Pentose Phosphate Pathway Flashcards
In the PPP, glucose-6-phosphate in the cytosol is is oxidized to
- Ribose 5-phosphate –> nucleotide synthesis
- CO2
-
NADPH –> used for other pathways like
- FA and steroid synthesis
- Monooxygenase detoxification
- Glutathione defense system against reactive oxygen species

If the cell has a lot of NADH, it gets used for ___
If the cell has lot of NADPH, it gets used for ____, requiring an active PPP.
NADH –> E production via ETC
NADPH –> biosynthetic reactions, requiring an active PPP
What are the purposes of the oxidative & nonoxidative phases of the PPP?
Oxidative phase: generate 2 NADPH and the 5-carbon phosphopentose sugar; counter ROS damage
Nonoxidative phase recycles the pentose phosphate back into useful glycolytic intermediates, which can be further metabolized
What are the 4 enzymes of the PPP oxidative phase, in order?
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (oxidation)
- Lactonase (hydrolysis)
- 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (oxidative decarboxylatoin)
- Phosphopentose isomerase (isomerization)
–> D-Ribose5-phosphate
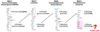
Which is the pathway commitment step of PPP?
Describe its regulation.
Glucose 6-phosphate + NAD –<em>G6P</em> <em>dehydrogenase</em>–> 6-phosphoglucono-lactone + NADPH
Allosteric regulation - high [glucose-6-phosphate] from glycolysis promotes this rxn; high [NADPH] inhibits it
When does the ring structure of lactone get hydrolyzed into its straight chain linear form?
6-Phosphoglucono-lactone –<strong><em>Lactonase</em></strong>–> 6-Phosphogluconate
In the third PPP reaction,
- 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase oxidizes 6-phosphogluconate
- Another NADPH is produced
- CO2 formed, generating Ribulose 5-phosphate
Fourth PPP reaction
Ribulose 5-phosphate –phosphopentose isomerase–> Ribose 5-phosphate
This is a ketose-to-aldose conversion
___ is a precursor for nucleic acid synthesis
Ribose 5-phosphate
(an aldose)
Cells that actively synthesize steroids or FA (need NADPH, but not nucleotide synthesis), need to get rid of all the Ribose-5-phosphate from the oxidative phase.
What happens to it?
Nonoxidative phase converts it into intermediates for glycolysis, glycogenesis, or PPP
First reaction of the NONoxidative phase is catalyzed by an epimerase that converts what to what?
Ribose5-phosphate –> Xylulose 5-phosphate (ketose)
Second step of the nonoxidative phase
Transketolase transfers a 2C fragment from Xylulose 5-phosphate to Ribose 5-phosphate
- Turned these 5C sugars to a 3Cand 7C sugar.
- Cofactor: thiamine pyrophosphate
Thiamine pyrophosphate
derivative of vitamin B1; necessary cofactor for the second step of the nonoxidative phase - transketolase
The third step of the PPP nonoxidative phase
Transaldolase transfers a 3C fragment from a 7C compound to the 3C Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate –> fructose-6-phosphate
–> 7C sugar bcomes a 4C sugar
3C sugar becomes a 6C sugar (F6P)
Final step of the PPP nonoxidative phase
Transketolase transfers a 2C fragment from a second molecule of Xylulose 5-phosphate to the 4C sugar
- Xylulose 5-phosphate -> Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (3C)
- 4C sugar -> Fructose 6-phosphate (6C)
The two ___ and one ___ generated in the nonoxidative phase are glycolytic intermediates, which can be converted to ____ that can be used for ___
The two fructose-6-phosphate & one Glyceradehyde 3- phosphate can be converted to glucose 6-phosphate.
Can be for glycogen storage, glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, or feed back intothe PPP
___ inhibits glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase
NADPH
RBCs don’t need nucleotides (don’t have a nucleus), but does need a lot of NADPH to protect its membranes from oxidative damage.
So what does it do w glucose 6-phosphate from the nonoxidative phase?
Glucose-6-phosphate produced from the nonoxidative phase can reenter the PPP oxidative phase
If a cell only needs Ribose 5-phosphate, but not NADPH, then
Oxidative phase is shut down by NADPH inhibiting G6P dehydrogenase
Nonoxidative phase is run in the reverse, using both fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to generate the phosphopentose
Xylulose 5-phosphate as a regulator of carbohdyrate and lipid metabolism
- Xylulose 5-phosphate activates phophoprotein phosphatease (PP2A), which will dephosphorylate the PFK-2/FBPase-2 enzyme,
–> activates PFK-2, inhibits FBPase-2
–> increased Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate activates glycolysis, inhibits gluconeogenesiss
–> NADPH from PPP and Acetyl-CoA from glycolysis stimulate FA synthesis.
Glutathione exists in 2 states because of its sulfhydryl R-group. Describe them.
RBCs use NADPH to ___ glutathione.
Oxidized glutathione (GSSG) forms a disulfide bond between two glutathione molecules
Reduced glutathione molecules (2GSH) does not
RBCs use NADPH to reduce glutathione –> 2GSH preferred
ROs are produced in the mitochondria through ionizing radiation, oxidizng rxns, sulfa an dantimalarial drugs, etc; can cause tissue damage
How do we reduce them?
- Glutathione peroxidase & Glutathione reduces hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to H2O and O2 –> 2GSH oxidized to GSSG
- Glutathione reductase uses NADPH from PPP to reduce GSSG back to 2GSH
Drug-induced hemolytic anemia is caused by
G6P dehydrogenase deficiency –> NADPH levels drop –> less GSH
Usually asymptomatic unless you have a sudden increase in ROS from infection, drugs, or favabeans –> damaged RBC membranes –> hemolytic crisis & anemia
What are some sources of hemolytic crisis (yellow skin, mucus, and urine; rise of body temp; fatigue; rapid pulse; fast breathing)
- Oxidative/sulfa drugs
- Ex) Quinine used protect against malaria, but causes G6PDH deficiency
- Fava beans
- Alcoholics have thiamine pyprophosphate deficiency
Is the PPP more active when well-fed or starved?
Well fed, becuase [glucose-6-phosphate] is higher and NADPH is beign used for FA synthesis
Why would RBCs be more sensitive than other tissues to defects in pyruvate kinase (PK)?
They don’t have mitochondria, so they only get ATP from glycolysis.
Need pyruvate kinase


