Pediatric Gastroenterology Flashcards
(13 cards)
Treatment of choice for children > 6 months with functional constipation and impaction
Osmotic agent of some sort, usually polyethylene glycol
Effective both in disimpaction and in reducing complications, such as fissures and recurrent constipation
Adults get anal fissures because ___.
Kids get anal fissures because ___.
Adults get anal fissures because they are constipated and have high anal tone.
Kids get anal fissures because something external made a hole there – iatrogenic or abuse. (often from rectal exam)
Anal fissure diagnosis + treatment in kids
Diagnosis is clinical, treatment is reassurance – no need for sutures, baby stool is soft
Classic presentation of intussusception
- Typically 3 months - 3 years of age
- Abrupt onset of colicky abdominal pain
- Knee-chest position brings relief
- If you wait long enough, bowel will die, slough off, and become “currant jelly diarrhea”
- “Sausage-shaped” abdominal mass
Currant jelly stool
Result of dead bowel sloughing off – any etiology
Diagnosing intussusception
- Best definitive diagnostic test is air enema, and is also the treatment of choice – propelled air pushes telescope back out
- Important accessory tests:
- Kidney-ureter-bladder plain film - rule out perforation and obstruction
- Ultrasound may be used to track progress, highly sensitive (“Target sign”)
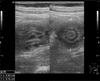
When does a child with intussusception need to go to surgery?
Frank peritonitis
Perforation
Failure of air enema
Meckel’s diverticulum
- Remnant of the vitelline duct, made of gastric contents that can secrete acid
- May bleed itself or may cause a “peptic ulcer” in the terminal ileum or colon
- Painless, intermittent hematochezia (BRBPR)
- Rule of 2’s: Presents in toddlers <2 years old, 2x as likely in males, found 2 feet from ileocecal valve, about 2 inches
- May be associated with iron deficiency in a male or FOBT +
- Diagnosis: Tc99 scan for kids, CT for teens.
- Treatment: Resection.
Common mimics of GI bleed in kids
- Baby swallows mom’s blood during delivery and then has melena
- Apt test can tell you if it is baby’s blood or mom’s blood
- Epistaxis-induced melena
- Iron supplementation
- Beats
- Medications
- Milk protein allergy (change to hydrolzed formula)
- Milk/soy protein-induced colitis
Crohn’s presents as ____ while UC presents as ____.
Crohn’s presents as watery diarrhea with weight loss while UC presents as dysentery.
Rule for IBD colon cancer screening
For pancolitis: Begin 8 years after diagnosis, screen every 1-2 years
For L sided colitis: Begin 15 years after diagnois, screen every 1-2 years
What is the ONLY medical indication for soy formula?
Galactosemia


