Perineum I Flashcards
(32 cards)
What is the general position/shape of the perineum?
Between the thighs
Below the pelvic diaphragm (wedge shaped)

Describe the boundary of the perineum from anterior to posterior
- From anterior to posterior
- pubic synphysis
- inferior pubic ramus
- ischial ramus
- ishcial tuberosity
- sacrotuberous ligament
- coccyx
- Roof
- Pelvic diaphragm (levator ani)

What two triangles are shown in the provided image?
What landmark separates the two triangles?

Red: urogenital triangle
Blue: anal triangle
Ischial tuberosity = most inferior portion

What is the perineal body?
Where is it located?
What are the boundaries of the perineal membrane?
Why is this an important landmark
- Perineal body
- confluence of tendinous tissue, connective tissue & where we see a lot of muscles anchoring
- location
- anterior to the anus (closer to anus than pubic symphysis)
- posterior to vagina in female
- Progression anteriorly from perineal body is the perineal membrane
- traversed by
- urethra & vagina in females
- urethra in males
- vasculature, nerves & glandular ducts
- anchored to ischial pubic rami back towards ischial tuberosities
- anterior aspect is transverse perineal ligament (thickened edge)
- posterior aspect is the perineal body
- Important to separate superficial & deep perineal spaces
- traversed by

What structure exists between the pubic symphysis and the transverse perineal ligament?
deep dorsal vein
of penis or clitoris
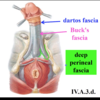
Identify the muscle indicated by the photos & the highlighted components

- External anal sphincter
- Deep: continuation of the puborectalis
- Superficial: anchored to perineal body & coccyx via analcoccygeal ligament
- Subcutaneous: most superficial aspect
- Function: voluntary defecation

What is the name of the space adjacent the anus & surrounding the anal triangle?
Boundaries?
Ischioanal fossae - Right & Left
some continuity that exists between the two sides - intermitent anterior to the anus but more continuos posterior
(between ischial tuberosity & anus)
- Lateral wall
- obturator internus (the portion below the pelvic floor levator ani)
- obturator internus fascia
- Pudendal canal containing internal pudendal nerve & artery
- Ceiling
- fascial covering levator ani
- Floor
- inferior superficial skin

What neurovasculature is shown in the provided image?
It supplies what areas?

Inferior Rectal Nerve & Artery
from internal pudental nerve & artery
- external anal sphincter
- skin of the anus
- inferior surface of the fascia covering levator ani
- some of the levator ani
What is the name of the most anterior portion of the ischioanal fossa?
What is important about this anterior-most boundary?
Deep perineal pouch
anterior recess of the ischioanal fossa
continuous anteriorly (important for infection spread)

An anastamosis of what arteries feeds the rectum down to the anal canal?
- Terminal portion of inferior mesenteric is the superior rectal
-
Terminal portion of anterior division of internal iliac is the internal pudendal
- Internal pudendal will give off inferior rectal
- Anterior division of internal iliac gives off middle rectal
- Inferior rectal, middle rectal and superior rectal will anastamose

Describe the pathway of the internal pudental artery and
The terminal portion of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery is the internal pudendal artery. The internal pudendal artery & nerve go out of the pelvic cavity into the gluteal region through the greater sciatic foramen and come back into the perineum region throuh the lesser sciatic foramen to course their way forward into the urogenital triangle

Identify the indicated features of the provided image


What branches are shown in the provided image


What is the positioning of the pudendal canal along obturater internus?
anteromedially toward the pubic symphysis
with internal pudendal artery & pudendal nerve within the canal
The deep perineal space is continuous with what structure?
What structure creates the roof of the deep perineal space?
What structure demarcates the boudary between the deep and superficial space?
the deepest portion of the deep space is continuous with the ischioanal fossae
Roof of deep space is the inferior fascia of the pelvic diaphragm
Deep & superficial space are separated by the perineal membrane

What contents are located within the deep perineal space?
What contents are located within the superficial perineal space?
- Deep
- external urethral sphincter (female)
- bulbourethral gland (male)
- Superficial
- external genetalia

What are the components of the root & body of penis
- Root of Penis
- Bulb of penis is anchored to perineal membrane
- Crura of penis are anchored to ischopubic rami & perineal membrane
- Body of the penis
- from pubic symphysis out toward glans penis/head
- 3 erectile tissues w/ spongy urethra running through one of them
- from pubic symphysis out toward glans penis/head

What is anatomical position of the penis?
Identify the dorsal & ventral surfaces of the penis

Erect
Dorsum of the penis is anterior when flacid
Ventral/Urethral surface is opposing the scrotum when flacid
What features of the penis are indicated in the provided image?

- Yellow: Glans penis/Head
- Blue line: Corona/Crown
- Orange line: Neck (constriction where body & glans meet)
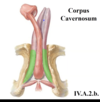
What is the name for the erectile tissue of the penis?
Describe where each is located
- Corpus Cavernosum
- bunch of vascular caverns running through
- so, if you pump blood into it, you will have an erection that occurs due to the increased pressure
- Erectile Tissue
- 2 crura (corpus cavernosum) that converge at the pubic symphysis to form one general body of cavernous tissue
- 1 corpus spongiosum – forms the bulb at the root & has spongy urethra running through it
- does not become as rigid as corpus cavernosum
Identify the indicated aspect of the provided image


Identify the indicated aspects of the provided image

Corpus Spongiosum
- Blue
- perineal membrane
- Brown
- bulb
- fuses to the perineal membrane
- Green
- body of corpus spongiosum
- Ventral portion that contains the spongy urethra
- Yellow
- glans penis
- notice that it is distal end of corpus cavernosum inserts up into the hollow end of the gans penis
What is the most narrow portion of the spongy urethra?
What is the most narrow portion of the system?
exeternal urethral orfice
membranus urethra (& least pliable)
What two types of glands are located within the spongy urethra?
- Throughtout spongy urethra
- Ducts of paraurethral glands
- mucous that conditions the inside of the urethra
- Ducts of paraurethral glands
- Openings in the bulb of the penis
- openings for bulbar urethal (preejaculation)
- glands sitting in the deep perineal pouch within the external urethral sphincter
- when external urethral sphincter contracts it will release some preejaculate