PHD - Human Herpesviruses (Kasman) Flashcards
A 28-year-old letter carrier presents with painful recurring vesicular eruption on the lip. Which of the following would you expect to see in a smear from the base of a vesicle? Select all that apply.
A. Cowdrey Bodies
B. Downey Cells
C. Heterophile antibodies
D. Owl’s eye cells
E. Tzank Cells
Cowdrey bodies and Tzank Cells (A and E)
Patient presentation indicates that he has HHV-1 because of the recurring vesicular “cold sore” on the lip.
Downey cells are manifestations of CMV and EBV
Heterophile antibodies indicate primary infection with EBV (mononucleosis)
Owl’s eye cells are indicative of CMV (Remember, you “C” with your eyes)
A 16-year-old high school student has been ill with fever, fatigue, pharyngitis, and swollen cervical lymph nodes. Physical examination reveals an enlarged spleen. A blood sample is obtained. Which of the following would you expect to see in a CBC with differential analysis of peripheral leukocytes?
A. High eosinophil count
B. High monocyte count
C. High lymphocyte count
D. High neutrophil count with bands
E. Multinucleated giant cells
C. High lymphocyte count
This question stem is describing EBV with infectious mononucleosis. Remember that this causes a proliferation of B-cells and CD8+ T-cells in the lymph nodes, leading to enlarged nodes.
A 16-year-old high school student has been ill with fever, fatigue, pharyngitis and swollen cervical lymph nodes for 2 weeks. Physical examination reveals an enlarged spleen. A heterophile antibody test is positive. What is another disease caused by this virus?
A. Burkitt Lymphoma
B. Herpes encephalitis
C. Herpetic whitlow
D. Multicentric Castleman’s Disease
E. Viral retinitis
A. Burkitt Lymphoma
EBV is a gamma-herpesvirus, meaning that it can lead to formation of tumors, in particular Burkitt Lymphoma.
B and C are incorrect because these are caused by HHV-1 and 2 (alpha-herpesviruses)
D is caused by HHV-8 (Kaposi)
E is caused by CMV
A 53-year-old lawyer is recovering from a kidney transplant 2 months prior when she develops viral pneumonia, fever, and signs of graft failure. Diagnostic tests are positive for herpesvirus. Which of the following is the most likely type of herpesvirus?
A. CMV
B. EBV
C. HHV-6 (Roseola)
D. HSV-1
E. KHSV (HHV-8)
A. CMV
Beta-herpesviruses (CMV, HHV-6 and 7) are typically associated with development of infections in immune compromised patients.
EBV is associated with Burkitt Lymphoma
C would be correct if the patient were between ages 4 and 6 (almost exclusively in kids)
D is associated with Herpes simplex encephalitis
E is associated with Kaposi Sarcoma
What herpesvirus induces the formation of Multicentric Castleman’s disease?
HHV-8
What is the enzyme that activates acyclovir from its prodrug to drug form?
Thymidine kinase
Roseola infantum is a condition caused by what herpesvirus?
HHV-6 and HHV-7
HHV-6 and HHV-7 primarily infect what cell type?
T-cells
What is the Tzanck smear used to diagnose?
HHV-1, 2, and 3

Which herpes virus can affect both, T and B lymphocytes?
Cytomegalovirus (HHV-4)
CMV starts by infecting epithelial cells, but then moves into the B-cells to replicate.
CD8+ T-cells become involved with infectious mononucleosis
IgM against early antigens (EA) or viral capsid antigen (VCA) is indicative of what?
Primary EBV infection
IgM against EBV-nuclear antigens (EBNA) also indicates EBV infection
CMV has what characteristic histological appearence?
Owl’s eyes nuclear inclusions
Remember: you “C” with your eyes, so CMV is indicated by owl’s eyes
Owl’s eyes are inclusion bodies surrounded by a halo in CMV infected cells.
What drugs are oftentimes prodrugs which need to be metabolically activated through phosphrylation to prevent viral DNA polymerase activation and promotes chain termination?
Cyclovir drugs
(Acyclovir, valacyclovir, gancyclovir, valagancyclovir)
These drugs have a preference for being activated in virally infected cells. The enzyme thymidine kinase expressed in virally-infected cells converts cyclovir drugs to the active form.
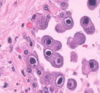
The histological sample below is indicavtive of what infection?
CMV
The histological slide shows Owl’s eye inclusions, which are indicative of CMV-infected cells.
What drug can be used to treat herpes encephalitis?
Acyclovir
Herpes encephalitis is a consequence of HHV-1 infection that causes unilateral lytic lesions of the temporoparietal brain
What age is primarily affected by HHV6 and HHV7?
6 months to 4 years old
Roseola infection is almost exclusively limited to this age range.
In what age group is HSV1 and 2 fatal?
Neonates
What is this condition and which pathogen causes it?
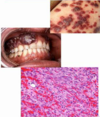
Kaposi Sarcoma caused by EBV
EBV is one of the gamma-herpesviruses. These viruses are tumorigenic. EBV infection is associated with development of Kaposi Sarcoma, which is characterized by dark lesions caused by infiltration of tissue with blood.
Which herpesvirus induces retinits, and has mononucleosis-like symptoms?
CMV
Treat with gancyclovir
Which herpes virus almost always features symptoms?
Varicella-Zoster (HHV-3)
HHV-3 is the only herpesvirus that almost always features symptoms. The other herpesviruses tend to remain asymptomatic and rarely cause any sumptoms.
Explain how guanine analogs have low-toxicity and are specific to infected cells.
Guanine analogs are pro-drugs, so they don’t readily affect cells, making them less toxic.
These drugs require activation via the enzyme thymidine kinase. Virally-infected cells tend to have high levels of this enzyme, which makes these drugs more likely to work in infected cells.
What is herpes keratitis?
Herpes infection of the eye.
Typically seen in HHV-1 and 2
A 20 month old child presents with a high fever and seizures. 4 days later the fever breaks, and he develops a pink macular rash. What condition is this? And what test should be requested to confirm the diagnosis?
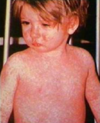
Roseola infantum (HHV-6 and 7)
Diagnosis of roseola is done by seroconversion. This is possible becasue this infection is lifelong and will always be present regardless of whether or not symptoms occur.
Typical Roseola patient: young child who started with fever that progressed to pink skin rash
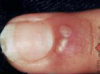
What is herpetic whitlow?
Herpes vesicle of the cuticle
This is a common finding in dental workers and is caused by HHV-1 and 2.
True or false: Neonates can only be affected by the mother’s herpes virus infection during the primary infection.
True
Herpesviruses tend to remain latent (secondary), but can go through a period of shedding (primary) in which the virus is easily transferred between people.
Women who are giving birth who have herpesvirus should deliver baby via C-section. Fetus is not harmed by the virus in the womb because of the mother’s antibodies to HHV.
What is the number 1 cause of deafness?
CMV
Congenital CMV infections can lead to birth defects, often involving the eyes and ears.
What are the drugs used to treat ALPHA herpesviruses?
Cyclovir drugs
(Acyclovir, valacyclovir, gancyclovir, valagancyclovir)
What is shingles?
Shingles is a reactivation of Varicalla-Zoster (HHV-3) in patients over the age of 50 that follows a dermatomal pattern and does not cross the midline.
HHV-3 resides in the nerves and remains dormant for many years. It can be reactivated in periods of increased stress and immunosuppression.

True or false: HSV1 and 2 infections are typically asymptomatic.
True
Herpes-simplex virus (HHV-1 and 2) are typically asymptomatic
What are the three viruses that induced oral cancer?
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
- Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8/Kaposi Sarcoma virus)
True or false: there is no effective treatment for GAMMA herpesvirus.
True
Gamma herpesviruses are not treatable with traditional cyclovir drugs.
Where in the herpesvirus is the tegument located?
Between the capsid and the envelope
Tegument contains proteins that aid in viral DNA replication and evasion of host immune system.
Which HHVs infect strictly B-cells?
Gamma herpesviruses - EBV and KSHV (HHV-8)
What is oral hairy leukoplakia and which type of herpesvirus typically causes it?
Oral hairy leukoplakia are white, non-painful plaques on the sides and bottom of the tongue.
These plaques are common in immunosuppressed patients, but are also a characteristic sign of Epstein-Barr Virus (HHV-5)

What is the mechanism of action of acyclovir and gancyclovir?
Both drugs are purine analogs that lead to chain termination and inhibition of DNA polymerase enzymes.
Remember that these are simply pro-drugs, and must be converted into their active forms via viral thymidine kinase to produce an effect.
True or false: HSV1 and HSV2 are antigenically identical
False
Herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 present similarly, but they are antigenically distinct from one another.
What is the condition that manifests as a rash which is on a dermatome and stops immediately at the midline?
Shingles
Shingles is the reactivated form of previously dormant Varicella-Zoster (HHV-3) virus that was present in nerve cells. Because the virus resides in nerves, it affects the patient along a dermatomal pattern and does not cross midline of the body.
Which group of herpesviruses present with skin lesions?
Alpha herpesviruses
Including: herpes simplex 1 and 2 (HSV-1/2) and varicella-zoster (HHV-3)
An otherwise healthy baby, with a normal physical exam at birth, is found to have profound hearing loss at 9 months of age. Which of the following congenital infections could account for this pattern of symptoms?
A. CMV
B. HSV-2
C. HHV-6
D. HHV-8
E. VZV
A. CMV
Cytomegalovirus is associated with the development of birth defects, deafness, and retinitis.
HSV-2 is characteristic of genital lesions
HHV-6 would present as fever that progressed to total body rash
HHV-8 would present as dark sores of the mouth and skin
VZV would present with macular lesions of the skin (chickenpox)
Which form of herpes appear in “crops?”
Varicella-Zoster (HHV-3) virus
What are three mechanisms by which herpesvirus can induce host cell death?
- Viral replication shuts down host cell metabolism by using up host cell enzymes
- Accumulation of unused viral proteins
- Virus causes cell lysis to release viral particles to infect other cells
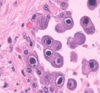
What type of cell is evidenced by the histological slide below and what type of viral infection typically causes this?

Downey Cell
Downey cells are CD8+ T cells that have been infected with either CMV or EBV
Classical features of downey cell: elongated nucleus, lots of cytoplasm, sometimes granules seen
In what stage of viral growth is the herpesvirus in, if its genome can be detected, but there are no infectious viruses that can be recovered?
Latent Phase
Herpes enchephalitis is due to infection of which specific nerve?
Trigeminal nerve root ganglion infection with HHV-1
Which of the following herpesviruses is neurotropic?
A. CMV
B. EBV
C. HHV-6
D. KHSV
E. VZV
D. VZV
Remember that alpha herpesviruses are neutotropic, so HHV-1, 2, and 3 would all be correct answers if given.
What is the correlation between symptom development and age, in the Epstein-Barr virus?
Symptoms are typically rare in infancy, but increase with age.
Generally anyone over 10 will have a more severe symptomatic stage
Which herpesviruses are considered to be in the beta category?
CMV, HHV-6 and 7 (Roseola)
Beta herpesviruses are very common in immunosuppressed patients and tend to produce flu-like symptoms
Latency of CMV occurs in what cells?
Monocytes, neutrophils, and endothelial cells
Herpes meningitis occurs due to infection by what virus?
HHV-2 (Herpes simplex 2)
What tests can be performed to determine if a patient is infected with CMV?
PCR of blood/fluids, nuclear and perinuclear involusions of cell enlargement
What is the causative agent of mononucleosis?
Epstein-Barr virus
Which viruses are gamma herpesviruses and what is their defining characteristic?
EBV and KSHV (HHV-8/Kaposi)
Gamma herpesviruses are tumorigenic, and are associated with Burkitt Lymphoma (EBV) and Kaposi Sarcoma (HHV-8)
What does the Monospot test measure?
Heterophile antibodies
Patient serum mixed with sheep, horse, and rabbit RBCs to see if agglutination occurs
Heterophile antibodies spontaneously produced during EBV infection
Polyclonal B-lymphocyte proliferation is induced by which herpesvirus?
Epstein Barr Virus (HHV-4)
Remember that EBV is a tumorigenic gamma herpesvirus that infects B-cells. Proliferation of B-cells leads to Burkitt lymphoma.
Latency of HHV-6 occurs in what cells? What about HHV-7?
HHV-6 resides in T-cells, macrophages, and monocytes
HHV-7 resides in T-cells
What are the 2 primary protective mechanisms against herpesvirus?
- Interferon alpha - innate immune response to viral infection
- T- and B-cells - adaptive immunity
- This is evidenced by the fact that immunocompromised patients have more herpesvirus infections that are more severe
The condition mononucleosis is due to which cell type?
T-cell
EBV, the virus that causes mono, infects epithelial and B-cells, causing polyclonal proliferation. However, the disease process of mono is caused by overactivation of CD8+ T-cells
Given that a patient is exposed to Simian Herpes B, what condition will likely manifest?
Ascending encephalomyelitis
Leads to death or severe mental impairment
Where does replication of herpesvirus take place and what cytological feature do they induce because of this?
Herpesviruses replicate in the nucleus
Replication here leads to the presence of nuclear inclusion bodies
Which herpes virus is transmitted through respiratory droplets?
Varicella-Zoster (HHV-3)
HHV-3 is the only herpesvirus that is spread through respiratory droplets. Most others require some form of direct contact.
What cell type does this histological sample indicate, and which virus would cause it?

Cowdry Body
This is typical in HHV-1, 2, 3, and 5
Droplet-like masses of acidophilic material surrounded by clear halos within the nuclei
True or false: CMV cannot be transmitted through breast milk.
False
Antigens, EBNA, VCA and EA are found in what virus?
EBV
EBNA = EBV nuclear antigen
VCA = viral capsid antigen
EA = early antigen


