GI organs Flashcards
(29 cards)
This is the location of where food is ingested, chewed and mixed with saliva, what does it open to?
oral cavity, opens to the pharynx
What is the common chamber shared by the digestive and respiritory system?
- construct
- function
phrynx
- musculofibrous tube
- transports the bolus of food from the oral cavity to the esophagus during swallowing
list the start and end ofthe portion of the digestive sytem located in the abdomen.
from the distal esophagus to the distal sigmoid colon

muscular tube connecting pharynx and stomach.
- begins
- traverses
- ends
esophagus
- begins in tthe neck, mostt of its length is in thoracic cavity
- traverses the diaphragm ~TX (esophageal hiatus)
- ends at the stomach
what are the contents of the esophageal hiatus?
- esophagus
- anterior and posterior vagal trunk
- anterior vagal trunk
- several smaller trunks, main contributor is the left vagus nerve
- posterior vagal trunk
- consists of a single trunk whose fibers mostly come from right vagus nerve
- anterior vagal trunk

list and describe the arterial supply of the esophagus
- gastric artery
- from the celiac trunk
- left inferior phrenic trunk
- left inferior phrenic artery

what asisst with control over the contents with in the esophagus?
gaurded at both ends by use of sphincters
- upper esophageal sphincter
- helps prevent the enterance of air - during resipration
- secondary linge of defense against reflux of gastric contents
- lower esophageal sphincter
- located at the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm
- first guard against gastrointestinal reflux
- vulnerable to damage from repeated exposure

dilated portion of the digestive tract, where food accumulates.
stomach
- undergoes partial enzymatic digestion into semi-liquid chyme
- produces
- HCL
- digetsive enzymes
- four partts
- cardia/cardiac region
- Fundus
- Body-major part
-
pyloric part
- pyloric antrum leading to a narrow pyloric canal

list the superficial structures of the stomach- 4
stomach
- lesser curvature
- facin superiorly and to the right
- greater curvature
- facing inferiorly and to the left
- cardial notch
- lies in the superior angle created shen the exophagus enters thestomach
- angular incisure
- a bend on the lesser curvature

longest part of GI tract
- primary site of
- sections- in order
small intestine
- primary site for the absorption of nutrients
- sections
- duodenum
- jejunum
- ileum

First 2cm of duodenum

duodenal cap or ampulla
- has a distint radiological appearance
- clinically important b/c it is the most frequent location of peptic ulcers

describe the pathway of content (enzymes and bile) into the duodenum
bile -> bile duct (sphincter control)
pacreatic enzymes->pancreatic duct (sphincter control)
bile duct + pancreatic duct-> hepatopacreatic ampulla
hepatopancreatic ampulla->major duodenal papilla (narrowest)-> descendin portion of the duodenum

what holds the duodenum in place (suspends)
ligament of Treitz- suspends the duodenum from the

list the surface modifications of the muscoal lining in the small intestine.
- function
- modifications
- increase the surface area for absorption
- modifications
- circular folds (plicae circultes)
- of mucosa-submucosa
- villi
- fingerlike projections of mucosa
- micorvilli
- microscopic projections on absorptive cells of the mucosa
- circular folds (plicae circultes)
first portion of the duodenum curves around the ____
pancreas

- portions of the duodenum
- superior
- descending
- inferior/horizontal
- ascending

bleeds have different characteristics. What landmark is allows for the distinction of these bleeds?
duodenojejunal junction
- junction between upper GI bleeding and lower GI bleeding, which have different clinical characteristics
proximal 2/5 of small intestine
distal 3/5 of small intestine
- jejunum forming the 2/5 and being located mainly in thte LUQ
- Ileum form the distal 3/5 and is located mainly in the RUQ

how are the jejunum and ileum distiguished?
location and blood supply
- jejunum have few arterial arcades and long vasarecta in mesentery with little fat
- few AA
- long VR
- lil fat
- Ileum has many arterial arcades, short vasa recta with mesetery laden with fat
- Many AA
- short VR
- much fat

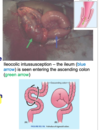
opening at end of Ileum.
discuss the embryonic development importance of a structure here.
ileocecal junction opens into the large intestine from the Ileum.
Ileal (Meckel’s) diverticulum, attaches from ileum to the ligament that was once the umbilical cord. ~2ft from the ileocecal junction.

chyme is highly ____. how is this handeled by the small intestine
chyme is highly acidic, buffered by pancreattic secretions containing high [HCO3]
main purpose of the large intestine, distinguishing structtures from small intestine.
Water absorption
- omental appendices
- appendices epiloicae, small fatty projections
- teniae coli
- three bands of longitudinal smooth muscle
- haustra-sacculations
1.

of the ducts and passages, where is a gallstone most liekly to be lodged?
major duodenal papula
list the sttructures of the large interstin
- cecum and appendix
- colon
- ascending
- transcverse
- descending
- sigmoid
- rectum
- anal canal