Central Nervous System (CNS) Flashcards

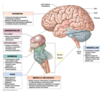
The brain is like an onion

Reptile- basic instincs- stay alive- the autonomic responses of the brain stem
Mammal- limbic systeminclude the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate gyrus. The amygdala is the emotion center of the brain, while the hippocampus plays an essential role in the formation of new memories about past experiences.
Gorrila- higher cognitive functions
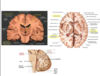
Lable the diagram below


What is the part of the brain highlighted below and what does it do?

corpus callosum
The bendy bit of white matter in the middle is the corpus callosum (consists mainly of axons)
The corpus callosum interconnects corresponding areas of the two hemispheres so there is constant conversation between the two hemispheres
What is the part of the brain highlighted below called?
What does this part of the brain consist of

Diencephalon
The area under the corpus callosum which looks a bit like an anteater is the DIENCEPHALON (consists of the thalamus and the hypothalamus)


Lable the diagram below and state what the brain stem is made up of?

medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain

Diencephalon is strongly attached to both hemispheres (it is sandwiched between the two hemispheres)
Just below the diencephalon you get the ……………….
The ………… is inferior to the midbrain and is recognisable because it has a characteristic bulge anteriorly
Attached to the bottom of the pons is the …………….. which merges with the top of the spinal cord as it goes through the hole in the base of the skull
Diencephalon is strongly attached to both hemispheres (it is sandwiched between the two hemispheres)
Just below the diencephalon you get the midbrain
The pons is inferior to the midbrain and is recognisable because it has a characteristic bulge anteriorly
Attached to the bottom of the pons is the medulla which merges with the top of the spinal cord as it goes through the hole in the base of the skull



The brain first develops into three main parts:
…………………
…………………
…………………
The cerebral hemispheres and the diencephalon develop from the …………………
The pons, medulla and cerebellum develop from the …………………
The midbrain stays more or less the same
The brain first develops into three main parts:
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
The cerebral hemispheres and the diencephalon develop from the forebrain
The pons, medulla and cerebellum develop from the hindbrain
The midbrain stays more or less the same
In the other diagram in the other question the diencephalon is over the midbrain. That is why it highlights the diencephelon when it should be the midbrain?
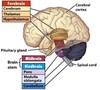
How many pair of spinal nerves do we have?
How many pairs of cervical nerves do we have?
How many pairs of Thoracic nerves do we have?
How many pairs of lumbar nerves do we have?
How many pairs of sacrococcygeal nerves do we have?

How many pairs of cervical nerves do we have?
8
C1–C8

How many pairs of thoracic nerves do we have?
12
T1-T12

How many pairs of lumbar nerves do we have?
5 Lumbar nerves
L1-L5

How many pairs of sacrococcygeal nerves do we have?
6
S1 -S5
Coccygeal nerve

Spinal cord lies in the ………………. …………. in the vertebral column
Along the sides of the vertebral column you have a series of holes called …………………………. ………………
Each of these ……………… have spinal nerves coming out of them
Spinal cord lies in the vertebral canal in the vertebral column
Along the sides of the vertebral column you have a series of holes called INTERVERTEBRAL FORAMINA
Each of these foramina have spinal nerves coming out of them

How many Vertebrae are there in the spine?
How many Cervical vertebrae are there?
How many Thoracic vertebrae are there?
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
How many saccrum vertebrae are there?
How many coccyx vertebrae are there?
The vertebral column usually consists of 33 vertebrae:
24 presacral vertebrae (7 cervical, 12 thoracic, and 5 lumbar)
sacrum (5 fused sacral vertebrae)
coccyx (4 frequently fused coccygeal vertebrae).

Why do we have 33 vertebrae and 31 pairs of spinal nerves?
There are equal numbers of nerves and vertebra EXCEPT there is an extra nerve above C1 so there are 8 cervical nerves
There is a coccygeal nerve which isn’t represented by an S6

There are equal numbers of nerves and vertebra EXCEPT there is an extra nerve above C1 so there are 8 cervical nerves
LOOK AT THE NOTE PART OF THE IMAGE

THE SPINAL CORD IS MUCH SHORTER THAN THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN
This is because the spinal cord finishes growing earlier in development and the vertebral column keeps growing
Cervical and thoracic segments of the spinal cord is more or less corresponding with the vertebral column levels

The lumbar and sacral spinal segments are considerably above the vertebrae where the spinal nerves have to come out
This area where there is no spinal cord is called the ……………. …………..
The lumbar cistern contains ……………. ………….. and a needle can be inserted between two lumbar vertebrae to obtain ……………. …………..
This bit where there is no spinal cord but a flurry of nerves is also called the ……………. …………..
The lumbar and sacral spinal segments are considerably above the vertebrae where the spinal nerves have to come out
This area where there is no spinal cord is called the LUMBAR CISTERN
The lumbar cistern contains cerebrospinal fluid and a needle can be inserted between two lumbar vertebrae to obtain cerebrospinal fluid
This bit where there is no spinal cord but a flurry of nerves is also called the Cauda Equina

What is the cauda equina?
This bit where there is no spinal cord but a flurry of nerves is also called the Cauda Equina
The cauda equina (from Latin horse’s tail) is a bundle of spinal nerves and spinal nerve rootlets, consisting of the second through fifth lumbar nerve pairs, the first through fifth sacral nerve pairs, and the coccygeal nerve, all of which arise from the lumbar enlargement and the conus medullaris of the spinal cord.

What is the lumbar cistern?
This area where there is no spinal cord is called the LUMBAR CISTERN
The lumbar cistern contains cerebrospinal fluid and a needle can be inserted between two lumbar vertebrae to obtain CSF
This bit where there is no spinal cord but a flurry of nerves is also called the Cauda Equina

At what levels of the spine are lumbar punctures done?
The spinal cord usually ends at the inferior border of L1 or the superior border of L2. Therefore, inserting the needle between L3 and L4 or L4 and L5 is relatively safe. This level corresponds to the lumbar cistern.



Why is there no ventral root ganglion?
The DRG is a collection of cell bodies for afferent nerve fibers (mostly sensory) that exists just outside of the spinal cord. There’s no ventral root ganglion because the motor efferent fibers have their cell bodies in the ventral horns (anterior portion of the grey matter) of the spinal cord.

The core consists of ……………. …………… which mainly contains neuronal ……….. …………….
There is a wrapping around of the white matter containing …………..
The grey matter is divided into ……………. and …………… areas
Dorsal horns of the grey matter are ……………… - they have cells which receive sensory information via spinal nerves
The cell bodies of the sensory axons is in the …………… ………… …………..
The axon then continues via the ………….. ………… and enters the dorsal horn
The sensory information is then carried up ascending pathways in the white matter to the brain for analysis
The ventral part of the grey matter consists of ……….. …………….
Axons of the motor neurons go out via the ……………. …………… and to the muscles
Dorsal - …………… the CNS
Ventral - ……….. from the CNS
Spinal Nerve - ………………..
The core consists of GREY MATTER which mainly contains neuronal cell bodies
There is a wrapping around of the white matter containing axons
The grey matter is divided into sensory and motor areas
Dorsal horns of the grey matter are SENSORY - they have cells which receive sensory information via spinal nerves
The cell bodies of the sensory axons is in the dorsal root ganglion
The axon then continues via the dorsal root and enters the dorsal horn
The sensory information is then carried up ascending pathways in the white matter to the brain for analysis
The ventral part of the grey matter consists of motor neurons
Axons of the motor neurons go out via the ventral roots and to the muscles
Dorsal - TOWARDS the CNS
Ventral - AWAY from the CNS
Spinal Nerve - BOTH DIRECTIONS

List 4 functions of the spinal cord?

The brain is composed of three parts: the brainstem, cerebellum, and cerebrum.
Another classsification system
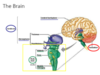
State the functions of the Brain stem?
Midbrain includes the ……………… …………….. which degenerates in Parkinson’s Disease
- Responsible for the control of many vital functions such as: breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, swallowing, balance etc.
- Responsible for defensive reflexes (cough, gag, sneeze…)
- Involved in sleep-wake cycles, alertness and consciousness
Midbrain includes the substantia nigra which degenerates in Parkinson’s Disease



What are the functions of the hypothalamus?
•Hypothalamus: integration hub. Regulates temperature, hunger, thirst, hormone (connected with pituitary) and autonomic function
Hypothalamus - found inferior to the thalamus and is important in coordinating homeostasis
Hypothalamus functions: (Hypothalamus wears TAN HATS)
- Thirst and water balance (supraoptic nucleus)
- Adenohypophysis control via releasing factors
- Neurohypophysis releases hormones synthesized in the hypothalamic nuclei
- Hunger (lateral nucleus) and satiety (central nucleus)
- Autonomic regulation (ant hypothalamus regulates parasympathetic activity), circadian rhythms (suprachiasmatic nucleus).
- Temperature regulation (post hypothalamus regulates heat conservation and production when cold; ant hypothalamus regulated cooling when hot) **Remember A/C = Ant = cooling.
- Sexual urges and emotions (septate nucleus)

State the functions of the thalamus?
Thalamus: integration centre for somatic and special senses information and projection to cortex. Involved in emotional status, consciousness, appropriate motor response.
Thalamus - higher area of the diencephalon - this is a relay station for information going between the cerebral cortex and other parts of the CNS in both directions



What is the corpus striatum made up of?
Caudate + Putamen = Corpus Striatum - connected to cortex, thalamus, nigra

What is the lentiform nucleus made out of?
•Putamen + Globus Pallidus = Lentiform nucleus

Corpus Striatum

Lentiform Nucleus



Basal ganglia Function?
Function:
•Control of movement:
facilitating voluntary movement, inhibiting unwanted or inappropriate movements, “fine tuning”
Cerebral Cortex Lobes




Study the image
There are TWO types of cortex in the hemisphere:
Name these
There are TWO types of cortex in the hemisphere:

Primary Cortical Areas
Association Cortex
What is wernickes area important for?
Wernicke’s Area = important for understanding language

What is brocas area important for?
Broca’s Area = important for speech

What happens in the association cortex?
The rest of the areas that are NOT primary cortex are ASSOCIATION CORTEX
Association cortex is where much of the higher functions take place e.g. learning, perception, thinking etc.
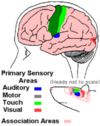
Primary Auditory Cortex = first to receive information from the ears
Primary Visual Cortex = first to receive information from the retina

Primary Motor Cortex - the cells of this cortex send axons down through the descending pathway to stimulate motor neurons in the spinal cord - the spinal motor neurons then stimulate the muscle via the peripheral nervous system
The primary motor cortex has a SOMATOTOPIC arrangement
Somatotopic = arranged like a body map - area at the bottom controls movement of the head, middle is movement of the arms and top is movement of the legs - It’s like a little man standing upside down
So depending on where the damage is to the primary motor cortex you’d expect to have loss of voluntary movement in a particular place
Remember, the cerebral hemisphere relates to the contralateral side of the body (opposite side to the side of the brain affected)


The Cortex

What happens if you have a lesion in the somesthetic association area?
You will be able to describe an object and feel it but not recognise it- this is if the patient hasn’t seen the object

What happens if you have a lesion in the visual association area?
You will be able to see it decribe it and draw it but not tell what it is?

What areas of the brain are only found in the dominant side?
Broca area
Wernickle area

What are the primary structures within the limbic system?
What is the function of the limbic system?
The primary structures within the limbic system include the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate gyrus.
The amygdala is the emotion center of the brain, while the hippocampus plays an essential role in the formation of new memories about past experiences.
motivation,
instinctive behaviour,
emotion,
memory



FORAMEN=HOLE




What are the 3 layers of meninges?
dura mater,
arachnoid mater
pia mater





There are two large C shaped ventricles with a spur at the back
These are the …………… …………….
There is a lateral ventricle in each hemisphere
The two lateral ventricles, via a tiny foramen, join up with a single midline ventricle called the ….. …………….
The 3rd ventricle lies in the middle of the ……………
At the base of the third ventricle there is narrowing to form a fine channel called the …………… …………….
The aqueduct passes through the midbrain and at the top of the midbrain it opens up again into a tent shaped …………… …………….
The pons and medulla is in front of the …………… ……………. and the cerebellum is behind it
At the lower part of the medulla the fourth ventricle narrows again to form a very fine channel called the …………… ……………. which goes down into the spinal cord

There are two large C shaped ventricles with a spur at the back
These are the LATERAL VENTRICLES
There is a lateral ventricle in each hemisphere
The two lateral ventricles, via a tiny foramen, join up with a single midline ventricle called the 3rd VENTRICLE
The 3rd ventricle lies in the middle of the diencephalon
At the base of the third ventricle there is narrowing to form a fine channel called the CEREBRAL AQUEDUCT
The aqueduct passes through the midbrain and at the top of the midbrain it opens up again into a tent shaped 4th VENTRICLE
The pons and medulla is in front of the fourth ventricle and the cerebellum is behind it
At the lower part of the medulla the fourth ventricle narrows again to form a very fine channel called the CENTRAL CANAL which goes down into the spinal cord
View of the ventricles in a mid-sagitally sectioned image of the brain:
What prroduces cerebrospinal fluid?
choroid plexus

What are the composition differences between CSF and blood?

What is the function of CSF?

CSF flow

Do the tutorial and also look at MM slides for hydrocephalus
One with the MRI scan


