Practical: Horse Flashcards
Foramen mandibulae: Nerve block

Describe the nerve-block of the bicipital bursa
- 6cm distal from the cranial part of major tubercle
- 7cm cranial from the deltoid tuberosity
- Proximomedial direction
- Aim at the intertubercular groove
Difficult to reach, accessed in a standing horse

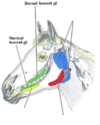
Foramen supraorbitale
Found in a dimple: Root of the zygomatic process of the frontal bone
Describe the primary nerve-block of the shoulder
- Between the cranial and caudal pars of the major tubercle
- Horizontal needle
- Caudomedial direction

The horse should be in a standing position
Trochanter major
- Divided into low cranial and high caudal portions
- Palpated under the biceps femoris


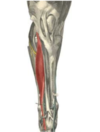
M. extensor digitorum lateralis
(FL)
Lymph node of the head
- Mandibular: Intermandibular space, forms a ‘V’ shape near the facial notch
- Lateral retropharyngeal: Found in clumps around the pharyngeal wall, caudal to the guttural pouch

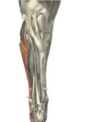
M. extensor digitorum lateralis
(HL)
Caudoventral border of the lung
- 16th IC space - Tuber coxae
- 14th IC space - Tuber ischiadicum
- 10th IC space - Shoulder joint
Diaphragm is located between ribs 8-17
Tuberositas deltoidea
- Craniolateral aspect of proximal humerus

Age ‘determination’
2.5 years → 10 years
- I1 erupts : 2.5 years
- I2 erupts : 3.5 years
- I3 erupts : 4.5 years
- Dental star on I1 : 5 years
- Dental star on I2 : 6 years
- Dental star on I3 : 7 years
- White spot apears in I1 dental star : 8 years
- White spot apears in I2 dental star : 9 years
- Cup disappears from I2 maxilla : 10 years
Describe the arthrocentesis of the centrodistal joint
- Small depression halfway between:
- Tuberculum of the talus
- Os tali centrale
- Long medial tarsal collateral ligament
- Needle directed perpendicular to the limb
- 1-2 cm deep

Describe needle access to the carpal joint (dorsal approach)
- Lateral/medial from the common digital extensor
- Palpable depressions between the bone rows
The limb should be flexed
Describe needle access of the distal digital flexor tendon sheet (Dorsolateral approach)
- Slightly dorsal from the lateral collateral ligament
- Eminences of Ph-1-2 are palpable
- Needle directed lateromedially under the digital extensor tendon
The limb can be weight-bearing or extended whilst it is held

Nasal opening of the nasolacrimal duct
- Found on the floor of the nasal vestibule
- Red/pink dot at the base of the septum
Give the borders of the conchal sinus
- Dorsal border: Fuses with the conchofrontal sinus
- Middle border: Communicates with the ethmoidal meatus
- Ventral border: Connects with rostral maxillary sinus
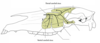
Ostium ileocaecale
May be detected with a stethoscope a few cms ventral to the paralumbar fossa

List the patellar ligaments
- Lateral
- Intermediate
- Medial
- Lateral femoropatellar

Age ‘determination’
6 days → 18-24 months
- Id1 erupts : 6 Days
- Id2 erupts : 6 Weeks
- Id3 erupts : 6 Months
- Id1 cup disappears : 10 months
- Id2 cup disappears : 12 months
- Id3 cup disappears : 18-24 months
(Id1 = First Deciduous incisor)
Describe needle access of the coffin joint (dorsal approach)
- Just over the tip of the extensor process
- Needle direction either:
- Parallel to the ground
- Perpendicular to the skin
The limb should be weight-bearing, in the midline

Maxillary sinus
- Caudal border: Opens into: Conchofrontal + sphenopalatine sinus
- Rostral border: Opens into the ventral conchal sinus

Accessory ligament
- Attaches DDF to the metacarpus
- Approx. 4cm proximal to the head of the splint bone

M. extensor carpi radialis
Describe the needle access of the fetlock joint (distal palmar/plantar approach)
- Between:
- Lateral proximal sesamoid bone
- Base of Ph-I
- Dorsoproximal needle direction
Dorsal from the lateral digital artery
The limb should be weight-bearing

Mandibular gland
- Extends from basihyoid → Atlantal fossa

Deep and rarely palpable
Pulse point: Artery name

Digital artery

Small intestine
- Duodenum: Found on the right, turns to the left at the point of L3
- Jejunum: Fills the left craniodorsal quadrant
- Ileum: Short, approaches the caecum from the left

Briefly give the needle access of the coffin joint (lateral approach)
This method is barely used
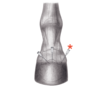
M. extensor digiti longus
Found in the extensor groove of the tibia
Lateral on HL only
Describe the arthrocentesis of the tarsocrural joint (__plantarolateral approach)
- Between:
- Calcaneal tuber
- Tibia
- Trochlea of the talus
Flexura pelvina
- Transition from the left ventral colon to the left dorsal colon
- Found medial to the body/wing of the ilium

Describe arthrocentesis of the medial femorotibial joint
- Between:
- Medial collateral ligament
- Medial patellar ligament
- 1 cm proximal to the tibia
- Needle perpendicular to the limb

Weight-bearing limb
Frontal sinus borders
- Opens into the caudal maxillary sinus
- Rostral: Midway between medial canthus and infraorbital for.
- Caudal: Temporomandibular joint

The elbow joint may communicate with…
The bursa of the lateral carpal extensor muscle
Describe needle access of the distal digital flexor tendon sheet (Proximal approach)
- Palmar/plantar to medial interosseus muscle
- Proximal to annular ligament + proximal sesamoid bone
- Needle perpendicular to the limb
The limb can be weight-bearing or held
Give the significance of the radiohumeral and humeroulnar joints of the elbow.
The joints are not separated
Describe the arthrocentesis of the tarsometatarsal joint
- Between
- 0.5-1 cm above the basis of Mt-IV
- The lateral edge of the superficial digital flexor tendon
- Needle directed dorsomedially
- 1-2 cm deep

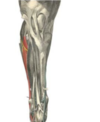
M. extensor digtorum lateralis
Lateral on HL + FL
Sublingual glands
Between:
- Body of the tongue
- Medial surface of mandible


M. abductor digiti I longus
Bones of the carpal joint
- Radial carpal bone
- Intermediate carpal bone
- Ulnar carpal bone
- Accessory carpal bone
- C2, C3, C4
M. interosseus medius
Suspensory ligament
Both HL + FL
Describe the needle access of the fetlock joint (dorsal approach)
- Between:
- Base of Ph-I
- Lateral/medial to the common digital extensor tendon

- The limb should be weight-bearing*
- More painful than other approaches*
Describe arthrocentesis of the tarsocrural joint (dorsomedial approach)
- 2-3 cm distal to the medial malleolus
- Cranial to the cranial branch of the medial saphenous vein
- Needle directed plantarolaterally at 45°

Weight-bearing limb
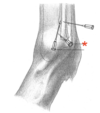
Describe the needle-access of the elbow joint (caudal approach)
-
1/3 of the distance between
- Proximal tip of the olecranon
- Lateral epicondyle of humerus
- 45° needle, pointing distomedially
- Through the tendon of the triceps
- Toward the olecranon fossa

Xiphoid process
Follow the costal cartilages to the ventral centre
Injection sites into the digital sheath
- Sheath begins 2cm above the fetlock, ending at the middle of Ph2

Describe the superficial fibular nerve block
- 10 cm proximal to the calcaneal tuber
- On the lateral aspect
- Between:
- Long digital extensor tendon
- Lateral digital extensor tendon
Weight-bearing limb
M. flexor digitorum profundus (tendon)
Located between:
- Superficial digital flexor tendon
- Suspensory ligament
Both HL + FL
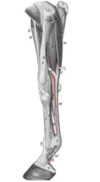
Lingual process
May be palpated on the ventral surface of the hyoid bone in the intermandibular space
M. extensor carpi radialis

Describe synovial cavity communication in the femorotibial joint for Equine
- Prox. + dist. recesses of the same side communicate with each other
- Medial + lateral cavities never communicate
- Med. femorotibial joint and the femoropatellar joint usually communicates
Describe the areas of synovial communication in the hock joint
- Between:
- Tarsocrural joint
- Talocalcaneocentral joint
- Between:
- Centrodistal joint
- Tarsometatarsal joint
List the four joints of the hock
- Tarsocrural joint
- Talocalcaneocentral joint
- Centrodistal joint
- Tarsometatarsal joint
Describe needle access of the proximal digital flexor tendon sheet (distal approach)
- Distal to retinaculum flexorium
- Proximally directed needle
- Between:
- Mc IV
- Deep digital flexor
Describe the needle access of the fetlock joint (proximal palmar/plantar approach)
- Depression found:
- Medial interosseus muscle
- Mc/Mt-III
- Lateral proximal sesamoid bone
- Head of lateral splint bone
- Needle perpendicular to the limb

- The limb can be held or be weight bearing*
- Sample may be contaminated with blood*
Parotid gland
Extends from:
- Base of the ear + wing of atlas
- ‘V’ formed by the linguofacial + maxillary vein

M. tibialis cranialis
Between:
- Long digital extensor
- Tibia
Medial aspect

Describe the common fibular nerve block
- At the origin of the long digital extensor
- At the head of the fibula

M. extensor digitorum longus
HL only
Describe the deep fibular nerve block
The same as the superficial, only 4-5 cm deep
Describe the nerve block of the tibia
- 10 cm proximal the calcaneal tuber
- Medial aspect
- Between:
- Common calcaneal tendon
- Tendon of the medial deep digital flexor
Weight-bearing limb

Tractus appositus
- Extensor branch from the suspensory ligament
- Locate the suspensory ligament (interosseus muscle)
- Follow over the pastern bone

Where is the communication of the carpal join cavities found?
Between 3rd + 4th carpal bones
Describe the needle-access of the elbow joint (lateral approach)
- Cranial or caudal from the lateral collateral ligament
- Perpendicular to the skin
- 3-4cm deep
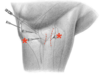
- The radial nerve is located cranially to here*
- The horse should be standing/have a flexed joint*
Caput caeca
Right abdomen, under ribs 15-18

R. palmaris block
Describe needle access of the pastern joint (Palmar/plantar approach)
- ‘V’-shaped depression on the palmar aspect
- Between:
- Distal trigone of the proximal phalanx
- Lateral crus of superficial digital tendon
- Ph-II
- No exactly perpendicular but slightly dorsal needle direction

Flex the distal limb
Greater tubercle
- Split into cranial and caudal parts

Describe arthrocentesis of the femorotibial joint (cranial approach)
- From a cranial direction
- Next to the intermediate patellar ligament
- Horizontal needle direction
Slightly flexed position

Buccal glands
Along dorsal + ventral oral vestibule (inside mouth)
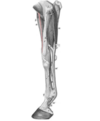
Describe the distal metacarpal/low palmar block
- Between:
- Medial interosseous muscle
- Deep digital flexor muscle
- 1 cm proximal to the head of Mc II/IV
- 1.5-2 cm deep

This block is close to the tendon sheet
Facial nerve
Can be seen passing over the masseter

1. in the figure
List the salivary glands of the horse
- Parotid gland
- Mandibular gland
- Sublingual gland
- Buchal glands
The tibial nerve block desensitises…
- Plantar tarsus + metatarsus
- Medial interosseus muscle
- Distal common calcaneal tendon
- Most of the foot
The shoulder joint may communicate with…
The bicipital bursa
Describe the needle access of the navicular bursa (Lateral/medial approach)
- Between:
- Ph-II
- Deep digital flexor

Cartilago nasi
Composed of:
- Dorsal lateral nasal cartilage
- Alar cartilage

Lacertus fibrosus
- Fibrous strand attaching biceps to the radial carpal extensor
- Located craniomedially
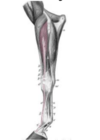
Injection sites into the carpal sheath
- Tendon sheath of SDF and DDF as they pass through the carpal canal
- Needle inserted palmar-laterally, either proximal or distal to accessory carpal bone

List the paranasal sinuses
- Conchal sinus
- Sphenopalatine sinus
- Frontal sinus
- Maxillary sinus
Thyroid cartilage
- Deep notch in the ventral aspect is palpable
- Behind the lingual process of the basihyoid bone
M. abductor digiti I longus
- Crosses the carpus, covering the tendon of the radial carpal extensor

The ulnar nerve-block desensitises…
- Skin of the forearm → fetlock (Laterally)
- Carpal canal
- Superficial digital flexor
- Medial interosseus muscle
M. extensor digitorum communis
Lateral aspect of forelimb only
Age ‘determination’
11 years → 24 years
- White spot appears on dental star of I3 : 11 years
- Enamel spot has disappeared from all lower incisors : 12 years
- Occlusal surace of I2 is triangular : 17 years
- Occlusal surface of I3 is trianglular : 18 years
- Galvayne’s groove runs the entire length of the tooth : 20 years
- I1 has a long oval occlusal surface : 24 years
Sphenopalatine sinus
Spenoid and palatine sinus are combined

Foramen mentale
Located ventral to the lateral commissure of the lips
Describe the needle access of the navicular bursa (Palmar/plantar approach)
- Between hoof bulbs
- Above the coronary band
- The needle should be driven distally
- Navicular bone should be touched

The limb should be weight-bearing
Describe the palmar digital nerve-block (PD block)
- Needle directed at the proximal borders of the lateral/medial ungular cartilage
- Subcutaneous

The limb should be held
Describe arthrocentesis of the femorotibial joint (lateral approach)
- Between:
- Intermediate patellar ligament
- Lateral/medial patellar ligament
- 4-5cm above the tibial tuberosity
- Horizontal needle direction
Slightly flexed joint
Describe needle access of the proximal digital flexor tendon sheet (Proximal approach)
- Close to the antebrachiocarpal joint
- 5cm proximal to the accessory carpal bone
- Between:
- Lateral digital extensor
- Ulnar carpal extensor
Effusion improves visualisation
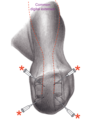
What is indicated in the image?
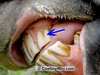
Galvayne’s groove
Appears on I3 at 11 years of age
Sesamoid bones
- 2 x proximal: Caudal surface of the fetlock joint
- Distal sesamoid (navicular) bone: Dorsal surface in contact with distal surface of Ph2
Describe needle access of the distal digital flexor tendon sheet (Dorsal approach)
The limb can be weight-bearing or extended whilst being held
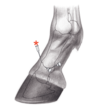
Cartilago ungulae
6 & 7
- Found on the palmar aspect of Ph3, on inner wall of the hoof

Is the IV injection sites
- Jugular vein
- Cephalic vein
- Deep/transverse facial veins
Anaesthetic injections to the shoulder joint may result in…
A suprascapular nerve block
M. extensor digitorum lateralis (Tendon, forelimb)
Between:
- Common digital extensor muscle
- Ulnar carpal extensor
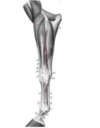
Describe the secondary nerve-block of the shoulder joint
- Locate the infraspinatus tendon
- Block caudal from the tendon
Describe the nerve block of the median nerve
- Caudomedial aspect
- Cranial to the origin of the radial carpal flexor
- Insertion of superficial pectoral muscle (of radius)
- 3-5cm deep
- Located next to the median artery + vein

R. communicans (Btw. palmar nerves)
- Middle of the metacarpus
- Passing over the superficial digital flexor
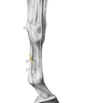
Describe arthrocentesis of the lateral femorotibial joint
- Caudal to the lateral patellar ligament
- Just above the tibia

Weight-bearing limb
Describe the nerve block of the ulnar nerve
- 10cm proximal to the accessory carpal bone
- Caudal aspect
- 1-1.5cm deep
- Between:
- Radial carpal flexor
- Lateral carpal extensor

Describe the needle access of the fetlock joint (collateral sesamoidean approach)
- Depression found between:
- Mc/Mt-III
- Lateral proximal sesamoid bone
- Through lateral collateral ligament of the sesamoid bone
- The limb should be held in order to increase space*
- Best way to draw a blood-free sample*
M. flexor digitorum superficialis
Most caudal tendon

Both HL + FL


