Pediatrics Flashcards
What are associated anomalies with this deformity?

Klipell Fiel
congential scoliosis
UE abnormalities
diastomeomyelia
renal disease
What is the classification of spregnel?

What are the procedures for spregnel
Done for stage 3/4 to improve cosmesis and abduction
Between ages 3-8, >8 is not a good candidate
Woodward with clavicular osteotomy is the preferred procedure
Procedure is done prone, tunnel subfacia anterior to do the clavicle

What are risk factors for brachial plexus palsy
large babies
difficult presentation
shoulder dystocia
forceps delivery
breech position
prolonged labor
What are prognostic factors for brachial plexus palsy?
90% will recover without intervention - can occur for up to 2 years
70% of those affected will develop glenoid retroversion
Good - biecps twitch by two months
Bad
lack of biceps function
preganglionic injuries; Horner’s syndrome, loss of rhomboid function
avulsion injuries (worst prognosis)
What is Erb’s palsy?
Mechanism
results from excessive displacement of head to opposite side and depression of shoulder on same side producing traction on plexus
occurs during difficult delivery in infants or fall onto shoulder in adults
Physical exam
clinically, arm will be adducted, internally rotated, at shoulder; pronated, extended at elbow (“waiter’s tip”)
C5 deficiency
axilllary nerve - weakness in deltoid, teres minor
suprascapular nerve - weakness in supraspinatus, infraspinatus
musculocutaneous nerve - weakness to biceps
C6 deficiency
radial nerve - weakness in brachioradialis, supinator
Prognosis - best prognosis

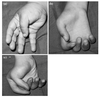
What is klumpke’s palsy?
Mechanism
rare in obstetric palsy
usually avulsion injuries caused by excessive abduction (person falling from height clutching on object to save himself)
other causes may include cervical rib, or lung mets in lower deep cervical lymph nodes
Physical exam
deficit of all of the small muscles of the hand (ulnar and median nerves)
clinically, presents as “claw hand”
wrist held in extreme extension because of the unopposed wrist extensors
hyperextension of MCP due to loss of hand intrinsics
flexion of IP joints due to loss of hand intrinsics
Prognosis
poorer
frequently associated with a preganglion injury and Horner’s Syndrome
Ptosis, myosis, anhydrosis

Draw the brachial plexus

What are indications for microsurgery associated with bracial plexus palsy
complete flail arm or horner’s at one month
Diagnosis? Incidence? Options for treament (general)

Brachial Plexus Palsy - No IR
-
At time of birth
- PT for ROM and monitor
- 90% will improve
-
Early micro surgery (graft or repair)
- fail arm at one month
- horner’s syndrome at one month
- root avulsion (only grafting)
-
contracture release (any age)
- pec, subscap z-lengthening, arthroscopic subscapular release
-
L’Episcopo lat dorsi/teres major transfer with pec major contracture release
- requires a congruent joint
- usually children < 4yo
-
Proximal humerus rotational osteotomy
- incongruent joint
- >5yo

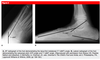
Deformity associated with madelung’s
Volar carpal subluxation
proximal radial synostosis
increased radial inclination
volar tilt
volar-ulnar tethering of vickers ligament
What is vickers ligament
thickening of radiolunate ligament - madelungs
What is leri-wiell
rare genetic disorder caused by mutation in the SHOX gene
SHOX stands for short-statute homeobox-containing gene
anatomically at the tip of the sex chromosome - pseudo-sex linked disorder
causes mesomelic dwarfism (short stature)
Normal intellegene
associated Madelung’s defomity of the forearm
What is the treatment for this deformity

watch if they are young, deformity is small; assess with serial XR
Consider OR for pain or functional deformity
Physiolysis or Vickers release - open physis with progression
Radial ostotomy, vickers release, +/- ulnar ostoetomy, +/- ulnar epiphyseodesis
What is the evidence for screening DDH
No evidence to screen
Imaging prior to 6 months in infants with clinical evidance, fam hx, breech,
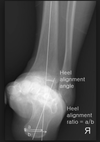
What factors are associated with increased incidence of LCP?
positive family history
low birth weight
abnormal birth presentation
children exposed to second hand smoke
Asian, Eskimo and Central European decent
What are the risk factors of LCP?
family history of disease in 1.6-20% of cases
has been found to be associated with ADHD in 33% of cases
bone age is delayed in 89% of patients
What factors are associated with poor prognosis in this patient?

bone > 6 years
female sex
decreased hip range of motion
Lateral pillar, head sphericity
Most patients will do ok until 6th decade

What are the caterall risk factors associated with LCP?
Gage sign - V-shaped radiolucency in the lateral portion of the epiphysis and/or adjacent metaphysis
calcification lateral to the epiphysis
lateral subluxation of the femoral head
horizontal proximal femoral physis
metaphyseal cyst
What are the lateral pillar and stulberg classfications
Lateral pillar (fragmentation phase)
A- none
B - >50% no height loss
B/C - >50% height loss
C - < 50% lateral pillar

What are treatment options for LCP?
Goal : low stulberg classficiation
< 8 = nothing, casting is controversial
> 8, lateral pillar B and B/C in fragmentation phase = femoral osteotomy or pelvic ostetomy containment procedure
C - later treatment
Outcomes you should know for LCP
no positive effect has been found for containment surgery performed after initial or early fragmentation stage
children with lateral pillar A and those with B under 8 years did well regardless of treatment
large recent studies show improved outcomes with surgery for lateral pillar B and B/C in children > 8 years (bone age >6 years)
poor outcome for lateral pillar C regardless of treatment
Risk factors for developing this pathology

males (male to female ratio is 3:2)
African Americans
Pacific islanders
obese children - single greatest risk factor
during period of rapid growth
bilateral in 20% (20-40% May go on to develop bilateral)
When would you consider endocrine WU for SCFE and what are you looking for?
child is < 10 years old
weight is < 50th percentile
- *hypothyroidism** (labs show elevated TSH)
- *renal osteodystrophy** (abnormal BUN and creatinine)
- *growth hormone treatment**