Posture and Gait Review Flashcards
Posture and Gait
Postural pattern?

Kyphosis – Lordosis posture
Posture and Gait
Kyphosis – Lordosis posture: elongated and shortened muscles

- Enlongated: neck flexors, upper back, external oblique, hamstrings
- Shortened: neck extensors, low back extensors, hip flexors
Posture and Gait
Postural pattern?

Flat-back posture
Posture and Gait
Flat-back posture: elongated and shortened muscles

- Elongated: hip flexors
- Shortened: hamstrings
Posture and Gait
postural pattern?

Sway back posture
Posture and Gait
Sway back posture: elongated and shortened muscles
- Elongated: hip flexors, external obliques, upper back extensors, neck flexors
- Shortened: hamstrings, upper portion of internal obliques

Posture and Gait
postural pattern?

lordosis posture

Posture and Gait
lordosis posture: elongated and shortened muscles
- elongated: anterior abdominal, hamstrings
- shortened muscles: low back, hip flexors

Posture and Gait
ideal posture by Kendall et al
- post coronal suture
- Through the external auditory meatus
- odontoid process
- middle of shoulder joint
- bodies of lumbar vertebrae
- sacral promontory
- slightly posterior to center of hip joint
- slightly ant to the axis of knee joint
- slightly ant to lat malleolus
- Through the calcaneocuboid joint

Posture and Gait
What is the role of the pelvis in gait in the sagittal plane?
Pelvic Tilt (sagiIal plane): 2.79° to 4°

Posture and Gait
What is the role of the pelvis in gait in the frontal plane?
Pelvic drop/list (frontal plane): 4° to 7.72°

Posture and Gait
What is the role of the pelvis in gait in the transverse plane?
Pelvic rotation (transverse plane): 10° to 10.4°

Posture and Gait
Characterized by a shorter step length and stance time on the side of the painful lower extremity; it may be accompanied by ipsilateral trunk lean with hip pain or a contralateral trunk lean with knee and foot pain.
Antalgic Gait
Posture and Gait
anything that makes the initiation of swing difficult: decreased trunk stability, inefficient AE of the pelvis, difficulty with hip flexion etc…
Backward trunk lean during initial swing
Posture and Gait
anything that makes the initiation of swing difficult (except the trunk control): inefficient AE of the pelvis, difficulty with hip flexion
Posterior pelvic tilt during initial swing
Posture and Gait
a relatively longer leg will create what type of deviation?
circumduction gait
Posture and Gait
Prosthetic Gait: abducted gait during stance
- avoiding a pinch
- or clearing a long leg
Posture and Gait
Prosthetic Gait: adducted gait during stance
fit of the prosthesis
Posture and Gait
limping gait, avoiding putting weight on the limb
antalgic gait
Posture and Gait
backward trunk lean during initial swing
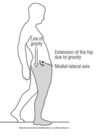
- any weakness for initiation of swing
- Purposeful to reduce demands on weakened stance limb gluteus maximus
- or to assist with limb advancement when hip flexion capability is limited.
- decreased trunk stability
Posture and Gait
Forward trunk lean during stance

- Compensation for quadriceps weakness. Forward lean reduces knee extensor moment and thus demand on vastii.
- May also be used to accommodating hip or knee flexion contractures.
Posture and Gait
pelvic hike during swing

Action of quadratus lumborum to assist with limb clearance when hip flexion, knee flexion, and/or ankle dorsiflexion are inadequate for limb clearance.
Posture and Gait
Ipsilateral pelvic drop during swing
- Contralateral hip abductor weakness
- hip adductor spasticity
- or hip adduction contracture.
Posture and Gait
Compensation for weak hip flexors or for inability to shorten leg for limb clearance
circumduction
Posture and Gait
knee hyperextension during stance

- flaccid/weak quadriceps: compensated for by excess plantarflexion and/or posterior pull on the thigh by gluteus maximus
- plantarflexion deformity/contracture
- impaired proprioception
Posture and Gait
what shortens the limb during swing
- pelvis elevation
- hip flx
- knee flx
- ankle DF
Posture and Gait
Entire foot simultaneously touches ground at initial contact: foot flat contact
- Plantarflexion contracture
- weak dorsiflexors
- knee flexion contracture that prevents optimal tibial alignment before initial contact
Posture and Gait
foot slap; loading response
Weak dorsiflexors or reciprocal inhibition of dorsiflexors
Posture and Gait
a presents with foot slap, this gait deviation will most likely occur during.
A. Heel strike
B. Loading Response
C. Pre-swing
D. mid-stance
B loading response
Posture and Gait
Ankle collapses into more than 5° dorsiflexion at midstance and/or more than 10° dorsiflexion at terminal stance
- weak plantar flexors to control tibial advance
- Knee flexion or hip flexion contractures.
Posture and Gait
Heel comes off ground in mid stance: early heel rise
plantar flexos contracture
decreased DF ROM
Posture and Gait
true or false: heel off occurs in double limb support
false
toe off occurs in double limb support

Posture and Gait
what happens in the gait cycle during push off
- Terminal Stance (heel off)
- Preswing (toe-off)

Posture and Gait
which parts of the gait cycle occur in double limb support?
- heel strike (initial contact)
- Preswing (toe off)

Posture and Gait
the swing phase comprises ___% of the gait cycle
40
Posture and Gait
Push Off =
terminal stance (heel off) + preswing (toe off, double limb support)
Posture and Gait
toe-off occurs during
Preswing of the stance phase
Posture and Gait
heel off occurs during
terminal stance of the stance phase

Posture and Gait
foot flat occurs during
loading response of the stance phase

Posture and Gait
gait cycle and muscles
- Heel strike (tibialis anterior, glut max)
- Loading response (quads)
- Midstance (triceps surae)
- Terminal Stance (triceps surae -heel off)
- Preswing (deep plantar flexors, rectus fem)
- Initial & mid-swing (contralateral abd, ilipsoas and rectus fem)
- Terminal swing (quads, tibialis anterior)

Posture and Gait
pelvis during gait
- Heel strike: pelvis AD
- Loading Response to Mid- Stance to Terminal Stance: pelvis PD
- Pre-Swing (Toe-off): relative pelvis PE (PE & AE)
- Initial Swing to Mid-Swing : pelvis AE
- Terminal Swing into HS: pelvis AD

Posture and Gait
FMT paradigm to what causes gait to become less efficient
- Mechanical Capacity
- Neuromuscular Control (initiation, strength, endurance)
- Motor Control


