Perineum II Flashcards
(28 cards)
Identify the indicated portion of the Vulva


Identify the indicated features of the vulva

-
labia minora
- devoid of hair/fat
- fibrous tissue covered with mucosa
- confluence posteriorly: frenulum of the labia
- confluence anteriorly bifucation
- lateral fold: comes together midline anterior to the clitoris & forms the prepuce/foreskin of the clitoris
- medial fold: combines posterior to the clitoris & forms the frenulum of the clitoris
-
Vestibule of the vagina
- inbetween the labia minora
- entryway to the vagina
- opening of the urethra & glandular ducts

Identify the indicated features of the provided image

-
Crura of the clitoris
- attaches to ischiopubic ramus
- come together to form a body
- the body ends at the glans clitoris
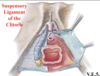
What is the function of the suspensory ligament of the clitoris?
- Clitoris is held to the pubic symphysis by the suspensory ligament of the clitoris
What structure is depicted by the provided images?
It is continuous with what structures?

Hymen
Fold of mucous membrane continuous with the labia minora & continuous with the interior of the vaginal canal
Rare that it is ever 100% closed
Hymeneal caruncles: apendiges that hang off where the hymen was

Identify the indicated features of the provided image
What penile features are the analagous to?

-
Vestibular bulb – analagous to the corpus spongiosum
- anchored to perineal membrane
- it connect at midline at the commisure
- posterior & deep to the bulb is the greater vestibular glands
- similar to bulbourethral glands for lubrication of the vestibule
- directly lateral to vaginal orifice

What problem can occur at the greater vestibular glands?
How will it present?
What is it called if it is infected?
Bartholin’s cysts
Will often present more in the labia minora
once it is infected it is called an abscyss

What are Skene’s glands?
Paraurethral (Skene’s) glands
open into the urethra & cause mucous secretions
open just adjacent to the external urethral opening in the vestibule

Identify the muscles shown in the provided image & indicated their attachments and functions

- Superficial Perineal Muscles (cover erectile tissue)
-
bulbospongiosus
- split at midline
- over vestibular bulb
- arrachment:
- perineal membrane & perineal body
- envelop a portin of the body of the clitoris
- function: squeeze down on the vestibular bulb causing blood to move forward into the commisure and push the clitoris out
-
ischiocavernosus
- covers crura of the clitoris
- attachment
- ischiopubic rami
- Function: pushes blood into the body & glans of the clitoris causing it to protrude
-
Superficial transverse perineal
- from ischial tuberosities to the perineal body
-
bulbospongiosus

Name the fascial layers of the female genetalia
- skin
- fatty superficial layer
- deep membranous layer IS the superficial perineal fascia
- formerly the boundary of the superficial perineal space
- continuous with Colles fascia &
- superficial perineal space
- perineal membrane
- deep perineal space

Why is it possible that an infection of the scrotum could migrate to the abdomen?
The fascia is continuous, allowing infection spread
- Scarpa’s (abdomen)
- Dartos (scrotum & penis)
- Colles’ (perineum)
- Fascia lata (thigh)
What structure is depicted in Green?
attachments?
Relevant continuations?

- Deep perineal fascial (investing fascia or Gallaudet’s fascia)
- cover superficial perineal muscles)
- anchored to perineal membrane
- continous up to the deep fascia of the penis
Identify the indicated features of the provided image

Deep to Colle’s fascia –> superficial pouch
Deep perineal fascia investing erectile tissue & superficial muscles
Deep to perineal membrane –> deep pouch

What are the contents of the superficial perineal pouch in a male?
- Boundaries
- Colles’ fascia: inferior border
- Perineal membrane: superior border
- Contents
- Bulb of penis
- Crura
- bulbospongiosus
- ischiocavernosus
- spongy urethra
- superficial transverse perineal
- branches of internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve

What are the contents of the superficial perineal pouch in a female?
- Contents
- bulb of vestibule
- crura
- greater vestibular gland
- bulbospongiosus
- ischocavernosus
- superficial transverse perineal
- branches of the internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve

What are the boundaries of the deep perineal pouch?
What are the contents in a male?
- Boundaries
- Superficial: Perineal membrane
- Superomedial: pelvic diaphragm
- lateral wall: obturator fascia
- Contents
- fat (majority)
- membranous urethra (male)
- bulbourethral glands (male)
- branches of internal pudendal artery and branches of pudendal nerve

What are the boundaries of the deep perineal pouch?
What are the contents in a female?
- Boundaries
- Superficial: Perineal membrane
- Superomedial: pelvic diaphragm
- lateral wall: obturator fascia
- Contents
- fat (majority)
- external urethral sphincter (female)
- sphincter urethrae & urethrovaginal
- compressor urethrae
- branches of internal pudendal artery and branches of pudendal nerve

Where do lymphatics of the perineum drain?
- Everything superficial to superficial inguinal lymph nodes
- EXCEPT
- glans penis & glans clitoris
- to deep inguinal lymph nodes
- testes can drain to para-aorticy lymph nodes
- Deep perineal pouch drains to internal iliac lymph nodes
- Anal canal
- above pectinate line: internal iliac lymph nodes
- below pectinate line: superficial inguinal lymph nodes

Identify the arteries indicated on the provided image

Internal pudendal artery
Perineal artery branches off of internal pudendal artery
Transverse perineal artery branches off of perineal artery
posterior labial artery is the terminal branch of the perineal artey
Artery of the bulb of the vestibule from internal pudendal
cavernosal (deep artery of penis/clitoris) is a terminal branch of internal pudendal
dorsal artery of clitoris/penis is a terminal branch of the internal pudendal
They travel on the superficial layer of the perineal membrane within the superficial peineal pouch

What is the trajectory of the internal pudendal artery within the perineum & vulva?
What about the perineal artery?
Transverse perineal artery?
Posterior labial?
Artery of the bulb of the vestibule?
Carvenosal artery?
Dorsal artery of the clitoris/penis?
- Internal pudendal
- toward ischoecavernous muscle
- Perineal artery
- toward
- Bulbousspongiosus muscle
- vestibular bulb
- greaters vestibular gland
- toward
- Transverse Perineal artery
- along superficial transverse muscle
- toward perineal body
- Posterior labial
- labia majora (female)
- posterior scrotum (male)
- Artery of the bulb of the vestibule
- bulb of vestibule/penis
- carvenosal artery
- deep artery of the clitoris/ penis
- dorsal artery of the clitoris/penis
- superficial aspect of clitoris/penis

What is the significance of the cavernosal artery?
if you cannot get blood through this system into the corpus cavernosum, there will be no erection
One way to enhance this is to cut off the outflow either mechanically or pharmacologically (viagra)
Identify the indicated arterial branches
Wha do they supply?

- Femoral Artery
- Superficial external pudendal
- antero/superior aspect of scrotum/labia majora
- Deep external pudendal
- general scrotum
- general labia majora
- Superficial external pudendal

Identify the indicated arteries


Identify the indicated arterial branches











