Pelvic region Flashcards
Sacrotuberous ligament - one of the strongest collagenous structures in the ms system (diagram)
wide as the thumb, found on palpation with px prone, between ischial tuberosity and inferolateral angle of sacrum

Diagram showing how long head of the biceps femoris blends with the sacrotuberous ligament
Action of Biceps femoris : flex the knee joint and laterally rotate

Impingement Test
Test to assess integrity of the acetabular labrum.
Patient is supine.
Practitioner initiates internal rotation.
Practitioner then passively flexes symptomatic hip to 90 degrees and adducts
Reproduction of symptoms in mid superior thigh inferior to the inguinal ligament indicates suspected labral tear or FAI
Symptoms may include pain and an audible click or just pain.
projection of the piriformis muscles (diagram)
a rounded structure that is firmer that its direct surroundings

what happens when the arms are elevated whilst px is lying prone?
it tenses the thoracolumbar fascia and impedes palpate of lumbosacral structures
Fitzgerald Test - Posterior Labrum
Test to assess integrity of the acetabular labrum
Patient supine
Practitioner passively fully flexes, adducts and internally rotates patient’s hip.
Practitioner then extends the hip whilst abducting and externally rotating in one continual movement.
Pain with or without an audible click is considered a positive test.
FABER Test:
General screening test for hip joint pathology.
Patient supine, practitioner instructs patient to cross symptomatic leg so that the ipsilateral ankle rests
above the contralateral knee.
Practitioner then stabilizes the contralateral ASIS and supports the ipsilateral knee until end of range
Practitioner then applies gentle downward pressure to the medial aspect of the patients knee
Reproduction of pain or inability to perform test due to pain is considered a positive test.
FABER (Patrick) test
- for hip joint pain
Flexion, abduction & external rotation of the hip joint passively with your patient supine.
This test can be used for the pelvis as part of a test cluster to differentiate hip joint pain from SIj pain.
It is assumed once the hip joint is at end of range this test will stress the anterior ligaments of the SIJ and the pubic symphysis
o Location of pain is an important factor in determining origin.
MET - improve external rotation of hip joint
Piriformis MET – Px. Prone
Knee flexed,
px. Resists movement towards the midline.
Practitioner holds piriformis muscle.
Exhale and move leg outwards.
What are the pelvic ligaments? (5)
interosseous sacroiliac ligaments
anterior sacroiliac ligaments
posterior sacroiliac ligaments
sacrotuberous ligaments
sacrospinous ligaments
Which nerve gets affected in the dysfunctional abductor muscle of Trendelenburg gait?
Superior Gluteal nerve
position of nerves in the gluteal region (diagram)

Diagram showing the superolateral border of the gluteus maximus (approx)

Femoroacetabular impingement image - Cam
What type of joint is the SI joint?
Arthroidal.
Hyaline cartilage on the sacral side, fibro-cartilage on the ilial side.
sciatica nerve exiting piriformis (diagram)
further down the sciatic nerve can be palpated laterally, between the ischial tuberosity and the superior aspect of g.t. (as line is drawn). It runs directly lateral to tuberosity.
Seated Flexion Test
ROM test

Both thumbs on inferior slope of each posterior superior iliac spine.
Patient bends forwards with arms between the knees, as far as possible.
The PSIS that moves furthest in a superior or anterior is +ve, indicative of restricted mobility on that side.
Observe lumbar and thoracic vertebrae.
This test takes out lower extremities as an influencing factor.
If iliac crest is unlevel when seated initially then innominates are unequal size.
Trendelenburg test
Test for weakness/atrophy of hip abductor muscles. (often occurs with a hip pathology)
Patient standing with feet hip width apart.
Practitioner instructs patient to stand on one leg and observes levels of iliac crests
Test is considered positive if the iliac crest is high on the stance leg and lower on the lifted leg
May indicate underlying hip joint pathology and weakness of gluteus medius
How can you palpate the G.T. in obese patients?
in prone position, flex the knee and rotate laterally and medially to move the G.T.
what structure might you find when palpating superiorly to the ischial tuberosity?
insertion of the sacrotuberous ligament
What tends to be affected in a degenerative hip joint?
Medial rotation
If long posterior sacroiliac joint is painful inferior to PSIS, what does this indicate?
SI joint pathology
where are the PSIS in relation to the lumbar dimples?
approx 2cm lateral and 2cm inferior
POSH (posterior shear) test
for the Sacro-iliac Joint
Patient supine
Practitioner passively flexes thigh at the hip and optionally places hand at the superior pole of the SIJ to palpate ROM, quality of movement and tissue texture.
Practitioner supports thigh at the knee with a broad secure contact using arm and axilla
Practitioner exerts a gradual even posterior compressive force into the SIJ taking care to note any signs of hip joint pain
Reproduction of SIJ symptoms is a positive test.
what do the interosseous sacroiliac ligaments do, and where are they?
NB. these are very short and richly supplied with nociceptors
act to maintain contact between the surfaces of the SI joint
located directly posterior to SI joints
Diagram of Iliotibial band
What’s the distal insertion
How can the proximal aspect be palpated?
Gerdy tubercle (lateral condyle of the tibia)
palpate laterally from the gluteus medius using transverse friction, a band 2-3 fingerwidths maybe felt betwen the iliac crest and the G.T.

Ober’s test
Test for assessment of Hip joint pathology, trochanteric bursitis and ITB contracture.
Patient sidelying with LEX to be tested uppermost, lower LEX slightly flexed at knee and hip.
Practitioner stands behind patient, stabilizes pelvis and passively flexes upper knee to 90 degrees whilst supporting knee and ankle
Practitioner then abducts and extends hip and lets supported LEX drop to assess ITB contracture. Pain over the greater trochanter is considered positive for trochanteric bursitis
Practitioner internally rotates hip to test for hip joint pathology.
what is the distance between the top of the iliac crest and the lowest rib?
two fingerwidths
Sacroiliac compression test
Patient supine, using both hands, practitioner applies bilateral and medial compression to the ilium to compress the SIjs.
Reproduction of SIj. symptoms is a positive test. Test stress ligaments (mainly posterior) of the SIJ
MET - hip extension
MET for psoas. Px side-lying
what is ligament dynamization?
the extension of muscles into capsular-ligamentous structures

Standing Flexion Test
ROM test
(test for SI evaluation)
Place thumbs on inferior slope of the posterior superior iliac spine
Patient bends forwards to try and touch the floor.
Test +ve if one posterior superior iliac spine moves further than the other
* also observe thoracic and lumbar vertebrae.
- *Thomas test**
- *Test for hip flexion contracture typically due to shortened Rectus Femoris or Iliopsoas.**
Patient supine and passively flexes hip and knee to bring knee to chest, whilst keeping other leg extended on the couch.
Practitioner observes for any elevation of the thigh or hip flexion in the extended leg.
Elevation of the straight leg indicates a positive test.
Significant increase in lumbar lordosis is also considered a positive test.
How do you active the glut maximus?
and.. what is its other main action?
prone. Px tries active extension (raises leg off table). Can be done against resistance.
Px can turn heel inwards to ext. rot. hip before extension. Operator can apply additional pressure to inside of thigh to stimulate adduction
strong external rotator of the hip

which ligaments are in the first kinematic sacral-vertebral column chain?
iliolumbar ligaments

what can be felt between the sacrum and the PSIS, on the posterior surface of the sacrum?
the multifidus muscles
If px increases lumbar lordosis then muscle contracts and tissue becomes firmer

Stork Test
ROM test
(test for SI joints)
Sensitive for SI restriction.
Place thumbs over left posterior superior iliac spine and the right thumb overlying the sacrum at the same level.
Patient flexes left hip and knee to minimum 90% flexion.
A negative test finds the left thumb on the PSIS move downwards in relation to the right thumb on sacrum.
how do you palpate for the ischial tuberosity in prone position?
palpate medially along the gluteal fold with the thumb
Gillets (Stork) Test
as described previously. Can be used as a test. Positive if painful.
Normal motion would see PSIS move slightly inferiorly to S2 as the hip is flexed and the SIJ engaged. With abnormal SIj motion the PSIS may appear to hitch up and move superiorly.
Pathologies of the hip (3)
what can be located at the level of the PSIS?
S2 SP
Diagram of the long posterior sacroiliac ligament
size - 3/4 cm long and 1-2 cm wide

Log Roll Test
Patient supine
Practitioner passively internally and externally rotates femur of asymptomatic side using hand on the mid thigh to test range and quality of movement.
Practitioner then tests symptomatic side in the same way
Reproduction of symptoms and increased external rotation of the hip is a positive test.
what is a common cause od coccyx pain after falling?
overstretched ligamentous conections
where is the main trochanteric bursae located?
between the g.t. and the gluteus maximus or iliotibial tract
Diagram showing positive and compensated Trendelenburg sign
How can you palpate the posterior inferior iliac spine?
draw line from PSIS to sacral horn and half it. Firm deep pressure needed midway along line
MET - hip flexion
Px. Supine.
Hold flexed hip under armpit, and leaning over px, hold contralateral leg to prevent flexion.
what ligament merges with the sacrotuberous ligament and is the ony ligament that restricts countermutation?
long posterior sacroiliac ligament
connects PSIS with edge of sacrum, about 3cm long.
felt as a grounded structure with transverse palpation
Sacroiliac distraction test
Patient supine.
Practitioner places both thenar eminence on medial aspect of ilium at the ASIS with arms crossed.
Practitioner applies a lateral and slightly posterior compression force.
Reproduction of symptoms is a positive test
This test stresses the anterior ligaments of the SIJ
Fitzgerald Tests - Anterior
Test to assess integrity of the acetabular labrum.
Patient supine
Practitioner passively flexes, externally rotates and abducts hip.
Practitioner then extends, internally rotates and adducts hip from previous position in one continual movement
Pain with or without an audible click is considered a positive test.
SI Joint - Active ROM testing
Done in this order…
Standing flexion test
Stork test
Seated flexion test
which one ligament can help limit counternutation?
long posterior sacroiliac ligament
Image of Femoroacetabular impingement - Pincer
What is the job of the biceps femori tendon as it attaches into the sacrotuberous ligament?
It prevents the sacrum from nutating, and it stabilizes the SI joint directly before the landing phase.
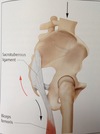
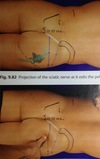
Diagram showing sacroiliac joint projection
approx 2 cm lateral and parallel to the line connecting PSIS and sacral horn

Location of trochanteric bursa
Special tests
for SI joint/ lumbar-pelvic region (5)
POSH (posterior shear) test for the Sacro-iliac Joint
Sacroiliac compression tests
Sacroiliac distraction test
FABER (Patrick) test
Gillets (Stork) Test
when palpating the PSIS, it could be painful on some px. Why?
long posterior sacroiliac ligament being sensitive to pressue due to possible SI pathology


