posterior abdominal walls and kidneys Flashcards
anterior to the 12th ribs with one higher than the other
retroperitoneal, anterior to the 12th ribs with the left kidney slightly higher than the right
- renal arteries and veins

describe general surface anatomy of the kidneys
- 2 surfaces
- anterior and posterior
- 2 poles
- superior and inferior
- 2 borders
- medial
- has HILIUM- continuous with the renal sinus
- VAU + lymphatics and
- has HILIUM- continuous with the renal sinus
- lateral
- medial
differentiate the Left and Right kidney relationships
left
- anterior
- stomach
- spleen
- pancreas
- left colic flexurwe
- descending colon
- jejunum
- posterior
- anterior to 11-12 ribs
right
- anterior surface
- liver
- descending duodenum
- right colic flexure
- small interstine
- anterior to the 12th ribs
both
- nerves
- iliohypogastric
- iliolingual
- muscles
- diaphragm
- psoas major
- quadratus lumborum
- transversus abdominis

detail the construct of a kidney
- cortex
- pyramids
- renal papilla- apical projecrions feeding in to the minor calyx
- pyramids
- medulla
- minor calyx
- major calyx- 2-3
- hilum
- renal pelvus
- ureter
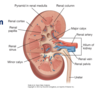
describe the arterial flow to the kidneys
- renal arteries
- feed into 5 segments, each recieving its own segmental artery
-
NO ANASTOMOSES=no collateral circulation
- impeding blood flow to an area leads to necrosis, can also be used when surgically removing a segment of the kidney
-
NO ANASTOMOSES=no collateral circulation
- acessory renal arteries
- extra hilar
- feed into 5 segments, each recieving its own segmental artery
- venous flow
- right
- straight to the inferior vena cava, no tributaries
- left
- tributaries with left gonadal and left suprarenal gland
- renal vein passes deep to the mesenteric artery, where it can be compressed
-
renal vein entrapment syndrome
3.
-
renal vein entrapment syndrome
- right

kidney translplant is placed where? describe
donor kidney may be transplanted to replace nonfunctional kidney
- placed within iliac fossa
- blood vessels
- external iliac artery/vein
- ureter directly into the bladder
- blood vessels
loin to groin pain is felt by Jerry, describe the nerves involved with the referred pain
- cutaneous areas
- T11-L2
- kidney stones may obstruct and cause loin to groin pain
- may lead to hydronephrosis-distension of the kidney and eventually kidney failure
describe the vascular supply to the ureters
- arteries
- longitudinal anastamoses
- upper- renal artery
- middle -gonadal, abdominal aorta, common ilian
- pelvic-internal iliac
- longitudinal anastamoses
- veins
- upper-renal v
- middle -gonadal
- pelvic cavity-internal iliac

what is the lymph drainage destination for the kidneys and ureters?
- kidneys
- paraaortic- nodes around the renal artery
- ureters
- upper- paraaortic
- middle-common iliac
- inferior-external/internal iliac nodes

describe the nerve supply of the kidneys and ureters
- kidney-symp/parasym
- ureters-symp/parasym
- kidney
- T10-T12
- vagus
- ureters
- T11-L2
- vagus + S2-S4

differentiate the two parts of the suprarenal gland and general secretion
- cortex
- secretes corticosteroir hormones important for carbohydrate and protein metabolism
- medulla
- collection of postganglionic sympathetic neuron cell bodies-
- catecholamines
- collection of postganglionic sympathetic neuron cell bodies-
- medulla

describe the vascularture of the suprarenal glands
- arteries- three segments, from three different locations
- both are the same
- inferior phrenic
- superior suprarenal artery
- abdominal aorta
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery
- inferior suprarenal artery
- veins
- right
- to the inferior vena cave
- left
- left suprarenal vein(deep to the mesenteric artery)
- inferior vena cava
- right

describe the nerves supply to the suprarenal gland
- presymp fibers: greater, lesser and least splanchnic nerves
- preganglionic nerve fibers with in the adrenal medulla
- postganglionic fibers - to blood vessels
- preganglionic nerve fibers with in the adrenal medulla

important vasculature that lies at T12
aortic hiatus of the diaphragm
where is the aortic haitus and the bifurcation into the common iliac
T12
L4
list the posterior, terminal, paired and unpaired visceral arteries from the abdominal aorta
- posterior
- inferior phrenic
- diaphragm
- lumbar arteries
- 4 pairs
- posterior wall of abdominal muscles
- median sacral artery
- inferior phrenic
- terminal
- common iliac arteris
- paired
- middle suprarenal artteries
- renal arteries
- kidneys and inferior portion of the suprarenal gland
- testicular or ovarian artery
- testes/ ovaries
- unpaired
- celiac artery L1
- forgut
- mesenteric
- L2
- inferior mesenteric
- L3
- celiac artery L1

describe the formation of the inferior vena cava- 11 tributaries
- formed by union of common iliac - L5
- tributaries
- common iliacs
- 5 lumbar veins
- 1&2 drain in azygos and hemiazygos via lumbar vein
- 3&4 drain directly into the IVC
- 5 drains in IVC via iliolumbar vein
- righ gonadal vein
- renal veins
- left drain left gonadal and suprarenal
- right suprarenal
- inferior phrenic
- hepatic veins

what acts as a collateral channel between upper and lower parts of the body in the IVC is blocked
azygos and hemiazygos
largest lymphatic vessel
thoracic duct- drains all of the body below the diaphragm and the left half of the body avove the diaphragm
chief muscle of inspiration
consists of.
attachements
diaphragm
- central tendon
- peripheral muscle fibers convergin to insert into the central tendon
- domes
- right
- arches as high as 5th rib
- left
- arches to 5th intercostal space
- right
attachments
- xiphoid process (sternal part)
- lower 6 costal cartilages and ribs
- lumbar vetwebrae and associated aponeurtotic arches (lumbar portion)

draw/describe the lumbar attachments of the diaphragm
- right crus
- L1-3
- left crus
- L1-2
- median arcuate ligament
- arching over the aorta
- medial arcuate ligmanet
- arching over the psoas major
- lateral arcuate ligament
- arching over the quadratus lumborum

apertures in diaphragm
- border and name for aperture that allows the IVC and right phrenic nerve. what level of the spine?
- border and name for aperture that allows the esphagul and anterior/posterior vagal nerve to pass. what level of the spine?
- caval opening
- central tendon
- T8
- esophageal hiatus
- muscle of the right crus for the esphagus
- level T10

describe the aortic hiatus, nerves and vessels involved with the daphragm
- passagways
- aortic haitus-anterior to T1/posterior to arcuate median ligament
- aorta
- thoracic duct
- sympathetic trunk
- aortic haitus-anterior to T1/posterior to arcuate median ligament
- nerves
- left phrenic nerve- pierces the diaphragm muscle
- right phrenic nerve- passes with IVC in the Caval Opening
- splanchnic nerves
- greater and lesser pass throug hthe crura on either side.
- arteries
- hemiazygos vein passes throug hthe left crus
2.
- hemiazygos vein passes throug hthe left crus

descreibe the innervation of the diaphragm: motor vs sensory.
- motor
- phrenic nerves
- anterior rami C3-C5
- phrenic nerves
- sensory
- phrenic nerves
- orgin to septum transversum
- lower 6 intercostal and subcostal nerves (T5-T12)
- Orgin to mesoderm from body wall
- phrenic nerves
- referred pain from diaphragm
- 2 different areas based on sensory innervation
- phrenic nerves- C3-C5
- T5-T12, costal margin of anteriolateral abdominal wall from peripheral regions of diaphragm
- 2 different areas based on sensory innervation

what could lead to paradoxical movement of the diaphragm?
one phrenic nerve is injured -> hemidiaphragm, ipsilateral paralysis.
leads to a paradoxical movement.

describe/draw the blood supply of the diaphragm
- arteries
- superior surface
- pericardiacophrenic
- musculophrenic
- superior phrenic
- inferior surface
- inferior phrenic
- superior surface
- veins
- superior surface
- pericardiacophrenic
- musculophrenic- tributaries to internal thoracic veins
- inferior surface
- right inferior phrenic->IVC
- left inferior phrenic ->supra renal vein
- superior surface

what are the muscles in contact and their involvment with the abdominal wall?
- iliopsoas
- two muslces
- psoas major
- spinal nerves-nerve-L1-L3
- illiacus
- femoral nerve-L2-L4
- psoas major
- origin- T12-L5 inserts= lesser tronchanter
- funciton
- flexes the thigh(from below) and the trunk(from above)
- two muslces
- psoas minor
- present in 60% of people
- T12-L1
- innervated- L1
- function
- weak flexion of the trunk
- quadratus lumborum
- origin= iliac crest, insert= 12th rib and lumbar transverse processes
- innervated by T12-L4
- funciton
- bilateral flexion
- stabalize 12th rib
- unilateral flexion
- lateral flexion
- bilateral flexion

lumbar plexus
- contributions
- location
- branches- anterior/posterior and lumbar involved
- contirbutions
- anterior rami
- spinal nerves L1- L4
- subcostal
- T12
- anterior rami
- origin
- anterior to the transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae, embedded with in the psoas major muscle
- branches
- anterior
- genitofemoral nerve-L1-2
- medial
- obtorator-L2-4
- lateral
- iliohypogastric-L1
- ilioinguinal-L1
- femoral-L2-4
- lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh
- anterior

describe/draw lumbar plexus
- origin(5)- destination(9)
- cutaneous involvment



