Path Pics Flashcards

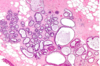
normal placenta
first trimester chorionic villi: central stroma surrounded by two layers of epithelium
double arrow (outer layer): syncytiotrophoblasts
single arrow (inner layer): cytotrophoblasts

normal placenta
third trimester chorionic villi: stroma with dense network of dilated capillaries surrounded by markedly thinned out syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast

Listeria: non-pasteurized milk, cheese
NECROTIZING INTERVILLOSITIS

chorioamnionitis: maternal inflammatory response
Umbilical Cord

INFECTION
top: phlebitis, arteritis in umbilical arteries and veins
middle: necrotizing funisitis due to long standing infection (right)
bottom: peripheral funitis (inflammation at periphery of umbilical cord) with CANDIDA

chronic villitis with CMV (OWL EYE nuclear inclusion)
left: Bone Marrow
right: placenta

Parvovirus B19: ERYTHEMA INFECTIOSUM (SLAP CHEEK)
left: viral inclusions in early erythroid precursors
right: erythroblasts in the lumen of capillary vessels of placental villi show eosinophilic nuclear inclusions
Fetal Membranes
Neg. iron stain

MECONIUM in amnionic cavity

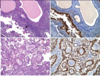
choroinic villi of plactenta
left: first trimester
right: 3rd trimester (increased vascularity)
cells: outer: syncytiotrophoblasts; inner: cytotrophoblasts

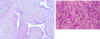
ectopic pregnancy in uterine tube

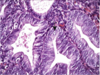
placenta accreta
placental villi interdigitate directly with the uterine myometrium, without an intervening decidual plate

abruptio placenta
BLOOD

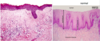
Amnion Nodosum
gross: multiple yellow tan superficial amniotic lesions, usually near insertion of umbilical cord
micro: nodules of eosinophilic fibrous material with entrapped squamous cells

Potters sequence
cranial anomalies, clubbed feet, pulmonary hypoplasia
due to oligohydramnios

Preeclampsia
top: small placenta due to preeclampsia
bottom: placenta with pale infarct (more than 1/3 to 1/2 becomes infarcted: blood supply to infant can become compromised and cause fetal demise)
can also find hematomas
placenta

Preeclampsia
villous ischemia: increased syncytial knots (purple nubbins on villi)
maternal vessels in decidua

Preeclampsia
fibrinoid necrosis

Complete hydatidiform mole
villous enlargement, edema, and circumferential trophoblast proliferation
ultrasound

Complete hydatidiform mole
SNOWSTORM

Partial hydatidiform mole
villi: some normal, others swollen, avascular and grape-like
minimal trophoblastic proliferation

Complete hydatifiform mole
grape-like

Partial hydatidiform mole

Choriocarcinoma
NO villi
mitoses
cytotrophoblasts, syncytiotrophoblasts

Choriocarcinoma
proliferating syncytiotrophoblasts, cytotrophoblasts
NO villi
mitoses