Pelvis Flashcards
What are the bones of the pelvis?
Two hip bones called the os coxae
A sacrum and a coccyx
Discuss the features of the Os Coxae
The hip bone, the os coxae, has three parts to it. At birth, the three bones which are joined by cartilaginous joints at the acetabula fossa – is where the head of the femur articulates with the hip. This is the hip joint. The ilium lies superiorly, the ischium, posteroinferiorly and the pubis, anteroinferiorly. They’re all joined by cartilaginous joints and are fused in the adult. It’s actually one large bone in the adult.

Ilium
The iliac crest is a flattened crest at the top of the ilium. It lies at the level of L4 and where the aorta bifurcates.
The iliac crest is a useful landmark to know because it marks the point of L4 and you know that the level of L4 is well below the end of the spinal cord. It’s a useful landmark for lumbar punctures.

Describe the divisions of the pelvic cavity.
The pelvis is divided by the pelvic inlet (pelvic brim):
- Greater pelvis or false pelvis - above brim
- Lesser or true pelvis - below brim

Diagram of the Bony Pelvis

Ligaments of the Pelvis
Ligaments of the posterior hip bone and and sacrum. Both the interosseus sacroiliac ligament and the posterior sacroiliac ligaments support the sacroiliac joint.
The posterior sacroiliac ligament blends with the fibers of the sacrotuberous ligament which attaches from the sacrum to the ischial tuberosity.

Image of Pelvic Ligaments

Image of Pelvic Ligaments (Female)

Pelvic Inlet (Superior aperature of the pelvis)
Boundaries
Posteriorly
- Sacral promontory
Each side
- Ant. margin of ala of sacrum
- Arcuate line of ilium
- Pecten pubis (pectineal line of pubis)
Pubic crest
Anteriorly
- Upper margin of pubic symphysis

Pelvic Outlet
Also called inferior aperture of pelvis
Anteriorly
Pubic symphysis
On each side
Ischiopubic rami
Ischial tuberosity
Sacrotuberous ligament
Posteriorly
Coccyx

Pelvic Inlet and Outlet

What is the sub-pubic angle?
Angle between ischiopubic rami and lower margin of pubic symphysis
Width of subpubic angle is determined by distance between right & left ischial tuberosity
Measured with gloved fingers in vagina during a pelvic examination
Approximately width of fist
Adequate Intertuberous diameter > 10 cm

Describe the Pelvic Cavity.
- Space between inlet and outlet
- ̈ Pelvic cavity is continuous above with abdominal cavity, limited below by pelvic diaphragm
- ̈ Cavity is more roomy (larger) in females than in males
Describe the contents of the pelvis.
Sigmoid colon and rectum – posteriorly
Urinary bladder - anteriorly
Genital septum - in between bladder and rectum Transverse septa made up of connective tissue
In male genital septa contains prostate,
In female it contains

Image of the anatomy of the hip

Sacroiliac joint
Sacroiliac joint is a plane synovial joint
Articular surfaces
Auricular surface of sacrum and auricular surface of ilium
Ligaments
Fibrous capsule, interosseous sacroiliac lig, anterior and posterior sacroiliac ligament
Transmits weight of body to the hip joint
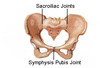
Pubic Symphasis
Pubic symphysis
Secondary cartilaginous joint between bodies of pubic bones
Two surfaces covered by hyaline cartilage and separated by a fibrocartilagenous disc
Sacrococcygeal joint
Sacrococcygeal joint
Secondary cartilaginous joint between sacrum and coccyx
Bones united by intervertebral disc
Measurement of the dimensions of the pelvis

Pelvic differences in males vs. females
Important differences
¡ Inlet is heart shaped in male and oval in female
¡ Greater sciatic notch are wider in female narrower in males
¡ In males inlet is much larger than outlet (funnel shaped) while in females inlet outlet are having less difference ( cavity cylinder)
¡ Subpubic angle is wider in females (>90 degree); narrower in males
¡ Body of S1 vertebra is wider than each ala of sacrum in males. In female both are equal
¡ Ischiopubic rami is markedly everted in male, slightly everted in female
¡ Preauricular sulcus is deeper in female
Muscles of the Pelvic Floor

Muscles of the Pelvic Floor 2



