Diabetes Mellitus Flashcards
DM
polydipsia
high thirst
DM
inability to produce insulin
TYPE I DM
DM
polyuria
frequent urination
DM
polyphagia
increased hunger
DM
insulin resistance OR a combination of inability to produce insulin AND insulin resistance
Type II DM
DM
Gestational DM is seen in pregnancy and is commonly caused by
insulin resistance
DM
the pancreas is a retroperitoneal organ located
posterior to the stomach and duodenum.

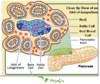
DM
there are 2 types of tissues in the pancreas
- endocrine islets of Langerhans
- exocrine (darker tissue)

DM
endocrine islets of Langerhans tissue in the pancreas has 2 types of cells
- Alpha cells: produce glucagon (raises blood sugar)
- Beta cells: produces insulin (lowers blood sugar
DM
insulin is secreted by the pancreas in response to
an increase in serum/blood glucose
DM
insulin decreases blood glucose levels by
- allowing cells in the body to uptake glucose
- allowing liver/muscles/fat to store extra glucose as glycogen
- inhibiting gluconeogenesis

DM
what is the sole source of energy of the brain
glucose
DM
which hormones prevent hypoglycemia (are counter-regulatory hormones) and allow glucose availability for brain use during fasting?
- glucagon: glycogen → glucose
- cortisol:
- growth hormone
- catecholamines
DM
previously called juvenile-onset diabetes and typically diagnosed in childhood, adolescence, or early adulthood
Type I DM
DM
the peak incidence of onset of DM type I
11-13 years of age
- There is also an incidence in people in their late 30a and early 40s, and the disease tends to present less aggressively
DM
Type I DM is caused by
the destruction of 80-90% of the beta cells in the pancreas by a lymphocytic infiltration (autoimmune) in a genetically predisposed individual (gene HLA-DR3/DR4)
DM
which gene is linked to DM type I
HLA-DR3/DR4
DM
pathophysiology of type I DM
b-cells in pancreas destroyed → no insulin → increased in blood glucose → glucagon initiates glycogenolysis adding more glucose to the blood stream → hyperglycemia
DM
classical manifestations of hyperglycemia (and Type I DM)
- polyuria (from drinking so much)
- polydipsia (the brain is going to try to dilute the sugar sirup syrup in the blood)
- polyphagia (cells cannot use the sugar)
- fatigue (due to increased catabolism)
- weight loss (body need energy so break down muscle → uses ketones as source of energy)
- Diabetic ketoacidocis

DM
major risk factors for type II DM
obesity and inactivity


