Practical: Dog Flashcards
Inguinal ring
- Located medially to the pectineus muscle
- Male:
- Within the skin fold suspending the prepuce
- Female:
- Deep to the mammary gland

Bladder
- Only palpable when full
- Caudoventral abdominal wall is grabbed
- Movement of urine can be felt
Canalis femoralis
Composed of:
- Sartorius
- Gracillis
- Vastus medialis

Structures located inside the femoral canal
- Femoral A./v.
- Proximal caudal femoral artery
- Saphenous nerve
What is cardiac border auscultation used for?
In order to locate the puncta maxima of the heart
List the cardiac borders
- Pulmonary trunk
- Aorta
- Left AV
- Right AV
Cardiac border: Pulmonary trunk
Left side:
- 3rd intercostal space
- Above the sternum
Cardiac border: Aorta
Left side:
- 4th intercostal space
- In line with shoulder
Cardiac border: Left AV
Left side:
- 5th intercostal space
- Distal 3rd
Cardiac border: Right AV
Right side:
- 4th intercostal space
- Genu costae
Cardiac dullness
- Percussion between the ribs
- Determines the borders of the heart
- Thickening of the lungs around the heart gives relative dullness
Cardiac dullness: Left side
- 4th-6th intercostal space
- Distal third
Cardiac dullness: Right side
- 4th-5th intercostal space
- Distal third
The loudest sound observed during percussion is referred to as…
Punctum maximum
List the nerve blocks of the hindlimb
- Tibial nerve block
- Fibular nerve block
Fibular nerve block
- Nerve passes over the head of the fibula
- Can be palpated with the fingernail
- Aspirate + Inject parallel to the skin
Tibial nerve block
- Nerve can be felt in the skin adjacent to the CCT
- Aspirate + Inject parallel to the skin
Radial nerve block
- Supplies extensors of the elbow, carpus + digits
- Enters the triceps distal to the teres major muscle
- Passes in front of the lateral epicondyle of humerus
- Inject in a ventral position

Ulnar nerve
- Supplies the flexors of the antebrachium
- Originates with the median nerve
- Travels on the medial aspect of the humerus
- Branches passes through the carpal canal
Ulnar nerve: Injection site
Between the tendons of:
- m. ulnaris lateralis
- m. flexor carpi ulnaris
At the level of the accessory carpal bone, accessed laterally

Mental nerve block
- Emerges from the mental foramen
- Acts on the lower lip and lower teeth
Inferior alveolar nerve block (‘Alveolaris mandibularis’)
- Enters mandibular foramen
- Supplying teeth and gums
- Needle is inserted medial to the mandibular notch

Lingual nerve block
- Originates from the mandibular nerve
- Travels rostrally to the tongue
- Between styloglossus + mylohyoid muscles

Median nerve block
Located between:
- Radial carpal flexor
- Superficial digital flexor
Accessed on medial side

Name the carpal bones

- Radial carpal bone (fused)
- Intermediate carpal bone (fused)
- Ulnar carpal bone
- Accessory carpal bone (palpable)
- 1st carpal bone
- 2nd carpal bone
- 3rd carpal bone
- 4th carpal bone

List the dorsal tendons found on the carpus
Tendon of:
- Ulnar carpal extensor
- Radial carpal extensor
- Lateral digital extensor
- Common digital extensor
- Abductor digiti I longus
List the palmar tendons found on the carpus
- Ulnar carpal flexor
- Radial carpal flexor
Give the major nerves and vessels located at the carpal joint
- Cephalic vein - Becoming accessory vein at the carpus
- Lateral + medial radial nerve
Approximate location of the cephalic + accessory cephalic vein

*Cephalic vein passes onto the palmar aspect

Approximate location of the branches of the radial nerve


Identify the arthrocentesis sites of the elbow joint

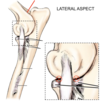
Identify the arthrocentesis sites of the carpal joint

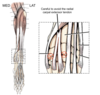
- Epidural anaesthesia site
- The volume of anaesthesia to give
- L7 - S1
- Passing through the interarcuate ligament
- Into the epidural space
- 2-6ml
List the notable ligaments of the canine forearm
- Medial/lateral glenohumeral ligament
- Olecranial ligament
- Lateral/medial collateral ligament (elbow)
- Lateral/medial collateral ligament (carpus)
Location of the kidneys in canine
- Left: L2 - L4
- Right: L1 - L3
Approximately under the last rib, dorsally
Large intestine: Organ locations
- Descending colon: Left dorsal abdomen
- Duodenum: Travelling laterally
- Jejunum: Fills the Left abdomen
- Ileum: Runs from left to right toward the cecum
- Transverse colon: Travels from right to left
Laryngeal cartilages + hyoid skeleton
From caudal → rostral direction
- Larynx:
- Cricoid cartilage (prominent)
- Thyroid cartilage (sometimes palpable)
- Hyoid:
- Basihyoid (ventrally)
- Ceratohyoid (laterally)
Liver borders
- Right side: IC 7-13
- (Left side: IC 7-9)
Cranial to the last rib, distal third

Lung borders
- Ribs: IC 13
- Vertebral Column: IC 12
- Tuber Coxae: IC 11
- Tuber Ischiadicum: IC 10
- Shoulder: IC 8
Lymph nodes
- Mandibular: Located near lingual vein
- Med. retropharyngeal: Ventral to ala atlantis
- Superficial cervical: Between omo. trapezius and cleidocerv.
- Popliteal: Behind the stifle joint
- Superficial inguinal: Medial to inguinal ligament

Glands of the head/neck region
- Parotid gland
- Mandibular gland
- Monostomatic gland

M. ulnaris lateralis; m. flexor carpi ulnaris; digital flexors
Lateral → Medial
- M. ulnaris lateralis
- (Fossa)
- M. flexor carpi ulnaris
- Superficial digital flexor

Nerve blocks: Mentalis; infraorbitalis; alveolaris mandibularis; lingualis
Ovaries, uterus, vagina
- Vagina
- Cervix
- Uterus: Palpable when pregnant/rectal exam
- Ovaries: Close to the kidneys between last rib and iliac crest
Locate: Deltoid muscle
Covers the hamulus process
Locate: Biceps muscle
Tendon of origin: Craniomedially to the shoulder joint, in the intertubercular groove of the humerus
Points to note: Shoulder joint
- Cranial + Caudal recess
- Caudal recess: Large, may extend to deltoid tuberosity
Small intestines
- Descending duodenum: Right abdominal wall, pressing dorsally against sublumbar muscles
- Jejunum: Palpable on ventral abdominal floor
- Ileum: From left to right towards caecum at L2-L3 (Not palpable)
Spleen
- Left side
- Left part of the greater curvature of the stomach
- Palpated caudal to the last costal cartilage in the left dorsal abdomen

Stifle
Palpable:
- Patellar ligament → tibial tuberosity
- Lat. + Med. femoral condyle
- Lat. + Med. femoropatellar ligaments → Sesamoids
- Long digital extensor (In front of lat. collat.)
Stomach
- Fundus: Located on the left
- Pylorus: Located on the right
- Only a full stomach will reach the ventral abdominal wall
- An empty stomach may not be palpable

Superficial cervical lymph nodes; scapula; v. jugularis externa
- Jugular: Press caudal jugular groove at sternocephalic muscle
-
Sup. cerv. ln.: Btw:
- Omo.
- Trapezius
- Cleidocervicalis
List the superficial muscles of the thigh
- M. sartorious
- M. gluteus medius
- M. gluteus superficialis
- M. biceps femoris
- M. semimembranosus
- M. semitendinosus

M. gluteus medius

M. sartorius

M. gluteus superficialis

M. biceps femoris

- M. semimembranosus
- M. semitendinosus


