Anatomy Directional & Motion Terminology Flashcards
Learn & feel comfortable with anatomical directional and motion terminology.
Anterior
In front of or front.
Posterior
After, behind, rear, following, or towards the rear.
Distal
Away from or farther from the origin.
Proximal
Near or closer to the origin.
Dorsal
Near the upper surface, towards the back.
Ventral
Toward the bottom, toward the belly.
Superior
Above or over.
Inferior
Below or under.
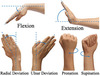
Lateral
Toward the side, away from the mid-line
Medial
Toward the mid-line, middle, away from the side.
Rostral
Toward the front
Caudal
Toward the back, toward the tail.
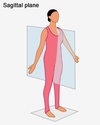
Sagittal Plane
A sagittal plane is an anatomical plane which divides the body into right and left halves.
Lateral Plane
- denoting a position farther from the median plane or midline of the body or a structure.
- pertaining to a side.
Frontal Plane (Also known as a Coronal Plane)
Is any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal (belly and back) sections.
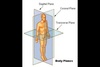
Transverse plane
The transverse plane (also called the horizontal plane, axial plane, or transaxial plane) is an imaginary plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts. It is perpendicular to the coronal and sagittal planes.

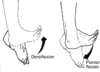
Palmar Surface
The palm or grasping side of the hand.
Proximal
Near to
Distal
Far from
Deep
Refers to something further away from the surface.
Superficial
Refers to something near the outer surface.
Intermediate
Between two other structures.
Parietal
Pertaining to the wall of a body cavity.
Visceral
A lining associated with organs within the body’s cavities.