GI vascular and innervation Flashcards
describe the embryonic derivatives of the gut vasculature-3
- caudal foregut
- supplied by celiac trunk(celiac artery)
- midgut
- supplied by the meseteric artery
- hindgut
- supplied by the inferior mesenteric artery

what does the embryonic forgut form?
- abdominal portion of the esophagus
- stomach
- duodenum, with respect to its union with the common bile and pancreatic ducts
- Liver and gallbladder
- pancreas
- spleen- not digestive, but closely related via proximity
which branches of the celiac trunk supplying derivatives of the embryonic caudal foregut?
- left gastric artery
- goes to
- STOMACH
- LOWER ESOPHAGUS
- goes to
- splenic artery
- goes to
- neck, body and tail of PANCREAS
- SPLEEN
- STOMACH
- goes to
- Common hepatic artery
- gastroduodenal artery
- STOMACH
- head of PANCREAS
- DUODENUM
- proper hepatic artery
- LIVER
- GALLBLADDER
- STOMACH
- gastroduodenal artery
list three locations and consequences of ulcerations with regard to the duodenum
- duodenal ulcers
- posterior
- erode directly into the gastroduodenal artery or more commonly on posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- fatal hemorrhage
- erode directly into the gastroduodenal artery or more commonly on posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- anterior
- erode into the peritoneal cavity
- peritonitis thereby causeing adhesion of greater omentum
- posterior
what does the embryonic midgut form in adults?
- duodenum
- jejunum
- ilum
- cecum
- appendic
- ascending colon
- transverse colon

describe the vasculature of the midgut
- branches of the superior mesenteric artery
- inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- head of the PANCREAS
- DUODENUM
- intestinal branches
- JEJUNUM
- ILEUM
- middle colic artery
- TRANSVERSE COLON
- right colic artery
- ASCENDING COLON
- ileocolic artery
- terminalILEUM,
- CECUM,
- ascending COLON
- appendicular artery
- APPENDIX
- inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery

DESCRIBE THE structures formed from the hindgut
- descending colon
- sigmoid colon
- rectum
- anal canal

describe the vasculature of the hindgut
- inferior mesenteric artery
- left colic artery
- DESCENDING COLON
- sigmoid arteries
- SIGMOID COLON
- superior rectal artery
- RECTUM
- ANAL CANAL
- left colic artery

branches where, allow for anastomose between the midgut and hindgut arteries?
- marginal artery
- runs parallel to the colon
- collateral circulation

describe the venous drainage of the abdominal organs
- venous drainage from the abdominal GI tract and spleen enters the hepatic portal vein for transport to the liver
- hepatic portal vein- has two main contributions
-
splenic vein
- the inferior mesenteric drains into the splenic vein
- superior mesenteric vein
- minor but clinically relevantportacaval anastomoses
- connect the hepatic portal vein to systems of the inferior venae cava
- become dilated when flow resistance patients with cirrhosis-portal hyotension
-
splenic vein

describe the route of cancer spreading from the GI tract
the blood flows from the GI tract to the liver first. This means that cancer from the GI tract often metastasizes to the liver

list some locations affected by portal hypertension
portacaval anastomoses taht amay enlarge include
- lower esophagus
- as esophageal varicies
- may be fatal
- as esophageal varicies
- anal canal
- hemorrhoids
- paraumbilical region-caput medusae
- varicose veins radiating outward from the umbilicus

describe the two nodes categorized in the flow of lymphatic fluid. list the categories, organs and important structures
- pre-aortic nodes
- where
- celiac
- superior mesenteric
- inferior mesenteric
- organs
- GI tract
- accessory organs
- unit to form intestinal trunk
- where
- para-aortic
- where
- lumbar
- organs
- body wall
- kidneys
- adrenal glands
- testes/ovaries/ uterus/uterine tubes
- collect to form the right lumbar trunk** and the **left lumbar trunk
- where
- confluence of all trunks appears as CISTERNA CHYLI
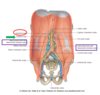
describe the sympathetic nervous innervation of abdominal organs
- consists
- preganglionic nerve fibers
- reach the prevertebral ganglia through splanchnic nerves
- postganglionic nerve fibers
- from cell bodies in prevertebral ganglia
- follow arteries to organs
- location
-
celiac trunk
- CELIAC GANGLIA
-
superior mesenteric artery
- SUPERIOR MESENTERIC GANGLION
-
inferior mesenteric artery
- INFERIOR MESENTERIC GANGLION
-
renal arteries
- AORTICORENAL GANGLIA
-
celiac trunk
- preganglionic nerve fibers

list the splanchnic nerves from contributions from the spine and destination
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- nerves
- greater splanchnic- T5-9
- lesser splanchin (T10-11)
- least splanchnic-T12
- location
- forgut (celiac trunk)
- midgut (superior mesenteric artery) territory
- nerves
- lumbar splachnic nerves
- nerves
- L1-2 (ocassionally L1-3)
- location
- hindgut ( inferior mesenteric artery)
- nerves

desceib the flow of autonomic nerve fiber to visceral organs. Hint ( they follow blood vessels)
- celiac ganglia nerve fibers
- route
- follow celiac trunk branches
- innervate
- forgut derivatives
- route
- aorticorenal ganglia fibers
- route
- follow renal artery branches
- innervate
- kidneys
- adrenal glands
- route
- superior mesenteric ganglia
- route
- follow superior mesenteric artery
- innervate
- midgut derivatives
- route
- inferior mesenteric nerves ganglia
- route
- mesenteric artery
- innervate
- hindgut
- route

describe the parasympathetic innervation of the abdominal cavity
two main sources: vagus and pelvic
- vagus nerves-CX
- route
- enter abdomen through esophageal haitus
- anterior and posterior vagal trunks
- formed esophageal plexus
- supply preganglionic parasympathetic input to ganglion cells located near or within the wall of tthe visceral sttructure
- anterior and posterior vagal trunks
- enter abdomen through esophageal haitus
- innervate
- forgut
- midgut
- route
- pelvic splanchnic-S2-S4
- route
- leave sacral spinal cord through anterior rami** and send **preganglionic fibers to hindgut
- innervate
- hindgut
- route
compare the functions of the sympathetic and parasympthetic autnoimc nervous inputs on thte abdominal contents
both manipulate the enteric nerous system
- sympathetic
- vasoconstriction
- reduced glandular secretion
- reduced peristalsis
- parasympathetic
- increase glandular secretion
- increase peristalsis, through smooth muscle
what type of fibers accompany sympathetic nerves and carry pain?
visceral afferent fibers accompany sympathetic nerves and carry parin from the abdominal viscera to the spinal cord.
describe the nerves involved with the reffered pain at the following locations.

-
GREATER SPLANCHNIC NERVE T5-T9
- forgut
- stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancrease, duodenum, spleen
- where
- dermatomes
- forgut
-
PHRENIC NERVE
- what organs
- diaphragmatic pleura
- pleuritis
- peritoneum
- cholecystitis
- ruptured spleen
- diaphragmatic pleura
- where
- ipsilateral shoulder
- why
- afferentt fibers of the phrenic nerve (C3,4,5) enter the same spinal cord segments as the supraclavicular nerves which supply cutaneous innervation to the shoulder.
- what organs



