Pelvic Floor and Women's Health Flashcards
(113 cards)
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
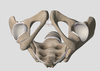
bony boundaries of the pelvic floor
- anterior: pubic symphysis
- anterolateral: inf pubic ramus
- lateral: ischial rami and ischial tubeorsity
- posterolateral: scrotuberous ligamet
- posterior: coccyx
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
triangles of the pelvic floor
- urogenital triangle
- anal triangle

Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
blood supply to the pelvic floor
- 2 pudendal arteries
- internal pudendal artery
- labial veins
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
The pelvis is innervated mainly by the sacral and coccygeal spinal nerves and the pelvic part of the
autonomic nervous system.
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
the lumbar plexus branches to the pelvis
- genitofemoral
- ilioinguinal
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
the sacral plexus branches
- pudendal
- levator ani

Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Lumbosacral nerves
- iliohypogastric (T12-L1)
- ilioinguinal nerve (L1)
- genitofemoral nerve (genital branch) (L1-L2)
- lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (perineal branch) (L2-L3)
- pudendal nerve (S2-S4)
- obturator L2-L4
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
detrusor muscle

Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Sympathetic input to the the pelvis:
- Provides motor innervation to vascular smooth muscle
- Provides constant tone in internal sphincters.
- Detrusor relaxation for filing & storage

Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Parasympathetic input to pelvic floor
- Provides motor & sensory to innervation to bladder
- Responsible for relaxation of internal anal sphincter
- Detrusor contraction, promotes bladder emptying
- Blood vessel dilation
- Erection of clitoris or penis

Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
70% of the muscle fibers in the pelvic floor are type…
type I (slow twitch)
30% are type II (fast twitch)
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Layer 1 (Urogenital Triangle) muscles of the pelvic floor
- perineum or superficial pouch
- bulbocavernosus (bulbospongiosus in men)
- ischiocavernosus
- superficial transverse perineal
- external anal sphincter

Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Layer 2 (Urogenital Diaphragm) muscles of the pelvic floor
- urethral sphincter (in men)
- compressor urethra (in men)
- sphincter urethral vaginalis
- deep transverse perineal
- perineal membrane
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Layer 3 (Pelvic Diaphragm) muscles of the pelvic floor
- levator ani muscle (pubococcygeus, puborectalis, iliococcygeus & coccygeus)
- Obturator internus
- Piriformis

Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Function of the PFM
- Support of the pelvic viscera
- Sphincteric (bladder & bowel control)
- Sexual functions

Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Abdominal Canister by Dianne Lee

- Balance bet. the diaphragm, PFM, transverse abdominus (TrA), other abdominal muscles & multifidus.
- Transmits intra-abdominal pressure during activities
- Keeps alignment of pelvis.
- Keep joints in optimal form closure.
- Keep optimal force closure.
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Pelvic floor dysfunction: Janda’s principles
Muscle contraction properties change in response to inflammatory process or pain → hypertonicity → impaired contraction & relaxation (coordination issues) → trigger points and muscle guarding development
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Musculoskeletal dysfunction of the PFM that may be the 1° cause of pelvic pain in response to pathology in the:
urologic, gynecologic, &/or gastroenterologic
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Pelvic floor dysfunction is often is a response to a 1° pain generator arising from…
bladder, rectal or vaginal pathology.
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Clinical Pearl of Wisdom in Treating PFD
Stretch wht’s tight → strengthen what’s weak → perform neuromuscular reeducation
(Note: “sometimes is weak from reciprocal inhibition.” Dr. Q)
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Postural Muscles Facilitation: Gets Shortened
(NOTE: Get shortened from excessive contraction)
- iliopsoas
- QL
- pectineus
- piriformis
- TFL
- lateral quad
- rectus femoris
- hamstrings
- short adductors
- PELVIC FLOOR
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Dynamic Muscles Inhibition: gets weak
- multifidi
- gluteals
- long adductors
- rectus abdominus
- TrA
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
What is muscle tone
Resistance to displacement at rest
Pelvic Floor and Women’s Health
Pelvic floor muscle tone is affected by…
Hormones (pregnancy, menstrual cycle, menopause)





















