Pediatrics Immersion Flashcards
(61 cards)
Red reflex
Use an opthalmoscope and visualize the retina in the back of the eye. There should be red coloration due to red blood vessels.
If you don’t see a red reflex, it may suggest a mass or something blocking the view of the retina, or cataracts.
Signs of respiratory distress in a baby
- Cyanosis
- Grunting
- Nasal flaring
- Tachypnea (>60 bpm)
- Subcostal or intercostal retractions (highly visible ribs)
Normal RR for an infant
40-60 breaths/min
Normal HR for an infant
Varys w/ age, but anywhere from 80-170 bpm
Acrocyanosis
A normal finding
Lips are not cyanosed, so this is not dangerous. May persist for several months, particularly in colder areas.

Scaphoid abdomen
Often suggests diaphragmatic hernia
Abdomen does not contain as many organs! You can hear bowel sounds over the chest where herniated intestines are.
Requires immediate surgery.
Syndactyly
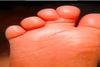
Kleinodactyly

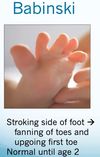
Babinski reflex presence is normal until age __.
Babinski reflex presence is normal until age 2.
Nephrotic syndrome is often mistaken for ___ in pediatrics.
Nephrotic syndrome is often mistaken for allergy in pediatrics.
The eyes become puffy first, and it tends to occur around the same time seasonally (since it can be triggered by a URI)
When an infant is relaxed, you can take advantage for the purposes of your physical exam by. . .
- Reviewing facial features when facial muscles are not contracted
- Look at exposed skin
- Examine breathing (rate/pattern)
- Listen for murmur/breath sounds
- Assess red reflex if eyes are open
Anterior fontanelle
If an infant has high intracranial pressure, this fontanelle will be very wide.
In older children, it will be bulging.

When you are examining an infant, especially when you are removing coverings to look at skin, it is very easy for the baby to become. . .
. . . cold!!!!
Whenever possible, use warming lights overhead to keep the infant warm, and keep this in mind throughout your exam.
Moulding of sutures
May cause bumps along the cranial suture lines on an infant’s head.
Usually due to pressure during delivery. Resolves over time.
Completely benign.
Neonatal extracranial and intracranial birth injuries

Caput
Edema under the skin, but above the fascia and periosteum. Causes swelling/bulging. Crosses suture lines. Usually present at birth.
Totally benign. Resolves usually within 48 hours. Just put a hat on the baby.
What to ask when examining an infant’s head bulge
- Does it cross suture lines?
- Is there pitting edema?
- Is there fluid wave?
Cephalhematoma
Major risk factor is vacuum-assisted deliveries.
Presents 12-24 hours after delivery. Does NOT cross suture lines. No fluid wave.
Not serious, but may cause some jaundice within ~ 1 week of appearance. Monitor carefully for jaundice development.
Subgaleal hemorrhage
Above the skull, but beneath the periosteum. Blood witihn the external periosteal space. Presents soon after birth and does NOT cross suture lines. Fluid wave is PRESENT.
Potentially serious. Can be so much blood loss into this space that the baby loses significant circulating volume. This requires transfer to NICU and administration of plasma or cryoprecipitate to facilitate clotting.
Subdural hematoma
Not visually apparent on exam, but may present as seizures. Quite serious.
Why is it important to check for cleft lips and palate on infantile exam?
Babies with cleft lips or palates may have difficulty feeding due to muscle coordination, and so they must be fed with specialized nipples that are designed to make this easier for them.
Otherwise, it could lead to malnutrition/failure to thrive.
Clefts may also be found in certain syndromes and may be an early clue to identifying a more serious pathology.
Why do babies grunt when they are in respiratory distress?
Babies “grunt” (Ehhh, ehhh, ehhh) reflexively by constricting their larynx. This maintains a positive end expiratory pressure in their lungs, holding the alveoli open, much like PEEP on a ventilator.
If you see this with a newborn, you should think of a surfactant problem.
Where is the best place to look for significant cyanosis on an infant?
The tongue!!!
All newborns have __ in the first couple minutes of life.
All newborns have low oxygen saturation (~65%) in the first couple minutes of life.