PreMidterm lab slides review Flashcards
Mod 4 Slide 30

Mycobacterium leprosy
Tuberculoid leprosy: Th1, granuloma, IL-2, IFN-gamma, well-formed granuloma, no bacteremia,
Lepromatous leprosy: Th2, more severe, lipid-ladened macrophages w bacteria, weak immune system so disorganised granuloma (histo fig.)
Mod 4 Slide 29

Bartonella Hensliae
Cat scratch disease can affect immunocompetent
necrotizing (non-caseous) of LN; mixed B & T hyperplasia; no Giant cells, stellate-shape

Lobular: bronchopneumonia, less virulent (staph. aureus, pseudomonas, E. coli, Klebsiella)
diffuse but can coalesce to look similar to lobar

Lobar: pneumococcal, pores of Kohn, virulent organisms (strep. pneumonia)

Staph infections: skin mostly
complications: mastitis, endocarditis from IV opiates, bacteremia, osteomyelits, bronchopneumonia
toxin-mediated: Scalded skin, TSS, food poisoning, enterotoxin, tampons
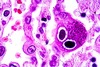
CMV: inclusion bodies both nucleus & cytoplasm; blindness in AIDS Pt, cottony-wool on fundoscopy; also affects lung

Rabies: negri bodies, inclusion bodies in cytoplasm only; spread thru neurons

VZV: inclusion bodes in nucleus, Tzanck smear for HHV 1, 2, 3 showing 3M (multinucleation, marginalized, molding); cowdry type A bodies w halo

Viral myocarditis: coxsackie viral infections; lymphocyte-mediated, patchy or big sheath necrosis; sx: fever, chest pain

Rickettsial infections
Epidemic typhus: R. prowazeki w Proteus, transmission: lice; painful hemorrhagic skin nodules; Dx: Weil-Felix; Complications: hepatitis, pneumonia, CNS nodules (typhus nodules)
Rocky MSF: Ricketsia ricketsia, transmission: tick bites in woods of GOAT states, sx: rash moves from centre to periphery, rash on palms & soles, fever, headache, myalgia; more severe CNS & lung involvement; fibrinoid necrosis of vessels (histopath image)

Candida (monoliasis): oral thrush, vagina, true membrane (easy to scrape off); pseudohyphae on PAS; risk factors: OCT & pregnancy; complications: abscess in kidney, liver, lung, heart

Cryptococcus: inhaled from pigeon or bat droppings; dissemination likes to go to brain/meningitis, Virchow-Robin perivascular space; India ink, mucicarmine, soap-bubble, latex agglutination,

Aspergillus: Acute angle pseudohyphae; always opportunistic; 3 types (allergic, colonizing/aspergilloma, invasive); halo sign; dissemination to heart, brain, kidney

Mucormycosis: non-septate; transmission thru nose -> black necrotic eschar in nose -> lungs & gut; likes to disseminate to brain; vascular invasion
batman

Histoplasmosis: can infect immunocompetent; transmission: bats & chickens/soil inhalation; sx: similar to Tb; CXR buckshot; budding yeasts from alveolar macrophages

Pneumocystis jiroveci: HIV+, pneumocystis pneumonia; H&E cotton candy exudate; Silver stain cup cysts exudate; Sx: dry cough (atypical interstitial pneumonia)

Tubercle requires 3 wks to develop -> cell-mediated immunity; composed of central caseation, giant Langerhans cells, epitheliod cells; no phagocytic activity; mycolic acid; sx: fever (low grade), night sweats/chills, bloody sputum
1o Tb: Ghon lesion in lung parenchyma; 1o complex (Ghon lesion + LN + spread); heals in most people w little caseation; lower part of upper lobe or upper part of lower lobe
1o progressive: large area of lung involved
Miliary Tb: hematogenous spread throughout body
2o Tb: re-infection, HIV+, reactivation; stronger immune response, large caseation at lung apex, cavitation & coughed out; healing & fibrosis in most people.
2o progressive: spread to bronchiole, pleural effusion, empyema, hematogenous spread -> miliary Tb
Complications: PID, Pott’s syndrome, Addison’s, cold abscess, gut ulcers & obstruction, peritonits


Actinomyces israeli
mouth, dental cavities
Gram +ve anaerobic bacilli,sulfur granules

lipoma w well-differentianted mature adipocytes, encapuslated, hormone-insensitive

leiomyoma non-encapsualted, fast-growing, hyperplastic, hormone-responsive

FAP: exophytic growth called polyps, APC

Teratoma, 2 germ layers, hair & teeth on ovary; specialised teratoma (struma ovarii Thyroid hormones & carcinoid 5HT & kallikrein)

hemangioma disorganized growth of endothelial cells
most common tumour of infancy

Anaplasia
atypical mitosis, irreversible, loss of functional & structural differentiaton
variable size and shape of cell & nucleus, hyperchromatic, incr. nuclear: cytoplasm, proliferation maker ki67, invasion