Pharmacology of Depression Flashcards
Sertraline Citalopram Fluoxetine Venlafaxine Mirtazapine
What is sertraline used for?
- Sertraline is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) indicated to treat major depressive disorder, social anxiety disorder and many other psychiatric conditions
What is the primary drug target of sertraline?
- Na+ dependent serotonin transporter
What is the drug target type of sertraline?
- Transport protein antagonist
What is the location of action of sertraline?
- Presynaptic neurones of the CNS
What is the mechanism of action of sertraline?
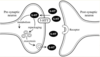
- Sertaline binds on the serotonin transporters on the presynaptic neurones of the CNS
- Inhibits the reabsorption of serotonin (5-HT)
- Accumulation of serotonin in the synapse
- Serotonin is the central nervous system plays a role in the regulation of mood, personality, and wakefulness
What are the main adverse effects of sertraline (4)?
- GI function (nausea / diarrhoea)
- Sexual dysfunction
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
What is the effect of sertraline on the other neurotransmitters (not serotonin)?
-
Dopamine:
- Mild inhibition of Na+ dependent dopamine transporter
-
Noradrenaline:
- Mild inhibition of Na+ dependent noradrenaline transporter → increase of noradrenaline in the synapse → May decrease SNS response activation → Increase heart tone
-
CYP2D6:
- Partial inhibition of CYP2D6 (encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes) at high doses
What is citalopram used for?
- Citalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) used in the treatment of depression
What is the primary drug target of citalopram?
- Na+ dependent serotonin transporter
What is the drug target type of citalopram?
- Tranport protein antagonist
What is the location of action of citalopram?
- Presynaptic neurones of the CNS
What are the main adverse effects of citalopram (4)?
- GI function (nausea / diarrhoea)
- Sexual dysfunction
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
What is the mechanism of action of citalopram?
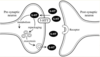
- Citalopram binds on the serotonin transporters on the presynaptic neurones of the CNS
- Inhibits the reabsorption of serotonin (5-HT)
- Accumulation of serotonin in the synapse
- Serotonin is the central nervous system plays a role in the regulation of mood, personality, and wakefulness

What is the effect of citalopram on the other receptors?
-
H1 receptors:
- Mild inhibition of muscarinic and histamine (H1) receptors → inhibiting the vasodilator effects of histamine → sedative
What is fluoxetine used for?
- Fluoxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor used to treat major depressive disorder, bulimia, OCD, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, panic disorder, and bipolar I