Peds_Exam3 Flashcards
1
Q

A
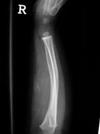
- Osteomyelitis
- Children
- Staph infecction, through bloodstream
2
Q
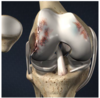
A
- Avascular Necrosis
- Common in shoulder and hip
- Caused by sickle, steroids, or fractures
3
Q

A
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
- onset of puberty 13 years.
- boys, obesity
- osteonecrosis complication
4
Q

A
- Legg Calve-Perthes Disease
- aseptic necrosis of femoral head
- boys 4-8 years
- skeletal age below chronological age
5
Q

A
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- most common osteoporosis syndrome in children
- light touching can cause a fracture.
6
Q

A
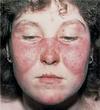
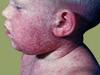
- Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
- autoimmune inflammatory process
- female predominse
- 2-3 years, or 8-10 years
7
Q

A
- Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
- dislocation, shallow acetabulum, subluxation
- born breech
- 80% females
- limited hip abduction
8
Q
What is this used for?

A
- Tx of DDH, preventing skin breakdown
9
Q
What is this?

A
- Congenital Club Foot
- forefoot adduction,
- midfood supination
- hindfoot varus
- ankle equinus
10
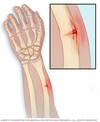
Q
What is the other name for this?

A
- Subluxation of the Radial Head
- children 1-3 years
- partial dislocation
11
Q
- What should you do if signs of nero impairment in a child with cast or brace?
- What psychological affects from wearing a brace or disabling condition?
- What are fractures indicative of?
A
- Contact HCP
- altered role performance, body image, fear, anger, isolation
- rare, warrant further investigation to rule out abuse
12
Q
- Priority Action for Extremity Fracture
- What assessment provides the earlies indication of an improvement, or detioration in neurological condition
- Action if cervical or spinal injury is suspected?
A
- Assess, immobilize extremity, if compound fracutre, cover with sterile dressing, elevate, COLD, monitor neuro stat, transport ER
- LOC
- immobilize neck and spine
13
Q
- If spinal injury is ruled after head injury, what is appropriate action?
- What are seizure precautions?
A
- elevate HOB 15-30 degrees, for venous drainage
- Raise side railes when sleeping, padding, waterproof mattress, carry med ID, should swim with companion, wear a helmet, alert caregivers
14
Q
- Signs of Brainstem involvement x5
A
- Deep, rapid or intermittent gasping respirations
- fluctuations or slowing of pulse
- fluctuations in BP
- Sluggish, dilated or unequal pupils
- NOTIFY HCP IF THESE SIGNS DEVELOP
15
Q
- What does drainage from nor or ears pos for glucose indicate?
- What is communicating hydrocephalus?
- What is noncommunicating hydrocephalus
A
- leakge of CSF, notify HCP
- impaired absorption w/in subarachnoid space
- obstruction of CSF in ventricular system
16
Q
- What could a high shrill cry be indicative of?
- It is appropriate to place tongue blade airway device over child’s mouth during a seizure
- What is a priority for a child with autism
A
- Increase Intracranial Pressure
- FALSE
- Ensuring a safe environment
17
Q
- Interventions for a seizure
A
- Ensure airway patency
- suction equipmen/oxygen available
- time the seizure
- ease child to floor, side lying position
- pillow under child’s head or own hands
- loosen clothing
- remove eye glassees
- clear the area
- prep meds
18
Q
Sickle Cell
- What is a vaso occlusive crisis
- what is a splenic sequestration
- hyperhemolytic crisis
A
- stasis of blood with clumping of cells, ischemias, infraction. Fever, swelling in hands, feet, joints abdomen
- pooling and clumping of blood in the spleen, profound anemia, hypovolemia, shock
- rapid RBC destruction, jaundice, anemia, reticulocytosis
19
Q
- What is an aplastic crisis
- What medication should be avoided for sickle cell disease?
- How should liquid iron be taken
A
- diminished RBC, caused by viral infection or lack of folic acid, anemia and pallor
- meperidine, can induce seizure
- thru straw, brush teeth after (stains the teeth)
20
Q
- What is hemophilia A
- what is hemophilia B
- What should be worn if child has a bleeding disorder?
A
- result of factor deficient VIII
- result of factor deficient IX
- Medic alert bracelet
21
Q
- Parent teaching child with mono
- Signs of splenic rupture
- How long do symptoms of flu last?
A
- monitor for splenic rupture,
- ab pain, LUQ pain, and left shoulder pain
- One week
22
Q
- Priority Action for administering Parenteral Vaccine
A
- verify prescription
- immunization hx
- info to parents
- parental consent
- lot #, expiration date, prep injection
- appropriate site
- admin
- document
- record for parents
23
Q
- Preterm children and vaccine admin
- Vaccine at 1month
- Vaccine at 2 months
A
- full dose at appropriate chornological age
- Hep B
- IPV, DTap, Hib, PCV, Rotavirus
24
Q
- Vaccine at 12-15 months
- Vaccine at 15-18 months
- Vaccine at 12-33 months
A
- Hib, PCV (pneumo), MMR, Hep A (2nd dose @ 6-18 months)
- dTAP
- Hep A
25
Q
- Vaccine at 4-6 years
- Vaccine at 11-12 years
A
- Dtap, IPV, MMR, Varicella
- MMR, Tdap, MCV4 (meningitis), HPV
26
Q
What is this?

A
- Non communicating hydrocephalus
- CSF in ventricles
27
Q
What is this an example of?

A
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt
- 10% infection rate
28
Q
What is this?

A
- Craniosynostosis
- premature closure of cranial sutures. Elongated skull
- surgical intervention (before 6 months of age)
29
Q

A
- Epidural hematoma
- between dura and skull
30
Q

A
- Subdural hematoma
- between dura and rachnoid membrane