treatment of schizophrenia
- Very fast onset of action, with lots of side effects
- The pro-drug increases time between doses due to depot like action- release slowly over time

Flupenthixol decanoate formulation
- With oral formulation there are lots of peaks and throughs- less time in TI can also dip into sub-therapeutic and toxic levels

Advantages of flupenthixol decanoate, a lipophilic ester
- Reduce the number and frequency of doses
- Reduce peak and trough effects
- Reduction in toxicity
- Reduce overall dosage required
- Eliminates night-time administration
- Better patient compliance
- Because of better control- behavioural
- Clear that dose has been delivered
Taste masking- solubility suppression
- Clindamycin
- Antibacterial
- Bitter tasting, taste masking will aid compliance
- Drugs to be tastes must be soluble in the mouth to interact with the taste buds, reducing solubilty while in the mouth will improve taste
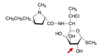
Clindamycin, antibiotic
- Hydroxy- groups = bitter taste
- The new formulation, injection
- Make ester pro-drug, which ester
- Palmitate, most lipophilic ester
- Paediatric formulation, USP unique selling point
- As you make the drug more lipophilic palatability increased
Taste masking clindamycin

Metabolic stability: Modification of stability of esters
- Ester hydrolysis in rat serum
- Esterase activity depends upon alkyl residue
- E.g. size modifying fit to the active site
- More complexity = greater half-life, increase stability means more likley the drug will reach its required site

Stability of esters, metabolic stability
- Acetate half life3 min= unstable, easily hydrolysed by esterase (enzymes)
- Isopropyl ester, t-butyl ester bulkier more stable
- More stable ester, ester of benzoic acid
- Aromatic ester, also most crystalline, best mp
Applications of prodrugs
- Site-specific delivery
- Transport system
- Site-specific enzyme activation
Pro-drugs
- Site-specific transporter system
- Selective site delivery by using a natural amino acid transporter
- Example: Levodopa
Site-specific delivery
Modification of transport
- Deficiency in Parkinson’s disease
- Hydrophilic and protonated at body pH
- Very water-soluble
- Low lipid solubility- poor GIT and BBB transport
- DA is not absorbed into the brain
Site-specific delivery
Use of natural carrier systems
- L-DOPA- absorbed by an amino-acid transport system and can cross BBB
- Undergoes activation to DA via DOPA decarboxylase
- But ~20% reaches circulation- rest suffers metabolism
- Decarboxylation- systemic dopa decarboxylase
- O-methylation- Catechol-O-methyl transferase
- Conjugation and oxidation
- Usually used with a DOPA-decarboxylase inhibitor
- Carbidopa
- Benserazide
Targeting specific transporters
- Levodopa is a substrate for the neutral amino transporters present at the BBB
- After brain entry, levodopa is decarboxylated to DA, which can act locally, being no longer a substrate for the neutral amino acid transporter
- To increase the systemic half-life of levodopa, it has become customary to co-administer peripherally acting inhibitors of DOPA decarboxylase
Prodrugs Site specific enzyme activation
- Selective cleavage at the site to active drug
- Minimal conversion elsewhere in the body.
- Fosfestrol
*
Site-specific delivery
Enhanced enzyme activity in cancer cells
- Probably result of rapid metabolism than unique occurence
- We use a phosphate linker; this is because in cancer cells there is a very high level of expression of phosphatase enzymes so rapid degradation in the target (cancer cells) will occur (there not high in other parts of the body)

Fosfestrol, phosphate prodrug
- Fosfestrol= stilboestrol diphosphate
- Synthetic oestrogen used in prostatic cancer
- Phosphate enhances water solubility
- Concept: Enhanced enzyme activity
- Concept- amidase, phosphatase enhanced activity in tumour cells
- Phosphate cleaved by enzyme phosphatase
- Phosphatase activity enhanced in a target tissue
- Overall selectivity delivered to the site of action, tumour cells with higher enzyme activity
Selective release phosphatase distribution
- Alkaline phosphatase is significantly raised in tumour lines

Limitations
- Phosphate esters are
- Polar
- Poorly absorbed
- Probably have to encapsulate in a carrier molecule (nanoparticle)
- Tumours are often
- Poorly perfused
- Difficult to access
What you should be able to do
- Define the term ‘prodrug’
- Identify strategies, which benefit from prodrug design
- Quote examples of each application
- And illustrate it with named examples
- Recognise prodrugs used in therapy
- By inspection of their structure
- And identify the advantages of prodrug design


