Physical development in adolescence Flashcards
what is the tanner stages of puberty in male genialias
stage- 1 prepubertal- testes less than 2.5cm
stage 2- scrotum and testes en;arge and reddending scortal skin
stage3- continual growth of penis and testes
Stage 4- development of the glans, continued growth and scrotal skin darkeneding
stage- post pubrtal

Describe feamle breast development- tanner stages
stage 1- prepubertal- elevation of pilla only
stage 2- areola enlarged and breats bud appears
stage 3- breast tissues grows beyond areola but without contour seperation
stage 4- projection of areola and papilla forms secondayr mound
stage 5- post puberty- adult breast contours with rprojection of papilla only
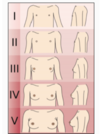
in male and females what hair will be present on the body in stage 1 and how does hare develop
villus hair only
- males–> base of penis—> thicker hair mons pubis—-> continues to psread–> medial thigh
- Females—> alongside labia—> hair coarser, pigmented- spreads acorss pubis—> spreads—–> medial thigh (not up tp linea alba)
stage 5 in both—-> spread to medial thigh

when do growht spurts begin in boys and girls
- 5 girls
- 5 boys- begin later but grow more
2 peaks- another 2 years later 12F , 14 M
max height- gilrs 17 years
21 years in boys
growht plates (epiphys fuse later in boys)

at what age do the following happen in girls
breats bud (thelarch)
pubic and axillary hair development (adrenarche)
growth spurts
menarch
breast bud- 10.5-11
pub and axillary hair (drive by adrenal androgrens form adrneal glands- 11 years
growth spurt- 11.5yrs
menarch- 13 years
ache too
when do the following begin to occur in males?
- increase in testicle volume
- pubic and axcillary hair development
- growht spurt
- spermarch
- adult penis and texitualr size
- adult bubic hair?
- increase in testicular volume- 11.5 yrs- penile and scortal enlargement occur a year after tesricualr enlargment
- pubic and axillary hair development- 12 yrs
- growht sput 12.5
- spermarch- first appearacne of psermatozoa in early uirne- nocutrnal emision begin
- adult penis and testicular size by 15yr
- adult pubic hair - ealry 20s
change in body compositon,acne, deeping of the voice, gynaecomastia
what is the hormonal basis of growhtspurts in males and femalses
- gonadal sex steriods (oestradial and testerone)
- growth hormone GH (due to increase in sex hormones- positive effect on pulsatile relase of GH from pituitary gland)
- insulin like growth hormone (IGF-1)- caused by increase in HG- causes omatic growht by meabolic actions
- in maels larynx and vocal cords enlarge
about a year before puberty we see a rise in FSH and LH in males and females form P.Pituitary
before this in childhood they are low- due to slow cycling of GnRH puls egenatori in hypothalmus
why does this lead to?
rise in FSH- females increase in oestrogen syntheiss and oogenesis- in males- onset of sperm production
Rise in LH- females- production of progesterone, in males increase in testosteron rpoduction
as a result of these hormonal changes get physical chnages associated with puberty
Describe the break theory of
- brake released for puberty to begin
- tiemd disinhibiaiton of inhbitory mechanims
- pre-pubertal low levels of steriod inhibit GnRH release
- this low sensitivtiy is lost and higher levels of steriod now needed to inhbit GnRH
- levels of FSH and LH rise= higher levels of steriod but not enough to negatively feed back
evidence agsisnt the brake theory
turner sysndrome- under developed ovaires (only has 1 X chromosome)
FSH/LH increase at puberty in absence of the gonadal steriods
Describe the accelerator hypothesis
- currentyl accepted hypotheiis
- central maturation of CNS- activation of stimulatory centres in CNS
- induce pulsatile relase of GnRH at puberty
- requires only changes in GnRH neurosectory neurones
what is the evidence for the accelatory hypotheiss
kallmans syndrome (delayed/absent puberty)
precoious puberty with CNS pituitary tumours
castrated male monkeys still go throuhg puberty
what is the function of Kisspeptin neurones?
inducer of pulstatile release of gnRH in the hypothtalsmus
increass Kiss1 level at puberty
induced precocouiosu puberty in monkesy.
what factors affect menarche age
- genetics (link with maternal age and hormones causing KISS1
- metabolisma nd nutriton
- gneeral health and well being
- envuronmentfla factors
- history-
- faily history
- underweight= delayed pibertyu
- medical/surgical history/ meeication
decrease in average age of menarch in last cewntruy probably due to improved nutriton and general health
describe the link between age at menarch and BMI?
onset of puberty has become eaerly due to rise in obesity- rearch ongoing
however, attianment of Criticial weighjt of 47kg must be activation of HPG axis

describe the relationship between menarch age and weight
evidence?
a criticla body fat and body weight are required for intiation of menarhce
this is supported by
- competitive athletes- dleayed puberty
- delayed menarch in malnutriton
- overweight girls have ealry menachred
- patients with anorexia nervosa have delayed menarhc/primary/secodnary amenorrhea.
describe the link between weighgt and puberty onset
pubity will not occur unless the boyd has enough reserves fot these high cost functuon
energy used must be less than energy taken in.stored- Psoitive enrgy balance
how would be describe delayed puberty in males and females
- males
- absence of testicualr development (vesticualr volume lwoer than 4m,l) by age 14
- in girls
- absence of breats developemnt by age 13 or primary ammenorrhea with normal breast development by age 15


