Pictures of B3; W1 Flashcards
Describe the different components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex & how they all fit together.
The core is a pentagonal dodecahedron, made up of 20 trimers.
E1 is arranged around the core & touches the lipoyl domain of E2.
E3 subunits are also in the core.

What structure is this? What does it require to function? What is it a part of? What does it help make?

TPP
requires Vitamin B1: Thiamine to function
a part of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
eventually helps make acetyl CoA from pyruvate
Which cofactor does this show? Attached to which enzyme? A part of which complex? What is the end product?

Lipoamide
E2/DLTA (dihydrolipoyl transacetylase)
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
pyruvate–>acetyl CoA
What structure is this? What does it help activate? What complex are we talking about?

Coenzyme A
DLTA
dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
Just a summary slide. Do you understand everything on here?

AHHH not yet!!
What process does this figure show? Do you understand each of the steps?

Gluconeogenesis
No! I don’t-hopefully soon, though.
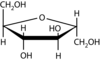
What is the structure? What are its components? What is this bond?

This is sucrose.
Made up of glucose & fructose…
beta 1,2 glycosidic bond
Identify this structure. What category does it fall into? What bonds does it have?

Amylose
Starch
alpha1,4 glycosidic bonds of glucose molecules
Identify this structure. What general category does it fall into? What bonds are present?

Amylopectin
Starch
alpha 1,4 glycosidic bonds & alpha 1,6 glycosidic bonds of glucose
Identify this structure. What general category does it fall into? What bonds are present?

Lactose.
Disaccharide w/ galactose & glucose
beta 1,4 glycosidic bond
What structure is this? What general category does it fall into?
Fructose
monosaccharide
What structure is this? What general category does it fall into?

Glucose
monosaccharide
What structure is this? Hint: found in the tongue…
What is its function? Is it abundant?

Fungiform Papillae
Located on the margin of the tongue…contains taste buds. 2nd most abundant type of papillae on the human tongue.
Identify this structure. Hint…found in the tongue. What is its function? Where is it located? Is it abundant?

Filiform papillae
located on the dorsum of the tongue
most abundant papillae on the human adult tongue
doesn’t have taste buds, but is meant for creating friction b/w the tongue & the food…scraping!!
Identify these structures.