Physiology of ANS. Pharmacology of ANS/ Anatomy of ANS Flashcards
SOMATIC=CONSCIOUS

Name the phrases associated with the sympathetic system and parasympathetic system?
“Fight and flight”
“Rest and digest”

What are the effects of the parasympathetic system and sympathetic system on the following organs?
Eye
Trachea and Broncheoles
Liver
Adipose
Kidney
Ureters and Bladder
Salivary Glands
Skin
Heart
Gastrointestinal
Blood vessels
Both parasympathetic and sympathetic are active at the same time, but it is the level which determines which system is dominant.

Breif Anatomy- Will be in other deck
Long pre-ganglionic neurone arises
from brainstem and lateral horn of
grey matter in sacral spinal cord
segments
Brainstem: pre-ganglionic neurone
travels with cranial nerves 3,7,9,10
oculomotor nerve, Vagus nerve, facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve
Sacral spinal cord: pre-ganglionic
neurone enters ventral rami of
S2-S4 spinal nerves
Sacral spinal cord: pre-ganglionic
neurones branch off to form pelvic
splanchnic nervesL


What neurotransmitter is released by the preganglionic neurone and the postganglionic neuron in the Parasympathetic Nervous sytem (PNS)?
ACh

Breif Anatomy of SNS
Sympathetic ganglia exist as
sympathetic trunks:
3 cervical ganglia
12 thoracic ganglia
5 lumbar ganglia
5 pelvic ganglia
Note: NOT just thoracolumbar
Ganglia contain cell bodies of post
ganglionic neurones
Short preganglionic neurone
synapses with longer post-ganglionic
neurone at same level or in
higher/lower ganglia (point of
divergence).

You want your responses to be coordinated in a sympathetic response. That is one preganglionic neuron branches of and innervates multiple postganglionic neurons
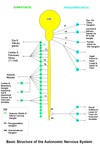
What is the only tissue in the body that is innervated by only one autonomic nerve and why is it like that?
All other have pre and post ganglionic set up?
Adrenal Medulla

Anything delivered by nerves the effects tend to be quite transient, for example noroadrenaline delivered to the heart will have an effect for a very short time. Adrenaline being delivered in the blood lasts for much longer. So you get a sympathetic effect working along with the nervous noroadrenaline.
What neurotransmitters does the sympathetic system release, how many pre and postganglionic neurons does it have and state 2 exceptions to this rule?
MOSTLY-Preganglionic neuron to Postganglionic neuron- ACh Postganglionic neuron to Organ-Noradrenaline
EXCEPTION 1- Adrenal Medulla has ACh as neurotransmitter and has only one preganglionic nerve innervating it
EXCEPTION 2- Some peripheral structures such as peripheral blood vessels, sweat glands and skin and those sympathetic nerves release ACh instead of noradrenaline

State the ratio of pre vs post for Sympathetic and Parasympathetic?
Sate weather the have little divergance or alot of divergence?

Why do we have a sympathetic ganglion chain?
They all synapse togethere so you can have a cordinated, fast, mass discharge to the whole of the peripheral nervous sytem controlling the sympathetic function

Draw a flow diagram from the hypothalamus showing a sympathetic nervous sytem response?
State what type of neurone (pre and Post) and state where they are found?

Draw a flow diagram from the hypothalamus showing a para-sympathetic nervous sytematic response?
State what type of neurone (pre and Post) and state where they are found?

Sympathetic Nervous System
Short pre-ganglionic neurone arises from …………… …………. ………. ……….. in T1-L3 spinal segments
Emerges from from …………… …………. ………. ……….. to join T1-L3 spinal nerves
Enters ………….. ………….. of T1-L3 spinal nerves
Detours via ……….. ………….. communicantes to enter sympathetic ganglion
Sympathetic Nervous System
Short pre-ganglionic neurone arises from lateral horn of grey matter in T1-L3 spinal segments
Emerges from from ventral root of spinal cord to join T1-L3 spinal nerves
Enters ventral rami of T1-L3 spinal nerves
Detours via white rami communicantes to enter sympathetic ganglion



PARASYMPATHETIC SYSTEM
Long pre-ganglionic neurone arises
from ………………… and…………….. ……………. ……. ……………. in ……………. spinal cord
segments
Brainstem: pre-ganglionic neurone travels with cranial nerves 3,7,9,10
Sacral spinal cord: pre-ganglionic neurone enters …………… ………. of S2-S4 spinal nerves
Sacral spinal cord: pre-ganglionic neurones branch off to form ……………… ……………. ……………….
Long pre-ganglionic neurone arises from brainstem and lateral horn of
grey matterinsacral spinal cord segments
Brainstem: pre-ganglionic neurone travels with cranial nerves 3,7,9,10
Sacral spinal cord: pre-ganglionic neurone enters ventral rami of S2-S4 spinal nerves
Sacral spinal cord: pre-ganglionic neurones branch off to form pelvic splanchnic nerves

Name the 4 special parasympathetic ganglia associated with cranial nerves?
Does the PNS have little or alot of divergance?
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic ganglia exist in wall of organ/viscera
4 special parasympathetic ganglia associated with cranial nerves:
Ciliary (CN3)
Pterygopalatine (CN7)
Submandibular (CN7)
Otic (CN 9)
Ganglia contain cell bodies
of postganglionic neurones
Long preganglionic
neurones synapse with
short post ganglionic
neurones (little divergence)

How does the parasympathetic sytem effect the eyes?
More specificallythe lens and cillary muscle?

Pupillary constriction
Contracts ciliary muscle; lens bulges for near vision
Think of it as a trampoline, when you contract the phrame of the trampoline it will bulge downwards. As the cillary muscle contracts it causes the lense to focus. When you read something and your eyes focus that is the parasympathetic system.

Enteric Nervous System
The enteric nervous system (ENS) or intrinsic nervous system is one of the main divisions of the autonomic nervous system and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract.[1] It is capable of acting independent of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, although it may be influenced by them. The ENS is also called the second brain.
The gut has very good local control. The gut can pretty much regulate its own function. The enteric nervous sytem can carry out actions independant of the brain, however, the brain can have an influence via parasympathetic and sympathetic.
Alot of it is done by its own- enteric nervous sytem.

What effect does the parasympathetic system and sympathetic system have on GI function?
Relax sphincters so food is moving along the gut- PARA

Draw a diagram showing the relationship between the heart, aterioles, veins, parasympathetic nerve, afferent nerve, CNS and sympathetic nerve and afferent nerve and arterial baroreceptor.
Have neurons that inhibit and stimulate
The interneuron inhibits sympathetic nerve
Higher the pressure the higher the Baror receptor’s firing rate

How does the sympathetic system effect Totat peripheral resistance and how does it do that?
It can increase TPR ( sympathetic activity goes up) and decrease TPR (decreased activity)

PNS and SNS determine heart rate and contractility hence effecting cardiac output
Write the equation for cardiac output
Write the equation for Blood pressure
CO = SV x HR where CO = cardiac output
SV = stroke volume HR = heart rate
BP = CO x TPR where BP = blood pressure
CO = cardiac output TPR = total peripheral resistance
Heart PNS and SNS summary
inotropic- modifying the force or speed of contraction of muscles.

How does the sympathetic nervous system increase
oxygen delivery to the lungs?
a) Directly inhibits parasympathetic nerves
b) Via noradrenaline/adrenaline from the adrenals
c) Stimulates increased breathing rate
d) Influences cardiorespiratory control centre in the brain
No sympathetic Nerves inervate the lung
Effectively it can do all of these things, however the most important is via adrenaline from the Adrenals

B- by some distance B is the most important
How does the parasympathetic system effect lungs?
The lungs are innervated by parasympathetic nerves, but not innervated by sympathetic nerves. The ACh causes constrictions of the bronchioles.
Adrenaline causes dilation of bronchioles- More oxygen

How does the parasympathetic system effect the bladder and what structure does it effect?
How does the sympathetic system effect the bladder and what structure does it effect?
What part of the bladder do we have voluntary control over?
The major effect is the parasympathetic effect.
The parasympathetic stimulates the Detrussor Muscle. causing it to contract so the urine gets pushed out of the bladder
The sympathetic nerve stimulates the internal sphincter and keeps the internal sphincter contracted so urine stays inside the bladder
We do have voluntary control of the bladder- External Sphincter

What is the Micturition Reflex?
Micturition= passing urine
contraction of the walls of the bladder and relaxation of the trigone and urethral sphincter in response to a rise in pressure within the bladder; the reflex can be voluntarily inhibited and the inhibition readily abolished to control micturition.
Sensory information that the bladder is full causes a reflex. There is a refelx activation of the parasympathetic system and reflex inhibition of the sympathetic system.

Name 3 catecholamines

What are the major neurotransmitters used in the autonomic nervous system?
ACETYLCHOLINE
NORADRENALINE (NOREPINEPHRINE)
ADRENALINE (EPINEPHRINE)
If you could block ACh action in autonomic ganglia, what effect would this have on the heart?
It depends weather you are in rest or in excercise.
At rest and if you block atonomic ganglia it will increases and the polar oposite is true as well
Name two receptors which can recognise acetylcholine
Musacarinic
Nicotinic
What is the Location, stimulus and type of an Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors?
Location: All autonomic ganglia
Stimulus: ACh/ nicotine
Type: Type 1 - Ionotropic- FAST RECEPTOR
The receptors is basically an ion channel linked receptor, when ACh binds to the receptor the channel opens and Na+ moves through the channel.

What is the Location, stimulus and type of an Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors?
Location: At all effector organs innervated by post ganglionic parasympathetic fibres
Stimulus: ACh/ muscarine
Type: G-protein coupled, type 2
Effect is slow

Summary- Whenever Ganglion Nicotinic
Whenever organ which is stimulated by Parasympatheic nerve fibre- Muscarinic

Which of the following effects would be observed after blockade
of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in an individual at rest?
- Bronchoconstriction
- Increased sweat production
- Constipation
- Increased urinary frequency
- Short-sightedness
3
What is the Location, stimulus and type of Adrenoreceptors?
Location: At all effector organs** innervated by post ganglionic sympathetic fibres
Stimulus: Noradrenaline and Adrenaline
Type: G-protein coupled, type 2

Why can the sympathetic NS cause constriction and dilation?
It is due to the different receptors found in differnt tissues.
Alpha 1 receptor causes constriction and is the predonminat receptor in the vasculature. Sympathetic activity tends to lead to constriction- generally sympathetic activity increases TPR
Alpha 1 responds well to noradrenaline.
Beta 2 receptor doesn’t respond well to noradrenaline but well to adrenaline and is the dilating receptor. Beta 2 is very prevalent in skeletal muscle.
What type of receptor is found in the sweat glands?
Name the receptors of the Sympathetic system on the effector organs beside the excemption?
What type of receptor is found in the sweat glands? Muscarinic
Name the receptors of the Sympathetic system on the effector organs beside the excemption? Adrenoreceptors- Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Beta 1 and Beta 2

Heart summary

List the principal steps for the biosynthesis and metabolism of ACh?

List the principal steps for the biosynthesis and metabolism of Noradrenaline?
Noradrenaline isn’t broken down in the synaptic cleft

List the principal steps for the biosynthesis and metabolism of adrenaline?

General

What is the autonomic nervous sytem responsiable for and name the 3 devisions of the autonomic nervous sytem
Responsible for involuntary control of the viscera
Divisions:
◦Sympathetic
◦Parasympathetic
◦Enteric
ANS Layout

Is the parasympathetic sytem and the sympathetic system localised or mass response?
Which does the following ( para or symp)
Conserves body energy
Mobilises body energies for increased activity
Parasympathetic
◦Localised
◦Conserves body energy
Sympathetic
◦Mass responses
◦Mobilises body energies for increased activity
Hypothalamus- centre of autonomic control
Two things that can initiate central control and central response - Higher brain centre- you do have to some extent some conscious control- your memory to previous experience.
Homeostatic Mechanism

Draw the basic pathway for all autonomic pathways?

Where are the ganglia found for the PNS and SNS?

For the sympathetic system where do the pre-ganglionic efferent fibres arise from?
Pre-ganglionic efferent fibres arise from:
◦Thoracic (spinal) nerves
◦Upper Lumbar (spinal) nerves (L1-3)
◦
ØThoracolumbar outflow

Sympathetic
Preganglionic neurons in the …………. ………… …………. …………… of spinal cord T1 to L3
Emerge from the spinal cord via the …………. ………… of the spinal nerve
Pass through ventral ramus to ……………… …………. ………… to ganglion
•Largest division of the ANS
Preganglionic neurons in the lateral column grey matter of spinal cord T1 to L3
Emerge from the spinal cord via the ventral root of the spinal nerve
Pass through ventral ramus to white rami communicantes to ganglion

Lateral colomn grey matter only found in T1 to L3

There are 3 possible routes of sympathetic nerve fibre distribution from one levl of the spinal cord.
UP or down the chain to another spinal nerve
At the same level through the black and green spinal nerve
Or straight through to one of these subsiduary ganglion



Sympathetic fibres pass from the spinal nerves to the sympathetic chain via:
White ramus communicans

Where does the sympathetic trunk start and end?
How many ganglia are in the cervical region?
How many ganglia are in the thoracic region?
How many ganglia are in the lumbar region?
How many Ganglia are in the pelvis ?
Sympathetic Trunks
Base of skull to coccyx
3 ganglia in cervical region
11 or 12 ganglia in thoracic region
4 or 5 ganglia in lumbar region
4 or 5 ganglia in pelvis

Sympathetic
Name the plexuses which emerge from the cervical region?
Cervical
◦Plexus around pharynx
◦Cardiac plexus
◦Thyroid plexus
◦Pulmonary plexus
Parasympathetic
Where do Pre-ganglionic efferent fibres arise from
Parasympathetic
Pre-ganglionic efferent fibres arise from:
◦Cranial nerves (BRAIN STEM)
◦Sacral (spinal) nerves
◦
ØCranio-sacral outflow

Parasympathetic
Sacral outflow
◦Anterior rami of S2-4
◦Visceral branches passing directly to pelvic viscera i.e. pelvic splanchnic nerves
◦Minute ganglia in wall of viscera giving rise to postganglionic fibres

Pelvic splanchnic nerves
Motor fibres to ……………
Motor fibres to …………….. ………….
Inhibitory fibres to ………… ………………
Erection of ………./………… via vasodilator fibres
Fibres also pass …………… to supply large part of the gut with visceromotor innervation
Motor fibres to rectum
Motor fibres to bladder wall
Inhibitory fibres to bladder sphincter- cause it to open
Erection of penis/clitoris via vasodilator fibres
Fibres also pass superiorly to supply large part of the gut with visceromotor innervation

Where does the Oculomotor nerve (CN III) provide postganglionic fibres to?
What is its name of its ganglion?
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
◦ciliary ganglion
◦postganglionic fibres to sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscle inside eye

What are the names of the two ganglion for the Focial nerve (CN VII)?
State where each ganglion provides postganglionic fibres to?
Facial nerve (CN VII)
◦Submandibular ganglion
◦postganglionic fibres to submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
◦Pterygopalatine ganglion
◦postganglionic fibres to paranasal sinuses and lacrimal glands

What is the name of the ganglion associated with the Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)?
Where do the postganglionic fibres from the ganglion go to?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
◦Otic ganglion
◦postganglionic fibres to parotid gland

Vagus nerve (CN X)
enters neck and thorax via …………… ………….
Name 5 places it branches to?

Vagus nerve (CN X)
◦enters neck and thorax via carotid sheath
◦branches to lungs, heart, oesophagus, stomach, intestines

Enteric System
In walls of alimentary tract
Sensory – monitoring mechanical, chemical and hormonal activity of gut
Motor – gut motility, secretion, vessel tone
Can be overridden by sympathetic and parasympathetic systems



